No products in the cart.
Sale
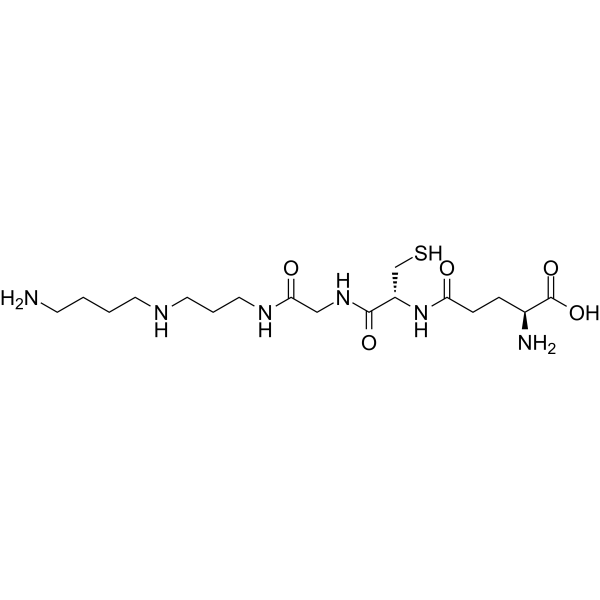
Glutathionylspermidine (CAS 33932-35-3) | GMP Supplier for Research Use
Original price was: $22.00.$16.00Current price is: $16.00.
Glutathionylspermidine (CAS 33932-35-3) is a peptide metabolite produced by Escherichia coli. It plays an important role in cellular redox balance, stress responses, and glutathione metabolism.
(Please contact our staff to place an order or learn about product wholesale prices, specifications, uses and lists)
Description
Contents
hide
Product Description
Background and Scientific Relevance
Glutathionylspermidine (CAS 33932-35-3) is a unique conjugate molecule formed by the enzymatic ligation of glutathione (GSH) and spermidine, both of which are critical biomolecules in cellular metabolism. It was first identified in Escherichia coli and related bacterial species, where it functions as part of an adaptive stress response mechanism. While glutathione is well known as a major antioxidant and spermidine is an important polyamine involved in cell growth, their conjugated form—glutathionylspermidine—exhibits specialized biological functions that cannot be attributed to either parent molecule alone.
This metabolite has become a valuable tool in biochemical research, microbial physiology studies, and cellular stress investigations. Its role in modulating enzymatic activity, redox homeostasis, and gene regulation makes it an important subject for laboratories interested in host–pathogen interactions, polyamine metabolism, and potential antimicrobial targets.
Chemical Nature & Source
Chemically, glutathionylspermidine is a peptide-polyamine conjugate, comprising glutathione (?-glutamyl-cysteinyl-glycine) linked via an amide bond to spermidine, a naturally occurring polyamine. It is not typically found in mammalian cells but is abundant in specific bacterial strains. This difference makes it an attractive biomarker for microbial presence and a research probe for distinguishing microbial vs. mammalian metabolic processes.
The biosynthesis of glutathionylspermidine is catalyzed by glutathionylspermidine synthetase (GspS), an enzyme encoded in bacteria. Interestingly, the bifunctional enzyme glutathionylspermidine synthetase/amidase not only catalyzes its formation but also regulates its breakdown, highlighting its dynamic regulation within bacterial physiology.
Purity and GMP Production Standards
Research-grade glutathionylspermidine must meet strict quality standards to ensure reliability in experimental outcomes. GMP-compliant synthesis ensures a purity ? 98% (HPLC verified), minimizing interference from related polyamines or glutathione derivatives. Stability testing demonstrates that lyophilized glutathionylspermidine maintains integrity for extended storage when kept under recommended conditions.
Importance in Research
Microbial Physiology – Glutathionylspermidine is a key factor in bacterial adaptation to oxidative stress, helping microbes survive under hostile environments.
Redox Regulation – The conjugate acts as a redox buffer, similar to glutathione but with added polyamine functionality.
Potential Antimicrobial Target – Since it is largely absent in mammalian cells, enzymes regulating glutathionylspermidine metabolism may serve as selective targets for novel antibacterial agents.
Model for Post-Translational Modifications – It represents a biochemical model for studying thiol conjugation, polyamine activity, and protein regulation.
Biomarker Potential – Its presence can serve as a molecular marker for bacterial metabolic states, making it useful in infection research.
