No products in the cart.
Sale
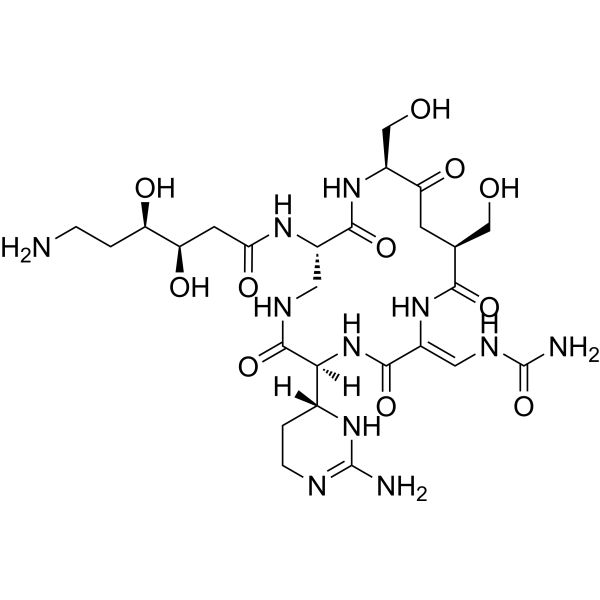
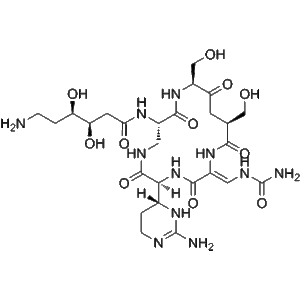
Enviomycin | CAS No. 33103-22-9
Original price was: $34.00.$25.00Current price is: $25.00.
Enviomycin (Tuberactinomycin N) is an antibacterial antibiotic with established activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It has been used in research focused on chronic cavitary pulmonary tuberculosis and provides valuable insights into the development of anti-TB therapies.
Description
Product Description
Enviomycin (CAS 33103-22-9), also referred to as Tuberactinomycin N, belongs to the tuberactinomycin family of antibiotics, first discovered in actinomycete species. This family is distinguished by its cyclic peptide backbone, which imparts high stability, strong antimicrobial activity, and selective binding to bacterial ribosomes.
Historical and Scientific Context
Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the most persistent infectious diseases worldwide, with high morbidity and mortality.
Drug-resistant strains, such as MDR-TB and XDR-TB, pose significant challenges to global health.
Enviomycin was first investigated in the mid-20th century as a next-generation anti-TB peptide, demonstrating high efficacy in in vitro and in vivo models.
Its activity is primarily against chronic cavitary pulmonary TB, a form that is difficult to treat due to persistent bacterial colonies in lung cavities.
Molecular and Biochemical Features
Enviomycin’s structure includes non-ribosomal peptide sequences that enable selective binding to mycobacterial ribosomes, disrupting protein synthesis.
The cyclic structure enhances enzymatic stability and cell permeability, allowing effective intracellular targeting of M. tuberculosis.
Extensive research demonstrates that Enviomycin’s mechanism is distinct from traditional TB antibiotics, offering a complementary approach to isoniazid or rifampicin therapy.
Research Applications
In Vitro Antimicrobial Studies
Demonstrates potent inhibition of M. tuberculosis growth in broth and agar media.
Provides a standardized tool to evaluate new combination therapies.
Chronic Cavitary TB Models
Used in animal studies to mimic human pulmonary cavities.
Helps determine drug penetration, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics in persistent infection sites.
Drug Resistance Research
Enables the study of resistance mechanisms in mycobacteria.
Supports development of synergistic drug combinations to combat MDR-TB.
Pharmacological Profiling
Investigated for absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties.
Serves as a reference compound for structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies in cyclic peptide antibiotics.
Translational Research Potential
While not approved clinically, Enviomycin remains a critical preclinical tool for designing next-generation TB therapeutics.
Provides a foundation for peptide-based anti-infective strategies.
Educational and Experimental Use
Used in biochemistry and microbiology laboratories to demonstrate antibiotic-bacteria interactions.
Serves as a model to study peptide stability, binding kinetics, and intracellular targeting.
Enviomycin’s versatility as a research reagent has cemented its role in both fundamental studies of mycobacterial physiology and applied antibiotic research.
Product Specifications
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Enviomycin |
| CAS No. | 33103-22-9 |
| Synonyms | Tuberactinomycin N |
| Molecular Type | Cyclic peptide antibiotic |
| Biological Activity | Antibacterial, anti-TB activity |
| Target Organism | Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
| Mechanism | Ribosome inhibition, protein synthesis disruption |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder |
| Purity | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Solubility | Water-soluble; compatible with PBS and culture media |
| Storage | -20°C to -80°C, protected from moisture and light |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months under recommended conditions |
| Applications | Chronic cavitary TB research, drug resistance studies, antibacterial assay development |
| Packaging | Lyophilized vial; custom sizes available |
Notes
Supplied in high purity suitable for cellular, microbial, and animal studies.
