No products in the cart.
Sale
Oxytocin (CAS 50-56-6) – High Purity Factory-Manufactured Freeze-Dried Peptide
Original price was: $36.00.$32.00Current price is: $32.00.
High-purity Oxytocin (CAS 50-56-6) is a research-grade peptide supplied as a freeze-dried powder for molecular, biochemical, and receptor-binding studies. Factory-manufactured with stringent quality control, it ensures reproducibility, stability, and analytical accuracy. Bulk, OEM, and wholesale options are available.(For research use only. Not for human or veterinary use.)
Description
Product Description
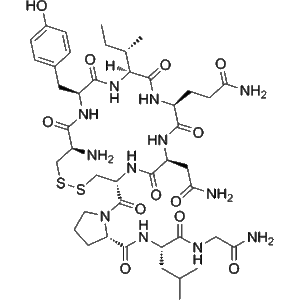
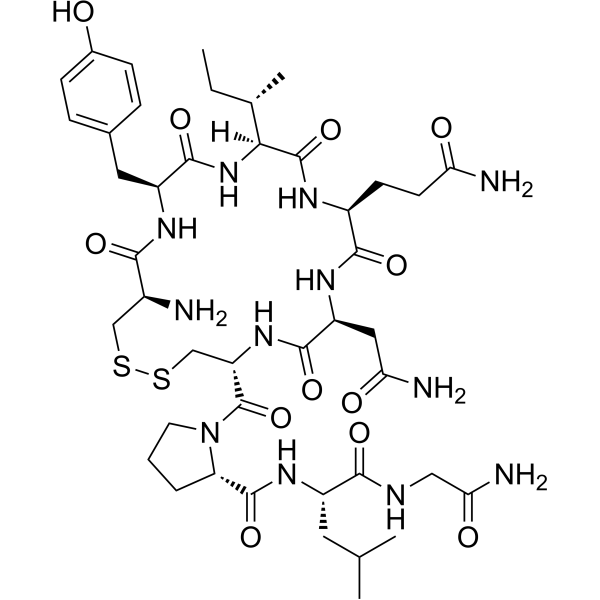
Oxytocin (CAS 50-56-6) is a highly characterized peptide extensively used in molecular biology, biochemical assays, structural modeling, and receptor interaction studies. Produced via solid-phase peptide synthesis and purified through advanced chromatographic methods, this high-purity Oxytocin peptide offers exceptional consistency and stability. Supplied as a lyophilized powder, it maintains structural integrity for long-term storage and flexible experimental use.
In research settings, Oxytocin is utilized to study ligand–receptor interactions, signaling pathways, peptide conformational dynamics, and molecular recognition events. Its well-defined disulfide-bonded cyclic structure and high solubility allow reliable reproducibility across analytical workflows, including HPLC, mass spectrometry, spectroscopy, and computational modeling. The peptide’s predictable behavior supports comparative studies, peptide library validation, and analytical calibration.
This high-purity Oxytocin is suitable for in vitro biochemical experiments such as receptor-binding assays, peptide–protein interaction modeling, structural conformation studies, and functional mapping. Its reproducibility ensures consistent assay outcomes and reliable reference standards. The lyophilized format allows precise reconstitution and controlled concentration preparation, making it ideal for laboratory protocols requiring strict experimental consistency.
Researchers may also use Oxytocin as a model ligand for evaluating G-protein coupled receptor interactions, exploring secondary messenger dynamics, and mapping receptor selectivity. Its chemical stability and defined sequence make it appropriate for molecular docking, SAR analysis, and multi-omics integration studies. Bulk packaging and factory-direct supply make it a convenient option for laboratories performing high-throughput peptide research.
Oxytocin is intended exclusively for laboratory research and should be handled according to standard safety practices. It is not for human or veterinary use, and all experimental applications must remain within controlled in vitro or analytical research environments.

