No products in the cart.
Sale
Latromotide (CAS 1049674-65-8) | Synthetic Antineoplastic Peptide
Original price was: $28.00.$23.00Current price is: $23.00.
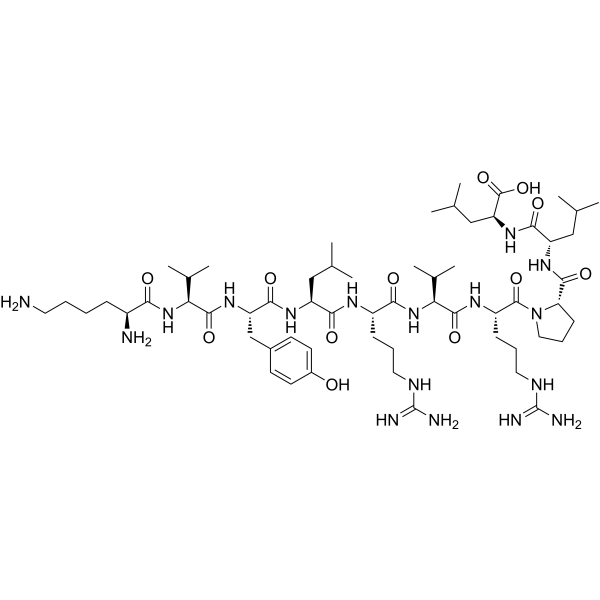
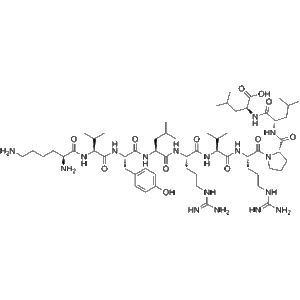
Latromotide is a synthetic decapeptide with antineoplastic activity, corresponding to residues 66–75 of the human kinesin-like protein KIF20A. With the sequence H-Lys-Val-Tyr-Leu-Arg-Val-Arg-Pro-Leu-Leu-OH, it is widely applied in cancer immunotherapy and tumor antigen research.
Description
Contents
hide
Product Description
Latromotide is a synthetic peptide engineered for research applications in cancer immunology and oncology drug discovery. Chemically, Latromotide consists of ten amino acids corresponding to residues 66–75 of the human kinesin-like protein KIF20A. The peptide sequence—H-Lys-Val-Tyr-Leu-Arg-Val-Arg-Pro-Leu-Leu-OH—is derived from a tumor-associated antigen, positioning Latromotide as a valuable research tool for studying immune responses against malignant cells.
Background and Research Relevance
The kinesin-like protein KIF20A is overexpressed in multiple cancers, including pancreatic, lung, gastric, and bladder cancers. It plays a critical role in mitotic spindle function and cellular proliferation. Due to its cancer-specific overexpression, KIF20A-derived peptides such as Latromotide are attractive candidates for peptide-based immunotherapies, particularly cancer vaccines designed to elicit cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses.
Latromotide is being evaluated in preclinical and translational research for its ability to stimulate tumor-specific immunity. Researchers use this peptide to study T-cell epitope recognition, dendritic cell presentation, and tumor rejection mechanisms. Furthermore, its defined amino acid structure enables reproducibility and standardization across laboratories, making it an excellent candidate for immunological investigations.
Structural Characteristics
Latromotide’s sequence is short yet immunologically potent, optimized for major histocompatibility complex (MHC) binding. Synthetic peptides like Latromotide provide the advantage of high purity, stability, and scalability compared to tumor cell lysates or longer antigenic proteins. As a lyophilized powder, Latromotide maintains stability under proper storage conditions and dissolves readily in aqueous buffers for use in cell culture or animal experiments.
Advantages Over Conventional Peptides
Compared to traditional long peptides or whole-protein antigens, Latromotide demonstrates:
Defined structure for reproducible immunogenic responses
High specificity toward tumor-associated targets (KIF20A-derived sequence)
Scalability for large-scale laboratory and preclinical use
Ease of modification, allowing researchers to create analogs or conjugates for enhanced stability or immunogenicity
In summary, Latromotide is more than a short synthetic peptide—it represents a precise immunological probe and potential therapeutic lead for advancing cancer vaccine development.
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Latromotide |
| Synonyms | KIF20A(66–75) peptide; H-Lys-Val-Tyr-Leu-Arg-Val-Arg-Pro-Leu-Leu-OH |
| CAS Number | 1049674-65-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C58H101N17O14 |
| Molecular Weight | 1231.5 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to off-white lyophilized powder |
| Purity | ≥ 98% (HPLC) |
| Solubility | Soluble in aqueous buffers, DMSO, and dilute acids |
| Stability | Stable in lyophilized form ≥ 24 months at -20°C |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C; avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles |
| Mechanism | Peptide antigen; immunological activation via KIF20A-derived epitope |
| GMP Compliance | Manufactured under GMP-certified facilities |
| Applications | Immunotherapy research, cancer vaccines, T-cell activation assays |
| Availability | Available in bulk (wholesale) and small-scale (retail) GMP-grade supply |
Commentary on Specifications
Molecular Details: The precise molecular formula and weight allow accurate molar dosing in experimental protocols.
