No products in the cart.
Sale
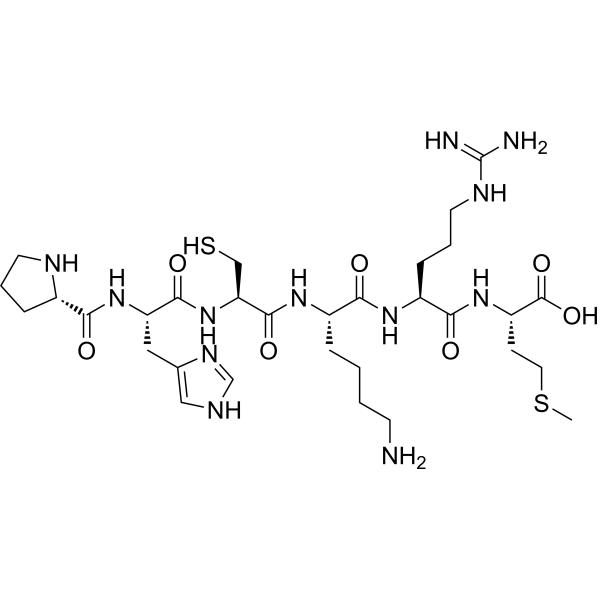
Antioxidant Peptide A (CAS 159147-88-3)
Original price was: $28.00.$22.00Current price is: $22.00.
Antioxidant Peptide A is a short synthetic peptide with alternating aromatic and sulfur-containing residues. Its structure provides potent radical scavenging activity, making it a valuable tool for investigating oxidative stress, cellular protection mechanisms, and cancer biology in preclinical models. GMP-grade purity ensures reproducible laboratory results.
Description
Contents
hide
Product Description
Antioxidant Peptide A (CAS 159147-88-3) is a short synthetic peptide engineered with alternating aromatic and sulfur-containing amino acids, which confer strong antioxidant and radical scavenging properties. This design allows the peptide to interact effectively with reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cellular environments, particularly in cancer cell models.
Background and Research Significance
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a dual role in cancer biology: they can induce cell damage but also contribute to cell signaling and proliferation. Antioxidant Peptide A is designed to:
Neutralize ROS and prevent oxidative damage in vitro.
Investigate oxidative stress pathways in cancer and other disease models.
Study the protective mechanisms of peptides in cell signaling and metabolism.
Its structure, rich in aromatic and sulfur-containing residues, enhances electron donation to radicals, providing effective radical scavenging activity. This makes it highly suitable for preclinical studies of oxidative stress, cancer biology, and therapeutic peptide development.
Chemical Properties and Structure
Compound Class: Short synthetic peptide
Target: Cellular ROS
Mechanism: Radical scavenging via electron-rich side chains
Activity: Antioxidant, cytoprotective in vitro
Stability: Lyophilized peptide for long-term storage
Applications: Oxidative stress research, cancer biology, preclinical peptide studies
Antioxidant Peptide A demonstrates high reproducibility, structural stability, and biological activity, making it a reliable tool for laboratory research.
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Antioxidant Peptide A |
| Synonyms | Antioxidant Peptide A |
| CAS Number | 159147-88-3 |
| Molecular Formula | C39H55N9O10S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 909.0 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to off-white lyophilized powder |
| Purity | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, PBS, DMSO |
| Stability | Stable ≥24 months at –20°C |
| Storage Conditions | Store at –20°C; avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles |
| GMP Compliance | Manufactured under GMP-certified facility |
| Applications | Oxidative stress research, cancer cell studies, radical scavenging studies |
| Availability | Wholesale & retail |
| Experimental Models | Cancer cell lines, in vitro oxidative stress assays |
| Safety Considerations | For laboratory research use only; not for human or veterinary use |
The specifications ensure high purity, reproducible antioxidant activity, and structural stability, supporting reliable experimental outcomes.
Mechanism of Action & Research Applications
Mechanism of Action
Antioxidant Peptide A exerts its biological activity by neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) via the side chains of its aromatic and sulfur-containing amino acids:
Electron Donation: Aromatic residues donate electrons to free radicals, stabilizing them.
Sulfur-Mediated Radical Scavenging: Sulfur-containing residues (e.g., cysteine or methionine) provide additional antioxidant capacity through thiol-mediated reactions.
Cellular Protection: Reduces oxidative damage to lipids, proteins, and DNA in preclinical models.
This mechanism makes the peptide highly effective in in vitro oxidative stress studies, particularly in cancer cell lines where ROS levels are elevated.
Research Applications
1. Cancer Biology Research
Study oxidative stress and radical-induced damage in tumor cell lines.
2. Antioxidant Mechanism Studies
Investigate peptide-based radical scavenging pathways in cellular models.
3. Cytoprotective Research
Assess the protective effects of antioxidant peptides on cells exposed to ROS-inducing conditions.
4. Preclinical Peptide Development
Serve as a model for designing therapeutic antioxidant peptides.
5. Oxidative Stress Assays
Use in DCFH-DA, ROS fluorescence, or cell viability assays to quantify protective effects.
6. Combination Studies
Evaluate synergistic effects with chemotherapeutic or cytoprotective agents.
7. Mechanistic Insights
Analyze electron transfer pathways, thiol redox cycling, and radical stabilization.
8. Drug Screening Models
Apply in vitro to test small molecules or compounds for oxidative stress modulation.
9. Translational Research
Inform development of peptides as adjunct therapies for oxidative stress-related diseases.
10. Laboratory Protocol Optimization
Supports robust experimental design for ROS and oxidative damage research.

Side Effects (For Reference in Research Models)
Preclinical observations include:
Dose-Dependent Activity: Higher concentrations may affect cell proliferation in sensitive lines.
Cell Type Variability: Effects vary depending on cell line and ROS baseline levels.
Stability Considerations: Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles to maintain antioxidant potency.
Combination Effects: Co-treatment with other compounds may enhance or reduce activity.
These observations are strictly for laboratory research reference. Antioxidant Peptide A is not for human or veterinary use.
Disclaimer
For laboratory research use only. Not for human or veterinary use.
Keywords
Synthetic radical scavenging peptide
Cancer cell ROS research peptide
GMP-grade Antioxidant Peptide A
In vitro oxidative stress peptide
Cytoprotective research peptide
Laboratory antioxidant peptide
Preclinical peptide studies
Aromatic/sulfur-containing peptide
Research use only antioxidant agent
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 53 × 26 × 53 cm |
2 reviews for Antioxidant Peptide A (CAS 159147-88-3)
Q1: What is Antioxidant Peptide A?
A1: A short synthetic peptide with aromatic and sulfur-containing amino acids for radical scavenging.
Q2: What is its CAS number?
A2: CAS No. 159147-88-3.
Q3: What is its primary research application?
A3: Oxidative stress studies and cancer cell biology research.
Q4: Can it be used in humans?
A4: No, it is strictly for laboratory research.
Q5: How does Antioxidant Peptide A work?
A5: Neutralizes ROS via electron donation from aromatic residues and thiol-mediated sulfur residues.
Q6: What experimental models are suitable?
A6: Cancer cell lines and in vitro oxidative stress assays.
Q7: What is its purity?
A7: ≥98% (HPLC).
Q8: How should it be stored?
A8: Store at –20°C; avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Q9: Is it GMP-compliant?
A9: Yes, manufactured under GMP-certified conditions.
Q10: Can it be purchased in bulk?
A10: Yes, available for wholesale and retail laboratory use.














jalalalnaser –
We found the product to be reliable for our ongoing sourcing needs. Communication and order handling were efficient.
Succi –
I am very satisfied with packaging and shipping speed!