Product Specifications
| Attribute | Specification | Extended Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Product Name | Oxytocin | Research-grade synthetic peptide for laboratory use. |
| CAS Number | 50-56-6 | Matches international chemical registry for accurate referencing. |
| Molecular Formula | C₄₃H₆₆N₁₂O₁₂S₂ | Full peptide backbone with disulfide-stabilized cyclic structure. |
| Molecular Weight | ~1007.19 Da | Verified through mass spectrometry for batch consistency. |
| Peptide Purity | ≥98% (HPLC) | High-purity standard for reproducible biochemical and analytical assays. |
| Sequence Format | Synthetic, lyophilized powder | Designed for stability and controlled reconstitution. |
| Appearance | White to off-white freeze-dried powder | Color variation reflects peptide dry-state characteristics. |
| Form | Lyophilized powder | Supports long-term storage and flexible experimental use. |
| Storage Conditions | -20°C, dry, protected from light | Preserves structure and activity over extended periods. |
| Reconstitution Solvents | Sterile water, compatible buffers | Fresh solutions recommended for experiments. |
| Recommended Working Concentrations | 0.1–5 mg/mL depending on assay | Optimized for in vitro research applications. |
| Stability (Lyophilized) | ≥12 months under proper storage | Moisture and light-sensitive; store sealed. |
| Stability (Reconstituted) | Use within 24–48 hours at 4°C | Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Packaging Options | 1 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 50 mg, bulk | Bulk and OEM options for high-volume labs. |
| Analytical Validation | HPLC, MS | Batch-specific verification of purity and identity. |
| Endotoxin Level | <1 EU/mg | Suitable for sensitive biochemical and analytical workflows. |
| Manufacturing Type | Factory-manufactured, wholesale available | Ideal for large-scale research laboratories. |
| Intended Use | Laboratory research only | Not for human or veterinary use. |
Solubility and Concentration Recommendations
Prepare fresh working solutions using sterile water or compatible buffers.
Gently mix; avoid vortexing that may induce aggregation.
Use low-binding consumables to maintain accurate peptide concentrations.

Oxytocin vial freeze-dried powder
Mechanism of Action
Oxytocin (CAS 50-56-6) functions as a well-characterized peptide ligand for in vitro receptor-binding, signaling, and structural studies. Its cyclic disulfide-bonded structure confers high stability and receptor selectivity, making it an ideal tool for laboratories investigating peptide–receptor interactions, conformational dynamics, and downstream biochemical pathways in controlled experimental models.
Receptor Binding and Affinity
Oxytocin engages the oxytocin receptor (OTR) analogs in laboratory assays, facilitating high-precision studies of ligand–receptor affinity and structural selectivity. The peptide’s cyclic conformation promotes consistent and reproducible binding events, which are essential for modeling receptor–ligand interactions, evaluating structure–activity relationships, and validating computational docking simulations. Researchers often employ Oxytocin in in vitro assays to compare binding kinetics among peptide analogs or to benchmark receptor activation models.
Signal Transduction and Secondary Messenger Investigation
Although used strictly in research settings, Oxytocin provides a reliable model to study molecular signaling mechanisms. Its interaction with receptor analogs can be leveraged to explore in vitro secondary messenger dynamics, such as cyclic AMP modulation, protein phosphorylation patterns, and downstream effector activity within controlled assay frameworks. These investigations enable the characterization of peptide-mediated pathway modulation and temporal response patterns under defined experimental conditions.
Conformational and Structural Dynamics
The cyclic disulfide-bonded structure of Oxytocin supports advanced structural analyses, including:
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy
Circular Dichroism (CD) spectroscopy
Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy
Computational peptide folding and docking simulations
These studies provide insights into peptide folding, stability, receptor interface geometry, and conformational flexibility, allowing researchers to understand structure–function relationships and peptide–protein interactions.