Purity: ≥ 98% purity ensures minimal interference from peptide impurities in immunological assays.
Solubility: The solubility in both aqueous buffers and organic solvents makes it versatile across different experimental setups.
Stability: With a 24-month stability profile in lyophilized form, Latromotide is suitable for long-term projects.
Applications: Particularly valuable in research involving tumor antigen identification, vaccine design, and immunogenicity studies.
Mechanism of Action & Research Applications
Mechanism of Action
Latromotide functions primarily as a tumor-associated antigen (TAA)-derived peptide, acting as an immunological probe. Its mechanism involves:
Antigen Presentation: Once introduced into an experimental system, Latromotide binds to MHC class I molecules on antigen-presenting cells (APCs).
T-cell Activation: The peptide-MHC complex is recognized by CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs).
Immune Response: Activated CTLs target and lyse KIF20A-overexpressing tumor cells, modeling how peptide-based vaccines may work in vivo.
Research Applications
Cancer Vaccine Development
Latromotide is widely studied as a candidate peptide for cancer vaccines. It enables the evaluation of epitope-specific immune responses in pancreatic and gastric cancer models.T-cell Response Studies
Researchers use Latromotide in vitro to stimulate T-cells, measure interferon-γ release, and assess CTL cytotoxicity, critical for understanding adaptive immunity against tumors.Dendritic Cell-Based Immunotherapy
Latromotide can be pulsed into dendritic cells, which are then used to prime T-cells in laboratory models, representing a promising strategy for adoptive immunotherapy.Oncology Models
By testing Latromotide in xenograft or syngeneic tumor models, researchers can investigate tumor growth inhibition, CTL infiltration, and overall immune modulation.Peptide Engineering and Analog Development
Scientists often modify Latromotide’s sequence to enhance MHC binding affinity or improve stability, allowing the design of next-generation peptide vaccines.Combination Immunotherapy
Latromotide research is often combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies) to explore synergistic effects in preclinical oncology.Translational Research
The peptide has translational potential, serving as a model for how short synthetic peptides can be incorporated into personalized or population-based immunotherapy trials.
Side Effects (For Reference in Research Models)
Although Latromotide is strictly for research use, some effects have been observed in experimental systems:
Immunological Overactivation
Strong T-cell stimulation may lead to non-specific immune responses or cytokine release in laboratory models.Cross-Reactivity
Peptides derived from conserved regions may occasionally show weak cross-reactivity with normal tissues, requiring careful monitoring.Dose-Dependent Effects
High concentrations may not improve immunogenicity but could alter cell viability in vitro or cause excessive inflammation in vivo.Peptide Stability Issues
Repeated freeze-thaw cycles may degrade the peptide, leading to inconsistent results in assays.Model-Dependent Variability
Effects can differ between murine, primate, and humanized models, reflecting differences in MHC binding and T-cell repertoires.Combination Therapy Reactions
When used with adjuvants or checkpoint inhibitors, exaggerated immune responses may occur in certain models.Limitations
Latromotide does not directly kill tumor cells—it relies on the immune system, which can vary greatly between models.
These side effects are laboratory observations only and not related to clinical use, as Latromotide is not approved for human or veterinary administration.
Disclaimer
For laboratory research use only. Not for human or veterinary use.
Keywords
- CAS 1049674-65-8
KIF20A-derived peptide
Antineoplastic research peptide
Cancer immunotherapy peptide
Tumor antigen synthetic peptide
GMP peptide supplier
Research-use-only peptide
Peptide-based cancer vaccine candidate
Immunological agent peptide
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 53 × 26 × 53 cm |
What is Latromotide?
A synthetic 10-amino-acid peptide derived from KIF20A residues 66–75 with antineoplastic activity.
What is the CAS number of Latromotide?
CAS No. 1049674-65-8.
What is its molecular formula and weight?
Molecular Formula: C58H101N17O14; Molecular Weight: 1231.5 g/mol.
What is the primary research use?
For cancer immunology, T-cell activation assays, and peptide-based vaccine development.
Is Latromotide GMP-compliant?
Yes, manufactured in GMP-certified facilities.
How pure is the peptide?
≥ 98% purity confirmed by HPLC.
What storage conditions are recommended?
Store lyophilized at -20°C; avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Is it soluble in aqueous buffers?
Yes, soluble in buffers, DMSO, and dilute acids.
Can it be used in combination therapy models?
Yes, often tested with checkpoint inhibitors or adjuvants.
Is Latromotide safe for human use?
No, it is strictly for laboratory research only.












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.