No products in the cart.
Sale
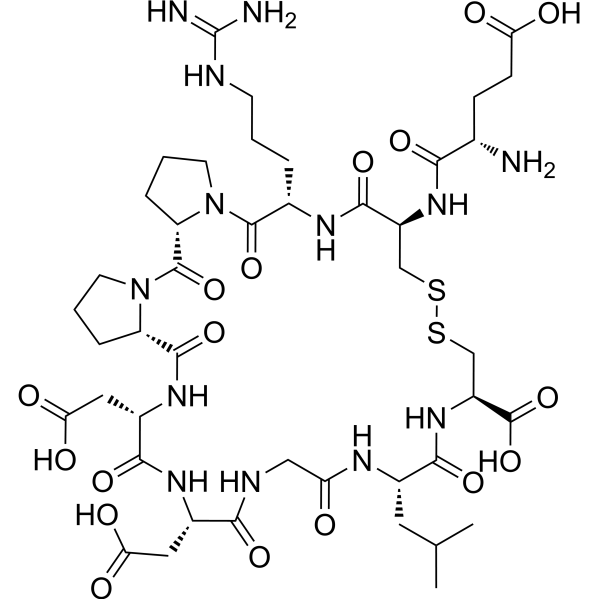
C-VGB3 | VEGFR2 Antagonist for Angiogenesis and Cancer
Original price was: $38.00.$23.00Current price is: $23.00.
C-VGB3 is a potent and selective vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) antagonist. By disrupting VEGFR2 signaling, it inhibits angiogenesis and induces apoptosis in tumor and endothelial cells. C-VGB3 is valuable for studying cancer biology, angiogenesis, and targeted therapy development.
Description
Product Description
C-VGB3 is a small-molecule antagonist of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2), one of the central receptors responsible for angiogenesis and vascular permeability in tumor development. VEGFR2, also known as KDR/Flk-1, is a receptor tyrosine kinase expressed primarily in endothelial cells and various types of cancer cells. Aberrant VEGFR2 activation is strongly associated with tumor vascularization, growth, and metastasis.
C-VGB3 binds to the extracellular domain of VEGFR2, competitively inhibiting the VEGF-A ligand from activating the receptor. This blockade prevents VEGFR2 dimerization and phosphorylation, leading to suppression of downstream pro-survival and pro-proliferation signaling pathways such as PI3K/AKT/mTOR and PLCγ/ERK1/2.
Through its inhibition of VEGFR2-mediated signaling, C-VGB3 induces apoptosis via both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. The intrinsic (mitochondrial) pathway involves activation of pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins, cytochrome c release, and caspase cascade activation, while the extrinsic (death receptor-mediated) pathway involves Fas/FasL and TNF receptor signaling. Together, these mechanisms lead to selective death of endothelial and tumor cells, impairing tumor vascularization and reducing tumor burden.
C-VGB3 has shown promise in preclinical models of angiogenesis-related cancers, including breast cancer, melanoma, and glioma. It inhibits capillary-like tube formation in vitro, reduces tumor microvessel density in vivo, and enhances the efficacy of other anticancer agents such as chemotherapeutics and kinase inhibitors.
Furthermore, C-VGB3 offers researchers a valuable tool for dissecting VEGFR2-dependent signaling events and their contributions to cancer progression, drug resistance, and metastasis. Its dual effects—angiogenesis inhibition and direct tumor cytotoxicity—make it a unique and versatile compound for oncology research.
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | C-VGB3 |
| Synonyms | VEGFR2 Antagonist C-VGB3 |
| CAS Number | — |
| Molecular Target | VEGFR2 (KDR/Flk-1) |
| Mechanism of Action | Selective VEGFR2 inhibition via ligand-receptor blockade |
| Pathways Affected | PI3K/AKT/mTOR, PLCγ/ERK1/2 |
| Biological Effects | Inhibits angiogenesis, induces apoptosis, suppresses tumor growth |
| Applications | Cancer research, angiogenesis, tumor microenvironment studies |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder |
| Purity | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, ethanol |
| Storage Conditions | -20°C, desiccated, protected from light |
| Stability | Stable for at least 2 years under recommended storage conditions |
| QC Tests | HPLC, NMR, Mass spectrometry |
Mechanism of Action
C-VGB3 functions primarily as a VEGFR2 antagonist. It exerts its biological effects through several interconnected mechanisms:
Direct VEGFR2 Blockade
C-VGB3 binds to the extracellular domain of VEGFR2, preventing the natural ligand VEGF-A from interacting with the receptor. This direct antagonism inhibits receptor dimerization and phosphorylation, effectively halting the VEGFR2-driven angiogenic signaling cascade.Inhibition of Downstream Signaling
PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway: Normally activated by VEGFR2 to promote endothelial cell survival and growth. C-VGB3 disrupts this pathway, leading to decreased phosphorylation of AKT and mTOR, resulting in growth arrest and increased apoptotic sensitivity.
