No products in the cart.
Sale
SHLP-5 | CAS 1191923-95-1 | Mitochondrial-Derived Peptide for Metabolic
Original price was: $36.00.$24.00Current price is: $24.00.
SHLP-5 is a mitochondrial-derived bioactive microprotein involved in regulating mitochondrial function, oxidative stress, and cellular homeostasis. It serves as a novel peptide target in diabetes, cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and prostate cancer research.
Description
Product Description
SHLP-5 (Small Humanin-Like Peptide 5) is a mitochondrial-derived peptide (MDP) encoded by the 16S ribosomal RNA gene (MT-RNR2). As part of the expanding family of Humanin-like peptides (SHLP1–6), SHLP-5 represents one of the newly discovered signaling peptides that mediate mitochondrial-to-nuclear communication and influence cellular survival, metabolism, and oxidative balance.
This peptide is a bioactive microprotein capable of modulating key physiological functions across multiple organ systems. Through its effects on mitochondrial bioenergetics, SHLP-5 helps maintain metabolic stability, cellular viability, and systemic homeostasis.
Biological Overview
Mitochondria are not merely energy factories; they serve as signaling hubs integrating metabolic status, oxidative stress, and cell survival cues. Recent discoveries have revealed that mitochondria can encode their own regulatory peptides — the MDPs — that act both locally and systemically. Among these, SHLP-5 has shown unique properties in supporting metabolic homeostasis, neuronal survival, and cardiovascular protection.
SHLP-5 expression has been observed in energy-demanding tissues, including brain, pancreas, heart, and skeletal muscle. These expression patterns suggest its involvement in managing energy production, apoptosis resistance, and antioxidant response.
Research Applications
SHLP-5 is widely studied as a pleiotropic mitochondrial microprotein with therapeutic potential in various research domains:
Diabetes Research: Enhances insulin secretion and pancreatic β-cell function under metabolic stress.
Alzheimer’s Disease Models: Provides neuroprotection by modulating mitochondrial ROS and preventing neuronal apoptosis.
Cardiovascular Research: Supports cardiomyocyte survival and improves mitochondrial respiration during ischemic stress.
Prostate Cancer Studies: Influences cell proliferation and mitochondrial signaling pathways involved in tumor metabolism.
Structural and Functional Characteristics
Like other SHLPs, SHLP-5 is a small peptide (approximately 2–3 kDa) that exerts its biological effects through autocrine and paracrine signaling. It binds to cell-surface receptors and intracellular targets, influencing mitochondrial metabolism and gene expression.
Key biochemical features include:
Regulation of oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS).
Stimulation of ATP production and oxygen consumption rate (OCR).
Enhancement of cell survival pathways (e.g., PI3K/AKT and AMPK).
Modulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and antioxidant defenses.
Collectively, SHLP-5 acts as a metabolic modulator that links mitochondrial status to organismal health, making it a potent research molecule for understanding age-related diseases and metabolic dysfunctions.
Product Specifications
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Name | SHLP-5 |
| CAS Number | 1191923-95-1 |
| Synonyms | Small Humanin-Like Peptide 5, Mitochondrial Peptide SHLP5 |
| Chemical Class | Mitochondrial-derived peptide (MDP) |
| Source Gene | MT-RNR2 (16S rRNA gene) |
| Molecular Formula | Peptide (sequence-specific) |
| Molecular Weight | Approx. 2–3 kDa |
| Sequence | SHLP-5 |
| Appearance | White lyophilized powder |
| Purity | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Solubility | Water, PBS, DMSO |
| Storage Conditions | –20°C, desiccated and light-protected |
| Stability | Stable ≥2 years under recommended storage |
| Applications | Diabetes, Alzheimer’s, cardiovascular, prostate cancer research |
| Safety Level | For research use only |
| QC Verification | HPLC, Mass spectrometry, peptide sequencing |
Mechanism of Action
1. Mitochondrial Energy Regulation
SHLP-5 primarily acts as a metabolic enhancer, boosting mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. It increases the oxygen consumption rate (OCR) and ATP synthesis, ensuring adequate energy supply during cellular stress. This process involves upregulation of mitochondrial complex I and IV activities, essential for efficient electron transport.
2. Oxidative Stress Control
A major function of SHLP-5 is its antioxidant and cytoprotective capacity. By enhancing the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), SHLP-5 minimizes ROS accumulation. It protects mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) from oxidative damage and prevents apoptosis triggered by oxidative stress.
3. Insulin and Glucose Metabolism
In diabetic models, SHLP-5 supports insulin sensitivity and β-cell survival. It maintains intracellular calcium homeostasis and protects β-cells from ER stress, contributing to improved glucose tolerance. SHLP-5’s activity in metabolic tissues indicates its role as a mitochondrial metabolic peptide linking energy sensing and insulin regulation.
4. Neuroprotective Pathways
In neuronal systems, SHLP-5 activates anti-apoptotic pathways and promotes neuronal survival. It stabilizes mitochondrial membrane potential, reduces cytochrome c release, and prevents caspase activation. These neuroprotective mechanisms make SHLP-5 a promising target in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative research models.