Analytical and Biophysical Research Applications
Oxytocin is widely used as a high-purity peptide standard in analytical and biophysical research. Applications include:
Method development for HPLC and LC-MS
Benchmarking peptide quantification assays
Investigating peptide-surface or peptide-material interactions in controlled laboratory setups
Validating reproducibility and sensitivity of biochemical detection methods
Summary
Overall, Oxytocin’s mechanism of action in research focuses on controlled receptor engagement, predictable peptide folding, and consistent biochemical signaling in in vitro models. Its structural stability, reproducible binding characteristics, and well-defined cyclic conformation make it a versatile tool for laboratories studying peptide–receptor interactions, molecular modeling, analytical method development, and peptide structural dynamics. High-purity, factory-manufactured Oxytocin provides reliable performance for laboratories seeking standardized reagents for advanced molecular and biophysical research workflows.
Applications
Oxytocin (CAS 50-56-6) is a versatile research peptide widely utilized in in vitro molecular biology, analytical, structural, and biochemical studies. Its high purity, defined cyclic structure, and reproducible behavior make it ideal for laboratories investigating peptide–receptor interactions, signaling dynamics, structural conformation, and method development.
1. Receptor-Binding and Molecular Signaling Studies
Serves as a model ligand for oxytocin receptor analogs in controlled in vitro assays.
Facilitates studies on receptor-ligand affinity, conformational selectivity, and binding kinetics.
Supports analysis of downstream signaling pathways, including secondary messenger dynamics and phosphorylation patterns in molecular research workflows.
2. Structural Biology and Peptide Conformation Research
Ideal for NMR, CD spectroscopy, and FTIR experiments to explore peptide folding, cyclic structure stability, and disulfide-bonded conformation.
Enables computational modeling and molecular docking studies to examine receptor interface geometry, peptide folding, and ligand-receptor interaction mechanisms.
Provides a reference standard for comparative analysis of peptide analogs and structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies.
3. Analytical Method Development and Biochemical Assays
Used as a calibration and reference peptide in HPLC, LC-MS, and spectroscopy-based analytical workflows.
Supports validation of assay sensitivity, accuracy, linearity, and reproducibility across laboratory experiments.
Allows reliable benchmarking of peptide quantification protocols, surface-binding assays, and material interaction studies.
4. Biophysical and Laboratory Modeling Applications
Applicable in peptide-surface interaction studies, adsorption profiling, and interface characterization.
Serves as a standardized peptide for method optimization, assay reproducibility, and comparative laboratory evaluations.
Useful for high-throughput screening of peptide libraries and evaluating ligand selectivity in controlled molecular systems.
5. Multi-Omic and Computational Integration
Facilitates integration into proteomics workflows, signaling network simulations, and computational modeling pipelines.
Acts as a model peptide in systems biology studies to understand receptor-mediated molecular interactions.
Enables cross-platform data comparison, linking structural, analytical, and biochemical results for reproducible research outcomes.
Summary:
High-purity Oxytocin supports diverse research applications, ranging from receptor-binding and signaling studies to analytical method development, structural conformation analysis, and computational modeling. Its consistent performance and defined cyclic structure make it a dependable tool for laboratories conducting advanced molecular, biochemical, and multi-omic investigations.
Research Models
Oxytocin (CAS 50-56-6) is widely applied in in vitro molecular, biochemical, structural, and analytical research models. Its high purity, defined cyclic structure, and reproducible properties make it an ideal tool for laboratories seeking precise, reliable, and controllable peptide behavior in experimental settings. The following research model categories illustrate its versatility and practical use.

1. Receptor-Ligand Binding Models
Oxytocin serves as a model ligand for oxytocin receptor analogs in in vitro receptor-binding studies.
Facilitates measurement of binding affinity, kinetics, and receptor conformational dynamics.
Supports comparative studies of peptide analogs and ligand selectivity assessments.
2. Intracellular Signaling Models
Used to study secondary messenger dynamics and downstream pathway regulation in controlled biochemical assays.
Allows investigation of cyclic AMP modulation, protein phosphorylation patterns, and effector activation in laboratory settings.
Enables detailed characterization of signaling pathways and temporal response profiling for mechanistic research.