PLCγ/ERK1/2 Pathway: VEGFR2-mediated activation of ERK1/2 drives proliferation and migration. C-VGB3 suppresses ERK phosphorylation, impairing these processes and preventing endothelial tube formation.
Apoptosis Induction
C-VGB3 triggers apoptosis in endothelial and cancer cells via both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways.Intrinsic Pathway: Mitochondrial membrane depolarization, cytochrome c release, and activation of caspase-9 and -3.
Extrinsic Pathway: Engagement of death receptors such as Fas and TNFR1, leading to caspase-8 activation.
This dual activation enhances the apoptotic response, even in cells resistant to single-pathway activation.
Anti-Angiogenic Effect
By blocking VEGFR2 signaling, C-VGB3 disrupts the formation of new blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to tumors. This “anti-vascular” mechanism leads to tumor starvation, growth inhibition, and reduced metastatic potential.Impact on Tumor Microenvironment
C-VGB3 reduces vascular permeability and inflammatory infiltration, altering the tumor microenvironment toward a less favorable state for tumor survival and metastasis.
Overall, the compound serves as a precise research probe for understanding VEGFR2’s multifaceted role in tumor angiogenesis, endothelial biology, and apoptotic signaling.
Side Effects
As a research compound, C-VGB3 is not approved for clinical or therapeutic use. However, preclinical studies and mechanistic analyses indicate possible experimental side effects that should be noted:
Vascular Effects: Potential to cause endothelial dysfunction and increased vascular permeability in non-target tissues.
Cytotoxicity: May induce apoptosis in normal endothelial cells during in vitro experiments.
Metabolic Disturbances: Inhibition of VEGFR2 may indirectly alter glucose metabolism or oxygen utilization in certain cell types.
Inflammatory Response: VEGFR2 blockade may transiently upregulate inflammatory cytokines in culture systems.
Mitochondrial Stress: Sustained apoptosis induction may lead to mitochondrial ROS accumulation in sensitive cell lines.
Safety Note:
All handling should be done under appropriate laboratory safety conditions (e.g., BSL-2). Use gloves, eye protection, and avoid aerosol formation.
Disclaimer
For research use only. Not intended for human or veterinary use, diagnosis, or treatment. The product should be handled by trained professionals in accordance with institutional biosafety guidelines.
Keywords
C-VGB3, VEGFR2 antagonist, anti-angiogenesis research, VEGFR2 inhibitor, apoptosis inducer, PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibition, PLCγ/ERK1/2 blockade, tumor microenvironment, breast cancer research, vascular biology.GMP manufacturers wholesale
Shipping Guarantee
All products are shipped with tax-inclusive customs clearance and full damage/loss insurance.
Transaction Guarantee
We accept T/T, PayPal, cryptocurrency, and other secure payment options. Contact our support team for more details.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.9 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 82 × 53 × 82 cm |
2 reviews for C-VGB3 | VEGFR2 Antagonist for Angiogenesis and Cancer
What is C-VGB3?
C-VGB3 is a selective VEGFR2 antagonist used in angiogenesis and cancer research.
What does VEGFR2 do?
VEGFR2 regulates angiogenesis and endothelial cell survival through PI3K/AKT and ERK signaling.
How does C-VGB3 work?
It binds to VEGFR2’s extracellular domain, blocking ligand interaction and preventing receptor activation.
What are the research applications of C-VGB3?
Studies of tumor angiogenesis, apoptosis mechanisms, and VEGFR2 signaling.
Can C-VGB3 be used in vivo?
It has shown efficacy in preclinical tumor xenograft models but is not approved for clinical use.
What pathways does it affect?
PI3K/AKT/mTOR and PLCγ/ERK1/2 signaling pathways.
Does C-VGB3 induce apoptosis?
Yes, it triggers both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways.
What types of cancers can it be used to study?
Especially useful for angiogenesis-related cancers such as breast, lung, and glioma models.
What precautions should be taken when handling?
Handle with PPE under BSL-2 conditions; avoid inhalation or direct contact.
How should it be stored?
Store at -20°C, in a dry, light-protected environment.













klmueth –
Product quality matches the specifications provided.
Rohnes –
it is an excellent trading platform