Subtotal: $280.00
Adarulatide Tetraxetan (CAS No. 1246013-02-4) – Copper-Labeled Diagnostic Imaging Agent
Original price was: $28.00.$23.00Current price is: $23.00.
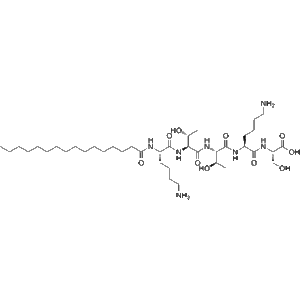
Adarulatide tetraxetan is a chelator-conjugated peptide compound used for radiolabeling and diagnostic imaging. It enables site-specific radiometal binding, particularly with copper isotopes, to visualize tumor targets in molecular imaging research.
Description
Product Description
Adarulatide tetraxetan (CAS No. 1246013-02-4), also known as Copper adarulatidum tetraxetanum, is a synthetic peptide conjugate that functions as a chelator-based diagnostic imaging agent. It incorporates the macrocyclic chelating group tetraxetan (DOTA derivative), which allows stable coordination with radiometals such as copper-64, gallium-68, or lutetium-177. This structural feature makes Adarulatide tetraxetan a highly valuable molecular imaging probe precursor.
Background and Development
Radiolabeled peptides play a critical role in modern diagnostic oncology. They combine high target selectivity (from peptide ligands) with the quantifiable imaging capabilities of radioactive isotopes. Adarulatide tetraxetan belongs to a new generation of radiopharmaceutical precursors that integrate targeting peptides with robust chelators to enable Positron Emission Tomography (PET) or Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) imaging.
The DOTA-tetraxetan moiety ensures excellent thermodynamic stability and kinetic inertness when complexed with radiometals, which minimizes transchelation in vivo and provides high-quality imaging contrast. When labeled with copper isotopes such as Cu-64, Adarulatide tetraxetan demonstrates reliable biodistribution, target retention, and renal clearance, essential properties for diagnostic accuracy and safety.
Diagnostic Applications
Adarulatide tetraxetan is primarily applied in molecular imaging for cancer diagnostics. It binds to specific receptors expressed on tumor cells, allowing real-time visualization and quantification of receptor density using PET or SPECT.
Key research applications include:
Radiometal chelation and radiolabeling studies
PET imaging of tumor-associated receptors
Biodistribution and pharmacokinetic profiling
Preclinical evaluation of novel peptide tracers
Development of theranostic agents (diagnostic + therapeutic hybrids)
Advantages of Adarulatide Tetraxetan
High Radiometal Affinity: Strong coordination with Cu, Ga, Lu, and Y isotopes.
Excellent Stability: Resistant to demetallation in physiological environments.
High Target Selectivity: Enables precise imaging of receptor-overexpressing tissues.
Versatile Platform: Can be adapted for both diagnostic and therapeutic labeling.
Biocompatible Design: Minimal toxicity and predictable metabolic clearance.
Product Specifications
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Adarulatide Tetraxetan |
| CAS Number | 1246013-02-4 |
| Synonyms | Copper adarulatidum tetraxetanum, Adarulatide DOTA conjugate |
| Chemical Class | Peptide chelator conjugate |
| Molecular Formula | C₆₅H₁₀₄N₁₈O₂₃ |
| Molecular Weight | Approx. 1500 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to off-white lyophilized powder |
| Purity | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, PBS, and DMSO |
| Storage Conditions | -20°C, desiccated, protected from light |
| Stability | Stable for 24 months under recommended storage |
| Formulation | Lyophilized peptide conjugate |
| Chelating Moiety | Tetraxetan (DOTA analogue) |
| Radiometal Compatibility | Cu-64, Ga-68, Lu-177, Y-90 |
| Applications | Molecular imaging, PET/SPECT tracer development, receptor binding assays |
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of Adarulatide tetraxetan lies in radiometal chelation and receptor-mediated targeting for imaging applications.
Chelation Chemistry
The tetraxetan (DOTA-like) macrocycle forms a highly stable coordination complex with radiometals.
This ensures that the radiometal remains tightly bound during circulation and imaging, reducing background signal.
Receptor Targeting
The peptide portion of Adarulatide specifically binds to receptors (e.g., somatostatin, integrin, or prostate-specific membrane antigen, depending on the analog).
This allows selective uptake in receptor-overexpressing tissues, enhancing imaging contrast.
Radiolabeling with Copper Isotopes
Commonly used isotopes include Cu-64 (β+ emitter) for PET imaging.
Copper-labeled Adarulatide demonstrates predictable pharmacokinetics and renal excretion.
In Vivo Imaging Pathway
After intravenous administration, the compound circulates systemically, accumulates in receptor-rich tissues, and emits gamma or positron radiation.
This radiation is detected by imaging instruments to reconstruct real-time molecular maps of receptor distribution.
Theranostic Potential
When labeled with therapeutic isotopes like Lu-177, Adarulatide tetraxetan can transition from diagnostic to therapeutic use, providing a unified “theranostic” platform.

