No products in the cart.
Sale
Balhimycin (CAS 140932-79-2) | GMP Supplier & Manufacturer
Original price was: $18.00.$12.00Current price is: $12.00.
Balhimycin is a naturally derived glycopeptide antibiotic from Amycolatopsis sp. It demonstrates strong inhibitory activity against staphylococci and anaerobic bacteria, making it an important research tool in antimicrobial resistance and drug discovery studies. Supplied in GMP-grade quality for reproducible laboratory applications.
Description
Product Description
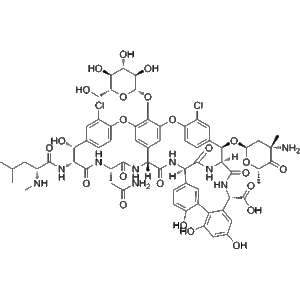
Balhimycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic (CAS No. 140932-79-2), is a fermentation-derived secondary metabolite produced by Amycolatopsis species. Structurally and functionally related to vancomycin, it belongs to a class of antibiotics known for their effectiveness against Gram-positive pathogens. Its discovery expanded the glycopeptide family, contributing to the development of novel antibacterial therapies and providing new tools for antimicrobial research.
At the molecular level, Balhimycin targets the bacterial cell wall synthesis machinery. It binds with high affinity to the D-Ala-D-Ala terminus of peptidoglycan precursors, preventing cross-linking and leading to bacterial cell death. This mode of action makes it especially effective against multidrug-resistant staphylococci and anaerobic organisms.
Balhimycin is often compared to other glycopeptide antibiotics like vancomycin and teicoplanin. While similar in antibacterial spectrum, it offers structural diversity that provides researchers opportunities to study resistance mechanisms, cross-resistance, and structure–activity relationships (SAR).
For experimental microbiology and pharmacology, Balhimycin is a valuable compound in:
Antimicrobial resistance research
Studies of glycopeptide biosynthesis pathways
Cell wall biology investigations
Comparative antibacterial pharmacology
Drug discovery pipelines
GMP-grade Balhimycin ensures high purity, reproducibility, and batch-to-batch consistency. The lyophilized powder is stable under proper storage conditions, making it suitable for both short- and long-term research studies.
Disclaimer: For laboratory research use only. Not for human or veterinary use.
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Balhimycin |
| Synonyms | Glycopeptide antibiotic Balhimycin |
| CAS Number | 140932-79-2 |
| Source | Fermentation product of Amycolatopsis sp. |
| Molecular Class | Glycopeptide antibiotic |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder |
| Purity | 98% (HPLC) |
| Solubility | Soluble in aqueous buffers; limited solubility in organic solvents |
| Stability | Stable for ? 24 months when lyophilized |
| Storage Conditions | Store at –20 °C; protect from light and moisture |
| Mechanism of Action | Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding D-Ala-D-Ala termini |
| Spectrum of Activity | Staphylococci, anaerobic bacteria |
| GMP Compliance | Manufactured under GMP conditions |
| Applications | Antimicrobial resistance studies, bacterial cell wall research, antibiotic drug discovery |
| Availability | Wholesale & retail supply |
| Safety Considerations | Laboratory use only; handle under biosafety protocols |
Mechanism of Action & Research Applications
Balhimycin acts as a potent inhibitor of bacterial cell wall biosynthesis. It exerts its antibacterial effects by binding to the D-Ala-D-Ala termini of peptidoglycan precursors, preventing the cross-linking of cell wall polymers. This disruption weakens the bacterial cell envelope, leading to osmotic instability and cell lysis.
Mechanism of Action Highlights
Peptidoglycan Inhibition: Balhimycin directly blocks transglycosylation and transpeptidation steps in bacterial cell wall assembly.
Target Specificity: Exhibits high selectivity for Gram-positive bacteria, particularly staphylococci and anaerobes.
Resistance Studies: Useful for studying glycopeptide resistance mechanisms, including van gene-mediated modifications of peptidoglycan termini.
Research Applications
Antibiotic Resistance Studies: Understanding how bacteria adapt to glycopeptide pressure.
Comparative Pharmacology: Benchmarking activity against other glycopeptides such as vancomycin.
Microbial Pathogenesis: Studying bacterial survival, virulence, and envelope stress under glycopeptide exposure.
Biotechnology: Engineering Amycolatopsis strains for novel glycopeptide derivatives.
Drug Discovery: Lead compound for new antibacterial agents against multidrug-resistant pathogens.
Balhimycin’s unique structure and activity make it a powerful research tool for both basic and applied microbiology.
Side Effects (For Reference in Research Models)
In experimental models, Balhimycin’s effects may vary depending on concentration, bacterial strain, and exposure duration.
Cytotoxicity: Minimal at standard research concentrations, but higher doses may affect mammalian cell cultures.
Resistance Induction: Prolonged exposure can drive adaptive resistance in Gram-positive bacteria.
Experimental Variability: Activity may differ across strains of staphylococci and anaerobes.
Solvent Effects: Dissolution medium may influence stability and observed activity.
Storage-related Changes: Degradation products may alter bioactivity if storage conditions are suboptimal.
These effects are reported only in laboratory research contexts and are not related to human therapeutic use.
Disclaimer
For laboratory research use only. Not for human or veterinary use.
Keywords
Balhimycin
Glycopeptide antibiotic research compound
Antimicrobial resistance research tool
Amycolatopsis glycopeptide
Cell wall biosynthesis inhibitor
Staphylococcus antibiotic research peptide
Anaerobe antibacterial compound
Laboratory use only Balhimycin
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 53 × 42 × 53 cm |
1. What is Balhimycin?
Balhimycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic derived from Amycolatopsis sp., active against Gram-positive bacteria.
2. What is its CAS number?
The CAS number of Balhimycin is 140932-79-2.
3. What bacteria are most sensitive to Balhimycin?
It shows activity against staphylococci and anaerobic bacteria.
4. How does Balhimycin work?
It inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to D-Ala-D-Ala termini.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.