3. Structural and Conformational Models
Employed in NMR, CD spectroscopy, FTIR, and computational modeling to examine peptide folding, stability, and cyclic disulfide conformation.
Supports peptide structure-function relationship studies and molecular docking simulations with receptor analogs.
Provides a reference standard for analyzing structural stability of peptide libraries and analogs.
4. Analytical Method Development Models
Oxytocin is a high-purity standard for HPLC, LC-MS, and spectroscopy-based method validation.
Used to benchmark assay sensitivity, linearity, and reproducibility.
Serves in surface-binding studies, peptide quantification validation, and analytical workflow optimization.
5. Biophysical and Interaction Models
Enables controlled investigation of peptide-surface interactions, adsorption kinetics, and interface characterization.
Useful for evaluating peptide-material interactions and biophysical assay performance.
Facilitates comparative evaluation of peptide binding across substrates or experimental platforms.
6. Computational and Multi-Omic Integration Models
Compatible with molecular docking, receptor modeling, and in silico peptide-receptor interaction studies.
Supports integration into proteomics workflows, signaling network simulations, and systems biology studies.
Provides a reproducible reference for cross-platform comparisons and modeling of peptide-mediated molecular interactions.
Summary:
High-purity Oxytocin offers a flexible platform for controlled in vitro research, supporting receptor-binding studies, signaling pathway analysis, structural conformation evaluation, analytical method development, and computational modeling. Its predictable structure, receptor-binding consistency, and chemical stability make it a dependable peptide for laboratories conducting advanced molecular and biochemical research.
Experimental Design Considerations
When using Oxytocin (CAS 50-56-6) in research, careful planning of experimental design is essential to ensure reproducibility, data accuracy, and safe laboratory handling. The following guidelines focus exclusively on in vitro, analytical, and structural research models, in line with controlled laboratory standards.

1. Define Experimental Objectives and Endpoints
Clearly identify primary and secondary research goals, such as receptor-binding affinity, secondary messenger dynamics, structural stability, or analytical assay validation.
Match assay formats to endpoints: binding studies for receptor kinetics, spectroscopy for conformational analysis, or LC-MS/HPLC for quantification.
Establish expected dynamic ranges and limits of detection prior to experimentation.
2. Peptide Concentration and Titration
Conduct preliminary titration experiments to determine the linear response range of the assay.
Typical working concentrations range from 0.1–5 mg/mL depending on the assay and detection method.
Prepare serial dilutions in compatible buffers; avoid extreme pH or high organic solvent concentrations unless specifically required.
3. Controls and Replication
Include negative controls (buffer only) and positive/benchmark controls (validated Oxytocin reference peptide) to ensure assay reliability.
Implement technical replicates (≥3) to improve precision and reproducibility.
Where applicable, replicate experiments under identical conditions to evaluate variability.
4. Reconstitution and Handling
Reconstitute lyophilized Oxytocin gently in sterile water or compatible buffers; avoid vigorous vortexing that may cause aggregation.
Aliquot reconstituted solutions into single-use volumes to minimize repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Use low-binding consumables to prevent peptide loss during preparation.
5. Buffer and Matrix Considerations
Use buffers that maintain structural integrity (e.g., neutral pH such as PBS or HEPES).
Assess matrix effects that could influence binding, retention time, or detection in analytical assays.
Validate buffer compatibility for downstream measurements such as spectroscopy or chromatography.
6. Analytical Validation and Calibration
Validate all methods (HPLC, LC-MS, spectroscopic assays) for linearity, precision, accuracy, and recovery.
Use internal standards or reference peptides to correct for instrument or sample variability.
Document retention times, fragmentation patterns, and calibration curves for traceability.
7. Data Documentation and Reproducibility
Record all experimental parameters: lot number, COA reference, peptide concentration, buffer composition, and instrument settings.
Maintain detailed laboratory notebooks or digital records to facilitate replication and verification.
