No products in the cart.
Sale
Antiflammin-1 | CAS 118850-71-8 | Anti-inflammatory and Antifibrotic Peptide
Original price was: $16.00.$13.00Current price is: $13.00.
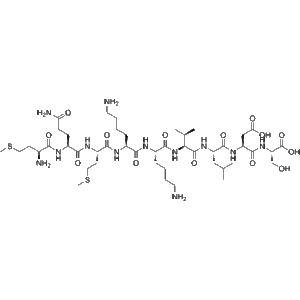
Antiflammin-1 is a small bioactive peptide (sequence: MQMKKVLDS) derived from uteroglobin, showing strong anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects. It has been widely used in studies on lung injury, pulmonary fibrosis, and tissue inflammation mechanisms.
Description
Product Description
Antiflammin-1 (CAS 118850-71-8) is a synthetic nonapeptide derived from the N-terminal region of uteroglobin, a multifunctional anti-inflammatory protein expressed in respiratory and reproductive tissues. This short peptide retains the biological activity of uteroglobin, particularly its ability to suppress inflammation and fibrosis in various experimental models.
Biological Background
Uteroglobin, also known as Clara cell secretory protein (CCSP), plays a central role in regulating pulmonary and immune homeostasis. Antiflammin-1 mimics its anti-inflammatory domain and acts as a modulator of cytokine activity, fibroblast proliferation, and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling.
Mechanistic Insights
Antiflammin-1 has been shown to significantly attenuate inflammatory responses and tissue fibrosis in models of bleomycin-induced pulmonary injury. Its mechanism involves inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression, suppression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and downregulation of TGF-β1/Smad signaling, a key pathway in fibrosis development.
It also acts on glucocorticoid-independent anti-inflammatory pathways, positioning it as an attractive peptide candidate for developing new anti-inflammatory therapeutics with fewer steroid-like side effects.
Key Research Applications
Pulmonary Fibrosis Studies: Mitigates fibrosis and inflammation in bleomycin-challenged lung models.
Anti-inflammatory Research: Reduces cytokine release and leukocyte infiltration in inflamed tissues.
Wound Healing: Modulates fibroblast activity and collagen synthesis.
Molecular Mechanism Studies: Serves as a model for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory peptide research.
In summary, Antiflammin-1 offers a compact and efficient molecular scaffold for the study of anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic, and tissue-protective mechanisms.
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Antiflammin-1 |
| Synonyms | AF-1; MQMKKVLDS; Uteroglobin-derived anti-inflammatory peptide |
| CAS Number | 118850-71-8 |
| Molecular Formula | C₄₄H₈₅N₁₅O₁₁ |
| Molecular Weight | 960.2 g/mol |
| Sequence | MQMKKVLDS |
| Origin | Synthetic peptide derived from uteroglobin |
| Appearance | White to off-white lyophilized powder |
| Purity | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, PBS, or DMSO |
| Storage Conditions | -20°C, desiccated, avoid repeated freeze–thaw cycles |
| Stability | Stable for ≥24 months under recommended conditions |
| Biological Activity | Anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic activity in vitro and in vivo |
| Applications | Lung injury, pulmonary fibrosis, and inflammation research |
| Quality Control Tests | HPLC, Mass Spectrometry, Amino Acid Analysis |
Mechanism of Action
Antiflammin-1 exerts its anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects through multifaceted signaling modulation at both the molecular and cellular levels.
1. Cytokine Suppression
Antiflammin-1 inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, in macrophages and epithelial cells. This reduces inflammatory cell infiltration and tissue damage in pulmonary and other inflammatory models.
2. COX-2 and NF-κB Inhibition
By blocking COX-2 expression and NF-κB activation, Antiflammin-1 decreases the synthesis of prostaglandins and inflammatory mediators. This pathway is central to its glucocorticoid-independent anti-inflammatory mechanism.
3. TGF-β1/Smad Signaling Blockade
Antiflammin-1 inhibits TGF-β1-induced Smad2/3 phosphorylation, preventing myofibroblast differentiation and ECM accumulation. This is particularly crucial in its antifibrotic action during lung injury or chronic inflammation.
4. Cellular and Tissue Protection
The peptide protects epithelial integrity, prevents apoptosis in alveolar cells, and reduces oxidative stress markers in inflamed tissues.
5. Downstream Pathways
Decreased Collagen Deposition: Inhibits fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis.
Reduced Oxidative Stress: Limits ROS generation and lipid peroxidation.
Enhanced Resolution Phase: Promotes macrophage polarization toward the M2 anti-inflammatory phenotype.
Together, these mechanisms make Antiflammin-1 a versatile peptide model for exploring anti-inflammatory pathways beyond corticosteroid therapy.
Side Effects
As a research compound, Antiflammin-1 is generally well-tolerated in experimental systems. However, researchers should consider the following:
Low Cytotoxicity: Exhibits minimal cytotoxic effects in vitro at experimental concentrations.
Peptide Degradation: Rapid enzymatic degradation in serum; formulation optimization is advised.
Immune Reactivity: May trigger mild immune responses in certain animal models.
No Known Systemic Toxicity: No organ-level toxicity reported in preclinical research models.
All handling should follow standard laboratory safety procedures for peptide-based reagents.
Disclaimer
For research use only. Not intended for diagnostic, therapeutic, or clinical applications. Handle using appropriate protective equipment and store under recommended laboratory conditions.
Keywords
Antiflammin-1, AF-1 peptide, uteroglobin derivative, anti-inflammatory peptide, antifibrotic peptide, pulmonary fibrosis research, bleomycin-induced lung injury, cytokine suppression, COX-2 inhibitor, TGF-β1 pathway inhibitor, inflammation model peptide.
Shipping Guarantee
All shipments are fully temperature-controlled and insured against damage or loss.
Transaction Guarantee
We ensure secure global transactions and provide documentation for smooth customs clearance.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 56 × 26 × 56 cm |
2 reviews for Antiflammin-1 | CAS 118850-71-8 | Anti-inflammatory and Antifibrotic Peptide
What is Antiflammin-1?
A nonapeptide derived from uteroglobin with anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic properties.
What is its CAS number?
CAS No. 118850-71-8.
How does it work?
It inhibits COX-2, TNF-α, and TGF-β1 pathways, reducing inflammation and fibrosis.
Which diseases can it be studied in?
Pulmonary fibrosis, lung injury, chronic inflammation, and tissue fibrosis.
Is Antiflammin-1 a natural or synthetic peptide?
It is a synthetic peptide derived from a natural uteroglobin sequence.
What is its amino acid sequence?
MQMKKVLDS.
What purity is provided?
≥98% by HPLC.
What solvents can it dissolve in?
Soluble in water, PBS, and DMSO.
How should it be stored?
At -20°C, protected from moisture and light.
Is it suitable for in vivo research?
Yes, it has been studied in animal models of lung injury and fibrosis.













simonrusic –
The supplier demonstrated strong coordination during the ordering process. Product consistency and packaging quality were both acceptable.
Anna –
I received a nice box. I think it is not a product, but a gife.