5. Cardiovascular and Prostate Effects
SHLP-5 enhances cardiac mitochondrial function and reduces ischemia-induced apoptosis. It supports endothelial cell energy metabolism and nitric oxide (NO) regulation, improving vascular health. Additionally, in prostate cancer models, appears to influence cell cycle control and mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis, making it a potential research molecule in onco-metabolic pathways.
6. Mitochondrial-Nuclear Signaling
SHLP-5 acts as a retrograde signal — a messenger from mitochondria to nucleus — regulating gene expression related to metabolism, stress response, and longevity. It is believed to work in concert with other MDPs (Humanin, MOTS-c) to maintain mitochondrial quality control and cellular resilience.
Through these synergistic actions, SHLP-5 supports the mitochondrial stress adaptation system, balancing energy production, redox state, and cell viability.
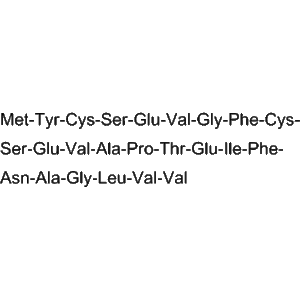
Side Effects
is used strictly for laboratory research, with no clinical data available. Nonetheless, in vitro observations suggest certain theoretical effects at supraphysiological concentrations:
Mitochondrial Hyperactivation: Excess energy production may disturb redox balance.
Altered Cell Cycle Activity: Overstimulation of survival pathways may affect proliferation in non-target cells.
Metabolic Overshoot: Excess ATP and insulin sensitivity could cause metabolic fluctuation in cell cultures.
Calcium Imbalance: High SHLP-5 levels might transiently alter intracellular Ca²⁺ dynamics.
Cytokine Modulation: Potential shifts in cellular inflammatory signaling.
Researchers should employ physiologically relevant concentrations and verify dose-dependent outcomes in vitro.
Disclaimer
For research use only. Not for human or veterinary use, diagnosis, or therapeutic purposes.
Keywords
SHLP-5, Small Humanin-Like Peptide 5, mitochondrial-derived peptide, MT-RNR2, mitochondrial bioenergetics, oxidative stress, ATP generation, neuroprotection, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, cardiovascular protection, prostate cancer research.
Shipping Guarantee
All products are delivered with full insurance against loss or damage and inclusive customs clearance.
Transaction Guarantee
We support multiple payment methods: T/T, PayPal, and cryptocurrency. Contact our sales team for secure ordering options.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 56 × 28 × 56 cm |
What is SHLP-5?
A mitochondrial-derived peptide encoded by the MT-RNR2 gene that enhances cellular metabolism and mitochondrial function.
What is the CAS number for SHLP-5?
CAS No. 1191923-95-1.
What is the main research focus of SHLP-5?
Diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, cardiovascular protection, and prostate cancer.
How does SHLP-5 protect neurons?
It maintains mitochondrial potential, suppresses ROS generation, and prevents apoptosis.
Is SHLP-5 involved in glucose metabolism?
Yes, it improves insulin sensitivity and supports β-cell viability.
What is the molecular origin of SHLP-5?
It is encoded by the mitochondrial 16S rRNA gene (MT-RNR2).
Does SHLP-5 have cardioprotective effects?
Yes, it enhances mitochondrial function and protects cardiac cells during stress.
What solvents are suitable for SHLP-5?
Water, PBS, and DMSO are recommended.
What storage conditions are optimal?
Store at –20°C in a dry, dark environment.
Is SHLP-5 safe for human use?
No, it is intended for laboratory research only.
Does SHLP-5 interact with other mitochondrial peptides?
It can act synergistically with other MDPs like Humanin or MOTS-c in metabolic signaling research.
Can SHLP-5 influence aging pathways?
Yes, it may modulate mitochondrial-nuclear communication linked to cellular longevity.

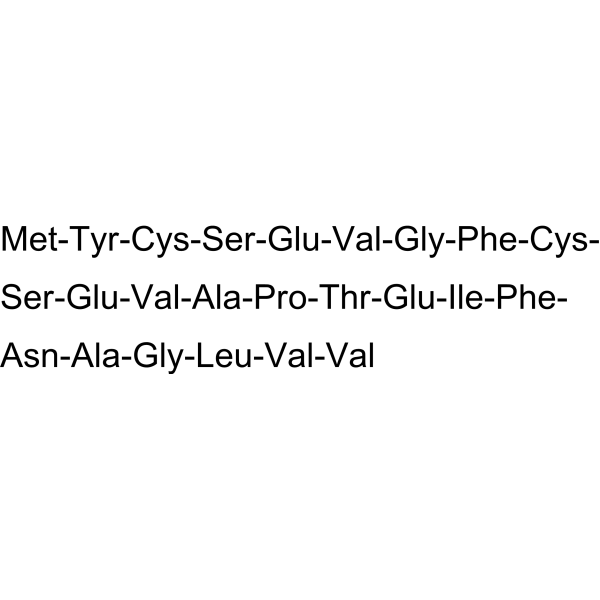












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.