Glutathione (GSH): Widely present in mammalian and bacterial cells, strong antioxidant. Glutathionylspermidine offers additional polyamine-based functionality.
Spermidine: Essential polyamine for DNA stabilization and cell proliferation. Conjugation with GSH adds redox-active properties.
Other Polyamine Conjugates: Rare in nature and often unstable, whereas glutathionylspermidine is biologically significant and enzymatically regulated.
Through these comparisons, glutathionylspermidine emerges as a uniquely bacterial metabolite with cross-disciplinary research significance.
Product Specifications
Product Specifications Table
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Glutathionylspermidine |
| CAS Number | 33932-35-3 |
| Synonyms | Gsp; Glutathione-spermidine conjugate |
| Molecular Type | Peptide-polyamine conjugate |
| Functional Role | Metabolite in bacterial redox & polyamine metabolism |
| Molecular Formula | C17H34N6O6S (approximate, depending on protonation state) |
| Molecular Weight | ~ 450–500 g/mol (varies by salt form) |
| Appearance | White to off-white lyophilized powder |
| Purity | ? 98% (HPLC verified) |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, PBS, and aqueous buffers; limited solubility in DMSO |
| Stability | Stable ? 24 months (lyophilized, sealed, -20°C) |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C, dry, protected from light and moisture |
| GMP Compliance | Manufactured under GMP-certified conditions |
| Applications | Microbial metabolism studies, redox biology, immunology, biochemical assays |
| Availability | Bulk & small-quantity supply (supports wholesale and retail research needs) |
Purity Assurance: High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) confirms ? 98% purity, reducing the risk of experimental variability.
Solubility Profile: Being water-soluble allows easy preparation of stock solutions for both in vitro and in vivo experiments.
Stability Data: Freeze-dried form ensures stability for extended storage; repeated freeze-thaw cycles should be avoided.
Packaging Options: Offered in both bulk (wholesale) and small vials (retail), allowing flexible purchase depending on research scale.
Compliance: Every batch is accompanied by a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) ensuring compliance with laboratory-grade standards.
Mechanism of Action & Research Applications
Mechanism of Action
Glutathionylspermidine is synthesized by glutathionylspermidine synthetase (GspS), an enzyme that ligates glutathione to spermidine. The resulting conjugate functions in redox regulation and polyamine metabolism.
Redox Function: The thiol group of glutathione remains available for redox reactions, allowing glutathionylspermidine to act as an antioxidant buffer.
Polyamine Role: Spermidine provides DNA-binding and stabilizing activity, contributing to nucleic acid protection under stress.
Enzymatic Regulation: Glutathionylspermidine can modulate protein function by conjugation, influencing transcriptional regulation and stress responses.
Research Applications
Microbial Stress Response Studies
Acts as a protective molecule in E. coli during oxidative stress.
Serves as a model to study bacterial adaptation to hostile environments.
Infection Biology
Since glutathionylspermidine is absent in mammals, its metabolic enzymes may serve as selective antimicrobial drug targets.
Provides a biomarker for bacterial metabolic states.
Redox & Antioxidant Research
Helps study the interface of glutathione and polyamine metabolism.
Valuable for experiments involving oxidative damage, antioxidant defense, and cellular detoxification.
Molecular Biology
Used to investigate gene expression changes under bacterial stress.
Helps define bacterial transcriptional regulatory networks.
Drug Development
A potential lead for antibiotic discovery, particularly in targeting E. coli and related pathogens.
Can be used to screen inhibitors of glutathionylspermidine synthetase.

Side Effects (For Reference in Research Models)
While glutathionylspermidine itself is a naturally occurring bacterial metabolite, researchers working with it should consider possible limitations:
Dose-Dependent Cellular Responses – At high concentrations, may alter redox balance in unintended ways.
Solvent Sensitivity – Dissolution in non-aqueous solvents may reduce stability.
Experimental Artifacts – Over-supplementation in mammalian cells can cause off-target effects.
Storage-Related Degradation – Repeated freeze-thaw cycles may degrade peptide structure.
Safety Consideration – For laboratory use only; not approved for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
Disclaimer
For laboratory research use only. Not for human or veterinary use.
Keywords
Glutathionylspermidine CAS 33932-35-3
Buy Glutathionylspermidine peptide
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 53 × 82 × 53 cm |














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.