Follow version-controlled SOPs for peptide handling, assay execution, and data analysis.
8. Troubleshooting and Optimization
Low signal: verify peptide integrity via HPLC/MS, reduce adsorption losses using low-binding materials.
High background: check buffer composition, solvent purity, and possible carryover.
Aggregation: optimize solvent, reduce peptide concentration, and apply gentle mixing techniques.
9. Safety and Compliance
Handle Oxytocin exclusively in laboratory environments with appropriate personal protective equipment.
Adhere to institutional safety protocols and chemical waste disposal regulations.
Material is for research use only and not intended for human or veterinary applications.
Summary:
Adhering to these experimental design principles ensures that Oxytocin provides consistent, reproducible results in receptor-binding studies, signaling pathway analysis, structural evaluations, and analytical method development. Careful attention to concentration, controls, buffer compatibility, and documentation maximizes data quality while maintaining safe laboratory practices.
Laboratory Safety & Handling Guidelines
Handle Oxytocin in a controlled lab environment with gloves, lab coat, and eye protection
Avoid inhalation or direct contact with powder
Store lyophilized peptide at -20°C, protected from light and moisture
Use low-disturbance techniques during reconstitution and preparation
Dispose of residues according to institutional safety and chemical waste protocols
Material is for research use only and must not be used in humans or animals

Oxytocin vial freeze-dried powder
Integration with Multi-Omic & Computational Studies
Oxytocin (CAS 50-56-6) is a high-purity peptide that can be seamlessly integrated into multi-omic and computational research workflows, providing a versatile platform for mechanistic studies, structural modeling, and systems biology investigations. Its defined cyclic structure, predictable receptor-binding properties, and stable biochemical profile make it an ideal reference peptide for laboratories exploring complex molecular interactions and signaling networks.
1. Proteomics and Signaling Network Integration
Oxytocin can be used as a standard in proteomic assays to assess peptide–protein interactions, receptor engagement, and post-translational modifications.
Incorporation into signaling pathway models allows for in vitro validation of peptide-mediated molecular events.
Supports comparative evaluation across peptide analogs, enabling researchers to map structural features to functional outcomes.
2. Computational Modeling and Molecular Docking
Serves as a reliable ligand for in silico receptor modeling and molecular docking studies.
Researchers can simulate Oxytocin–receptor interactions to predict binding affinities, conformational changes, and potential structural modifications.
Supports high-throughput computational screening for peptide analogs, providing a benchmark for virtual SAR (structure–activity relationship) studies.
3. Multi-Omic Data Integration
Oxytocin can be included in multi-omic workflows, such as proteomics, transcriptomics, and metabolomics, to examine peptide-mediated network responses under controlled laboratory conditions.
Enables correlation of peptide structural features with functional outcomes across datasets, enhancing mechanistic understanding of signaling pathways.
Facilitates cross-platform validation, linking in vitro observations with computational predictions to improve reproducibility and interpretability.
4. Systems Biology and Pathway Mapping
Provides a standardized tool for mapping receptor-mediated signaling networks in molecular simulations.
Can be used to model temporal dynamics of peptide-receptor interactions and downstream biochemical events.
Supports integration of experimental data into computational frameworks to predict pathway modulation, aiding hypothesis generation in laboratory research.
5. Analytical and Structural Computational Studies
Oxytocin’s defined sequence and cyclic conformation allow for benchmarking of structural prediction algorithms, folding simulations, and peptide–protein interaction models.
Facilitates method validation for computational workflows such as docking, energy minimization, and structural alignment.
Can serve as a reference standard for validating emerging computational pipelines in peptide research.
Summary:
High-purity Oxytocin is a versatile tool for integrating in vitro research with computational and multi-omic studies. Its stable structure, reproducible receptor interactions, and defined biochemical properties allow laboratories to bridge experimental assays with predictive modeling, systems biology analysis, and multi-layered omic data integration, enhancing mechanistic insight and data reproducibility.

