No products in the cart.
Sale
Cisplatin | CAS 15663-27-1 | Platinum-Based Antineoplastic for DNA Crosslinking and Cancer Research
Original price was: $5.00.$3.00Current price is: $3.00.
Cisplatin (CAS 15663-27-1) is a platinum-based coordination complex widely used in biochemical and oncology research. It acts as a DNA crosslinking agent that induces apoptosis by forming intra- and inter-strand DNA adducts, serving as a model compound for studying platinum chemotherapy mechanisms.
Description
Contents
hide
Product Description
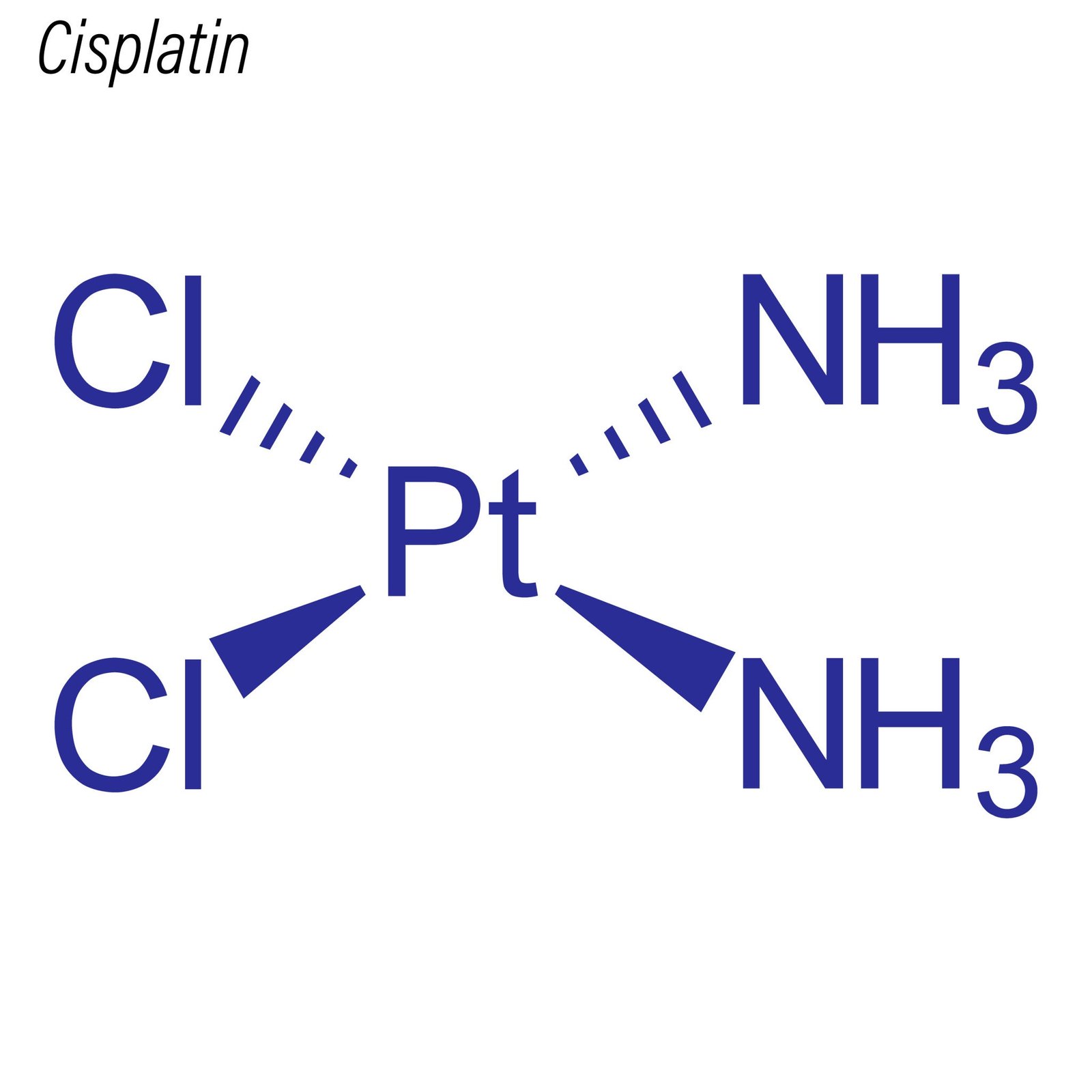
Cisplatin, chemically known as cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II), is a coordination complex that revolutionized the study of DNA-damaging agents and platinum-based chemotherapeutics. Structurally, it consists of a central platinum atom coordinated to two chloride ions and two ammonia ligands in a cis configuration. This unique geometry is critical to its ability to form covalent bonds with nucleophilic sites on DNA, particularly the N7 positions of guanine and adenine residues.