Side Effects
As a diagnostic imaging research compound, Adarulatide tetraxetan generally exhibits minimal toxicity in experimental settings. However, potential side effects in animal or in vitro studies include:
Mild Cytotoxicity: At high concentrations in non-target tissues.
Transient Radiation Exposure: Depending on the isotope used for labeling.
Renal Accumulation: As common with peptide-based tracers, though reversible.
Immunogenic Response: Minimal, due to synthetic peptide origin and neutral charge.
Metal Complex Stability: Poor labeling procedures may lead to unbound radiometal presence.
Proper handling, labeling optimization, and biosafety protocols are essential during research use.
Disclaimer
For research use only. Not intended for human or veterinary use, diagnosis, or treatment.
Keywords
Adarulatide tetraxetan, CAS 1246013-02-4, copper adarulatide, DOTA conjugate, radiometal chelator, Cu-64 PET imaging agent, peptide-based diagnostic tracer, molecular imaging probe, radiopharmaceutical precursor, receptor-targeted imaging
Shipping Guarantee
Global delivery with full tracking and temperature protection
Secure packaging ensuring compound integrity and purity
Shipment includes product data sheet and QC documentation
Transaction Guarantee
Purity ≥98% guaranteed by analytical validation
Secure international payment methods (T/T, PayPal, cryptocurrency)
Professional technical support for radiolabeling and storage guidance
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 56 × 28 × 56 cm |
It is a chelator-conjugated peptide used as a precursor for radiometal-based diagnostic imaging.
CAS No. 1246013-02-4.
It serves as a precursor for PET or SPECT imaging agents after radiolabeling.
Cu-64, Ga-68, Lu-177, and Y-90.
No, it is for research and preclinical use only.
How does it achieve imaging selectivity?
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) or SPECT.
Yes, it dissolves readily in water, PBS, and DMSO.
At -20°C, dry, and protected from light.
High radiometal affinity, structural stability, and biocompatibility.
Chelation of radiometals with subsequent receptor-targeted imaging.
Yes, with therapeutic isotopes like Lu-177, it can serve dual diagnostic and therapeutic roles.
Minimal toxicity under standard experimental doses.
It is a DOTA (tetraxetan) peptide conjugate with defined radiometal binding sites.
Via HPLC, NMR, and radiolabeling efficiency tests.

 Argireline acetate | CAS No. 2484708-86-1
Argireline acetate | CAS No. 2484708-86-1 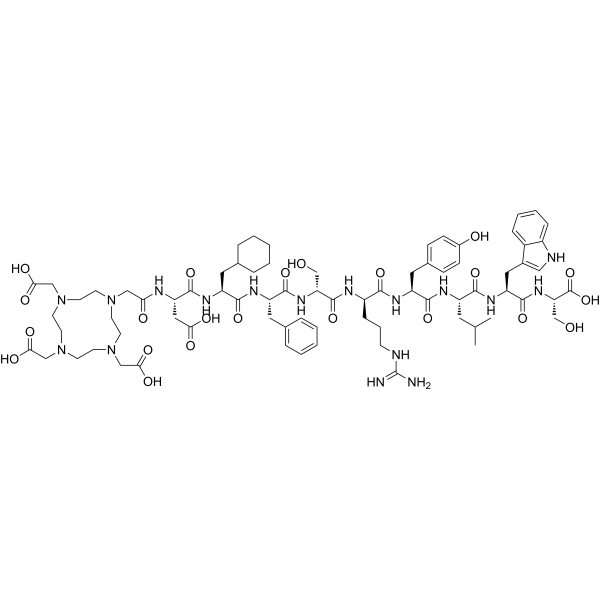








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.