Keywords
Oxytocin, Oxytocin peptide, CAS 50-56-6, high-purity peptide, freeze-dried peptide, wholesale peptide, laboratory-grade peptide, receptor-binding peptide, analytical peptide standard, peptide structural research
Shipping Guarantee
Temperature-controlled delivery preserves peptide stability during transit.
Tamper-proof packaging ensures safe and intact arrival.
Global logistics coverage guarantees reliable delivery to research laboratories worldwide.
Bulk packaging options available for large-scale research applications.
Trade Assurance
Factory-direct sourcing ensures authenticity and consistent high purity.
Verified COA documents accompany every batch for transparency.
Stable supply chain supports continuous laboratory research workflows.
OEM customization available for institutional or commercial research purposes.
Payment Support
Accepts bank transfer, PayPal, and major credit cards for secure transactions.
Supports corporate procurement channels for bulk or repeated orders.
Flexible payment methods facilitate seamless international and institutional purchasing.
Disclaimer
Oxytocin is intended exclusively for laboratory research purposes.
It is not for human or veterinary use, and no clinical or therapeutic applications are implied.
Researchers must follow all institutional safety protocols when handling this material.
References
PubChem – Oxytocin
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/OxytocinNCBI Protein Database – Oxytocin
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/RCSB Protein Data Bank (PDB) – Oxytocin-Receptor Structures
https://www.rcsb.org/ScienceDirect – Analytical Peptide Methods
https://www.sciencedirect.com/Nature Protocols – Peptide Structural Analysis
https://www.nature.com/nprot/Analytical Chemistry – Peptide Calibration Studies
https://pubs.acs.org/journal/anchamJournal of Peptide Science – Structural and Functional Studies
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/10991308Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences – GPCR-Peptide Interactions
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/molecular-biosciencesJournal of Chromatography B – Peptide Analytical Method Development
https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/journal-of-chromatography-bProtein & Peptide Letters – Analog Research
https://www.eurekaselect.com/journal/28
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 26 × 23 × 26 cm |
1. What is Oxytocin?
Oxytocin (CAS 50-56-6) is a high-purity research peptide used in receptor-binding studies, signaling pathway exploration, structural analysis, and analytical method development.
2. What applications is Oxytocin suitable for?
It is suitable for in vitro receptor-binding assays, peptide–protein interaction studies, structural conformation analysis, and multi-omic integration workflows.
3. Is Oxytocin suitable for human or veterinary use?
No. Oxytocin provided here is strictly for laboratory research only. It is not intended for human or veterinary applications.
4. What purity level does Oxytocin have?
Each batch is ≥98% pure, verified by HPLC and mass spectrometry to ensure consistent analytical and experimental performance.
5. Are certificates of analysis (COA) provided?
Yes. Each lot includes a detailed COA confirming peptide purity, identity, and analytical validation.
6. How is Oxytocin supplied?
Oxytocin is supplied as a freeze-dried, lyophilized powder for optimal stability and precise handling. Bulk and OEM packaging options are available.
7. How should Oxytocin be stored?
Store lyophilized peptide at -20°C, dry, and protected from light. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
8. How should it be reconstituted?
Reconstitute using sterile water or compatible buffers. Prepare fresh working solutions for each experiment and aliquot to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
9. Are there any special safety precautions?
Use gloves, lab coat, and eye protection when handling the peptide. Avoid inhalation of powder, and work in controlled laboratory environments.
10. Can Oxytocin be used for receptor-binding studies?
Yes, it serves as a model ligand for oxytocin receptor analogs in controlled in vitro assays.
11. Is it suitable for structural studies?
Yes. Its cyclic disulfide-bonded structure allows use in NMR, CD spectroscopy, FTIR, and computational modeling of peptide folding and receptor interaction.
12. Can it be used for analytical method development?
Yes. Oxytocin is ideal for HPLC, LC-MS, and spectroscopy-based validation, serving as a high-purity reference standard.

















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.