As one of the earliest discovered platinum compounds with potent cytotoxic activity, cisplatin has been extensively used as a model compound for understanding DNA repair mechanisms, apoptosis pathways, and cellular stress responses. In biochemical research, cisplatin serves as a benchmark for exploring the role of DNA damage in cancer cell death, oxidative stress, and cell-cycle arrest.
When introduced into an aqueous environment, the chloride ligands of cisplatin undergo a slow hydrolysis process to form reactive aqua complexes. These aquated species are electrophilic and capable of binding to nucleophilic DNA sites, resulting in the formation of DNA-platinum adducts. The most predominant lesion formed is the 1,2-intrastrand crosslink between adjacent guanine bases, which bends and unwinds the DNA double helix. This distortion disrupts replication and transcription, leading to replication fork stalling and activation of DNA damage response (DDR) pathways.
Cisplatin-induced DNA lesions are recognized by high-mobility group (HMG) proteins and other DNA-binding factors, triggering a cascade of molecular events that culminate in cell-cycle arrest and programmed cell death. The extent of DNA adduct formation, as well as the efficiency of DNA repair by nucleotide excision repair (NER) enzymes, determines cellular sensitivity to platinum compounds. Therefore, cisplatin remains an essential research reagent in the study of DNA repair, apoptosis, and chemoresistance mechanisms.
In addition to its direct DNA-binding effects, cisplatin has been found to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), which amplify cellular damage through lipid peroxidation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and oxidative modification of proteins. These secondary pathways provide valuable models for oxidative stress studies and for understanding redox biology in the context of cytotoxicity.
Researchers also use cisplatin in comparative studies of platinum analogs, such as carboplatin, oxaliplatin, and nedaplatin, to analyze structure-activity relationships. Such comparative models provide crucial insights into the pharmacodynamics and cellular transport mechanisms of platinum drugs.
In vitro, cisplatin’s biological effects are highly concentration- and time-dependent. Low doses primarily cause reversible DNA lesions and mild activation of repair pathways, whereas high doses lead to irreversible DNA crosslinks, cell-cycle arrest, and apoptosis. For this reason, cisplatin is frequently used in cell culture assays, comet assays, and DNA-binding kinetics studies.
Due to its wide-ranging applications in cancer biology, DNA chemistry, and pharmacology, cisplatin continues to serve as a cornerstone compound for molecular oncology and cytotoxic mechanism research.
Product Specifications
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Cisplatin |
| CAS Number | 15663-27-1 |
| Synonyms | cis-Diamminedichloroplatinum(II); CDDP; Cis-dichlorodiammineplatinum |
| Molecular Formula | Cl₂H₆N₂Pt |
| Molecular Weight | 300.05 g/mol |
| Purity | ≥99% |
| Appearance | Yellow to pale orange crystalline powder |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble in water; soluble in DMSO and DMF |
| Storage Temperature | 2–8 °C (protected from light and moisture) |
| Category | Platinum coordination complex |
| Applications | DNA crosslinking, apoptosis studies, DNA repair research, oxidative stress analysis |
| Formulation | For in vitro biochemical assays or cellular exposure experiments |
| Stability | Stable under recommended storage conditions; degrades in strong light or alkaline media |
| Shelf Life | 24 months |
| Supplier Type | Factory peptide and chemical supplier |
| Intended Use | For laboratory research use only |
Mechanism of Action
Cisplatin exerts its primary biochemical activity through covalent binding to DNA, leading to the formation of intra- and inter-strand crosslinks. The core mechanism involves the substitution of chloride ligands with water molecules under physiological conditions, generating aquated species that are highly reactive toward nucleophilic DNA sites.
1. DNA Binding and Crosslink Formation
Cisplatin’s electrophilic platinum center preferentially binds to the N7 atom of guanine residues. The most abundant adducts are 1,2-intrastrand d(GpG) and d(ApG) crosslinks, which induce a significant bend in the DNA double helix (up to 30°). This distortion hinders transcription and replication processes, activating DNA damage checkpoints and repair mechanisms.
2. Induction of Apoptosis
DNA damage caused by cisplatin triggers a cascade of intracellular responses, including p53 activation, upregulation of pro-apoptotic proteins (Bax, PUMA), and mitochondrial cytochrome c release. These events lead to caspase activation and programmed cell death. The mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis is particularly important in cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity, as ROS accumulation further amplifies mitochondrial damage.
3. Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Cisplatin indirectly promotes ROS production through interactions with mitochondrial complexes I and III. The resulting oxidative stress damages lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, contributing to secondary cytotoxic effects. Manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) and glutathione peroxidase play crucial protective roles in modulating these effects, making cisplatin a useful reagent for oxidative stress and antioxidant research.