Endotoxin-free, suitable for sensitive in vitro experiments.
Mechanism of Action
Enviomycin exerts its antibacterial effects primarily through selective inhibition of mycobacterial ribosomes, leading to disruption of protein synthesis.
Ribosomal Targeting
Binds specifically to 50S ribosomal subunit in M. tuberculosis.
Inhibits peptide bond formation and blocks elongation of nascent proteins.
Effectively halts bacterial growth and replication.
Intracellular Penetration
The cyclic structure facilitates penetration into bacterial cells, including those in granulomas and pulmonary cavities.
Enhances efficacy against persistent intracellular bacteria.
Activity Against Drug-Resistant Strains
Maintains activity against MDR-TB and certain XDR-TB strains, which are resistant to rifampicin and isoniazid.
Provides a complementary mechanism, reducing the likelihood of cross-resistance.
Pharmacodynamic Effects
Demonstrates time-dependent bactericidal activity, with prolonged exposure increasing killing efficiency.
Synergistic with other antibiotics, enabling combination therapy optimization.
Application in Preclinical Models
Used in murine and rabbit pulmonary TB models to evaluate penetration into lung tissue and efficacy in cavitary lesions.
Supports studies of dose-response relationships, toxicity thresholds, and pharmacokinetics.
Role in Antibiotic Discovery
Serves as a model cyclic peptide for designing novel anti-TB compounds.
Provides structural templates for next-generation peptide antibiotics targeting intracellular pathogens.

Side Effects
Observed in Experimental Systems
Dose-dependent nephrotoxicity in animal models.
Ototoxicity and potential vestibular effects at high doses.
General cytotoxicity in mammalian cells observed at supra-therapeutic levels.
Potential Research Risks
Excessive or prolonged exposure may alter experimental readouts due to cellular stress.
Risk of inducing antibiotic resistance in laboratory mycobacterial strains if misused.
Requires strict biosafety level 2 (BSL-2) or 3 (BSL-3) conditions depending on bacterial strain.
Laboratory Safety Notes
Use personal protective equipment (PPE) including gloves, lab coat, and eye protection.
Avoid direct inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact.
Store lyophilized powder under desiccated, cold, and dark conditions.
Reconstitute in sterile buffers immediately before use.
Safety Recommendations
Follow institutional biosafety guidelines for pathogenic bacteria.
Dispose of contaminated materials according to hazardous waste regulations.
Maintain accurate records of usage, dosing, and experimental outcomes.
Disclaimer
Enviomycin is for research use only and is not approved for human clinical applications.
Keywords
Enviomycin, CAS 33103-22-9, Tuberactinomycin N, anti-TB antibiotic, chronic cavitary pulmonary tuberculosis, cyclic peptide antibiotic, drug-resistant TB research, bacterial ribosome inhibitor, peptide antibiotic research.Peptide China Low Price Supplier
Shipping Guarantee
We provide reliable global shipping:
Customs-cleared and tax-inclusive delivery.
Full compensation for any loss or damage during transit.
Trackable, fast, and secure international logistics.
Transaction Guarantee
We support multiple safe payment methods:
T/T bank transfer
PayPal
Cryptocurrencies (BTC, ETH, USDT, etc.)
Other methods available upon consultation
Transactions are safe, transparent, and convenient for all research-grade products.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 56 × 52 × 56 cm |
What is Enviomycin?
It is a cyclic peptide antibiotic (Tuberactinomycin N) with activity against M. tuberculosis.
What is the CAS number?
33103-22-9.
What is Enviomycin used for?
Research on chronic cavitary pulmonary tuberculosis and antibacterial drug studies.
How does Enviomycin work?
By inhibiting bacterial ribosomal protein synthesis, leading to bacterial growth arrest.
Is Enviomycin effective against resistant TB strains?
Yes, it shows activity against certain MDR-TB and XDR-TB strains.
What purity is Enviomycin supplied at?
≥95% confirmed by HPLC.
How should Enviomycin be stored?
At -20°C to -80°C, protected from light and moisture.
Does it have toxicity in research models?
Yes, potential nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity at high concentrations in animal models.
Can Enviomycin be used clinically?
No, it is strictly for research purposes only.
How is Enviomycin applied in research?
In in vitro bacterial cultures, animal TB models, pharmacokinetics, and drug resistance studies.
Is Enviomycin water-soluble?
Yes, it is soluble in water, PBS, and most standard cell culture buffers.












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.