4. Signal Transduction Modulation
Cisplatin activates several key signal transduction pathways, including MAPK, JNK, and ERK cascades, leading to transcriptional regulation of apoptosis-related genes. It also influences the PI3K/Akt pathway, which contributes to cell survival and chemoresistance. These signaling networks make cisplatin a valuable model compound for studying stress response and drug resistance in cancer cells.
5. Transport and Detoxification
Cisplatin enters cells primarily via passive diffusion and copper transporters (CTR1), while efflux is mediated by ATP7A and ATP7B. Intracellular detoxification occurs through conjugation with glutathione, which forms platinum–glutathione adducts that can be exported by multidrug resistance proteins. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for studying platinum resistance and metallothionein-mediated detoxification pathways.

Side Effects
In research applications, cisplatin exhibits concentration-dependent cytotoxicity. At high levels, it induces apoptosis, necrosis, and DNA fragmentation. Typical cellular effects include mitochondrial swelling, ROS overproduction, and activation of stress kinases.
While cisplatin remains an invaluable research tool, it should be handled with caution. Laboratory studies have shown that prolonged exposure can affect cellular metabolism, disrupt protein folding, and induce oxidative injury in hepatocytes and renal epithelial models.
To ensure reproducible results and laboratory safety, researchers should:
Use personal protective equipment (PPE) including gloves, masks, and eye protection.
Prepare fresh solutions immediately before use to minimize hydrolysis.
Dispose of platinum-containing waste following hazardous material regulations.
Cisplatin is not intended for therapeutic or in vivo use, but only for controlled laboratory and biochemical experiments.
Keywords
Cisplatin, platinum coordination complex, DNA crosslinking agent, apoptosis inducer, oxidative stress research, chemoresistance model, DNA damage pathway, factory chemical supplier, bulk reagent China, high-purity platinum compound
Shipping Guarantee
All shipments are handled using validated cold-chain logistics to preserve compound integrity. Each package is sealed in moisture-proof containers with secondary protective wrapping and continuous temperature monitoring. Products are shipped via express international couriers with full tracking and insurance coverage.
Trade Assurance
We ensure product authenticity, verified ≥99% purity, and compliance with analytical standards (HPLC, MS, and NMR). Each batch is supplied with a Certificate of Analysis (CoA). Our trade assurance policy guarantees replacement or refund for any deviation from listed specifications.
Payment Support
We provide flexible and secure global payment options to support international research transactions. Accepted payment methods include PayPal, major credit cards (Visa, MasterCard, American Express), telegraphic transfer (T/T), and cryptocurrencies (USDT, Bitcoin, Ethereum). All transactions are protected by industry-standard encryption and verified payment gateways to ensure confidentiality and fund security.
Disclaimer
All products listed are intended for laboratory research use only and not for human or veterinary use. They are not drugs, medical devices, or diagnostics and should not be administered to humans or animals. Researchers must handle all materials in accordance with institutional biosafety and chemical safety guidelines. The information provided is for scientific reference only and does not imply therapeutic efficacy, safety, or regulatory approval.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 26 × 23 × 26 cm |
Q1: What is Cisplatin for Injection (Qilu) used for in research?
A: Cisplatin for Injection (Qilu) is used experimentally to model DNA crosslink induced cytotoxicity, chemotherapy resistance, and repair pathway studies in oncology.
Q2: How does Cisplatin for Injection work in experimental models?
A: It forms DNA crosslinks at guanine bases, blocking DNA synthesis and triggering apoptosis through caspase activation and DNA damage response mechanisms.
Q3: Why choose Cisplatin for Injection (Qilu) for research?
A: it provides consistent purity and formulation suitable for reproducible oncology research protocols.
Q4: Which research applications commonly involve Cisplatin for Injection?
A: Common use includes tumor cell viability assays, DNA repair studies, combination drug resistance screening, and pharmacokinetic exposure modeling.
Q5: Can I order Cisplatin for Injection in bulk?
A: Yes, both wholesale and retail orders are supported. Contact us for pricing, MOQ, and shipping logistics.
Q6: How should Cisplatin for Injection be stored for research use?
A: Store vials at controlled room temperature in a dry, light-protected environment. Reconstitute under sterile conditions; use immediately or refrigerate per lab protocol.
Q7: Can Cisplatin for Injection be used with other research agents?
A: Yes, it can be combined with DNA repair inhibitors, radiation models, taxanes, or platinum analogs to study synergy or resistance.
Q8: What adverse observations may appear in models using Cisplatin for Injection (Qilu)?
A: Potential observations include bone marrow suppression, electrolyte imbalance, mild GI symptoms, and allergic markers, depending on dose and protocol.
Q9: Is Cisplatin for Injection approved for clinical use?
A: this listing is strictly for laboratory research use only and not intended for therapeutic application.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.