No products in the cart.
Sale
LVGRQLEEFL (mouse) | CAS 608513-82-2 | ApoJ-Derived Peptide
Original price was: $43.00.$36.00Current price is: $36.00.
LVGRQLEEFL (mouse) (CAS 608513-82-2) corresponds to amino acids 113–122 of apolipoprotein J (apoJ), also known as clusterin. This G* peptide exhibits anti-inflammatory and anti-atherogenic functions by modulating lipid transport, oxidative stress, and immune responses. It is a structural component of HM-10/10, an apoJ mimetic peptide that forms a chimeric high-density lipoprotein (HDL) with potent cytoprotective and anti-oxidative effects, particularly beneficial for retinal and vascular research.
Description
Contents
hide
Product Description
LVGRQLEEFL (mouse) (CAS 608513-82-2) is a synthetic peptide fragment derived from amino acids 113–122 of apolipoprotein J (apoJ), also known as clusterin. ApoJ is a multifunctional glycoprotein involved in lipid transport, complement regulation, apoptosis modulation, and cellular stress response. Within apoJ, the LVGRQLEEFL sequence represents a highly conserved motif responsible for several of its anti-inflammatory and anti-atherogenic effects.
Origin and Structural Context
The LVGRQLEEFL sequence is positioned within the α-helical domain of apoJ that mediates interactions with lipid surfaces and other apolipoproteins. In the mouse apoJ structure, this peptide corresponds to residues 113 through 122, forming part of a lipid-binding amphipathic helix. This region is essential for the formation of HDL-like particles, lipid solubilization, and cell membrane stabilization.
The sequence LVGRQLEEFL has been isolated, synthesized, and studied as a functional peptide, often referred to as the G* peptide. It exhibits properties reminiscent of native apoJ, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-atherogenic actions.
Biological and Functional Role
ApoJ (clusterin) is an apolipoprotein expressed in nearly all tissues and body fluids. It plays a crucial protective role in lipoprotein metabolism, inflammation control, and tissue injury responses. The G* peptide (LVGRQLEEFL) recapitulates several of these beneficial properties by mimicking apoJ’s amphipathic helix, which interacts with lipid membranes and scavenges oxidized molecules.
Functional Highlights:
Anti-inflammatory activity: Suppresses macrophage activation and cytokine release.
Anti-atherogenic activity: Reduces lipid accumulation and oxidative stress in vascular walls.
Cytoprotective effect: Prevents oxidant-induced apoptosis in endothelial and retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells.
Lipid modulation: Enhances HDL-like particle formation and cholesterol efflux capacity.
These effects make LVGRQLEEFL a versatile research peptide in the study of atherosclerosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress-related diseases.
Integration into HM-10/10 Peptide
LVGRQLEEFL can be incorporated into HM-10/10, a synthetic chimeric HDL mimetic peptide designed to emulate both apoA-I and apoJ functions. HM-10/10 contains domains from apoA-I (responsible for cholesterol efflux and lipid binding) and apoJ (providing anti-inflammatory and antioxidative protection).
This hybrid structure enhances lipid binding, antioxidant capacity, and protective effects against oxidative damage in vascular and retinal tissues. HM-10/10 has demonstrated efficacy in preventing:
Retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cell death
Photoreceptor degeneration
Endothelial injury
Inflammatory cytokine accumulation
The apoJ-derived LVGRQLEEFL domain plays a critical role in the anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective profile of HM-10/10, making it a valuable tool for mechanistic and therapeutic studies.
Research Relevance in Atherosclerosis
In cardiovascular research, LVGRQLEEFL (mouse) is used to explore HDL functionality, lipid oxidation, and macrophage-mediated inflammation. ApoJ and its mimetic peptides are known to stabilize lipid rafts and prevent oxidation of low-density lipoproteins (LDL), a key step in atherogenesis.
Studies indicate that apoJ-derived peptides reduce the expression of adhesion molecules (e.g., VCAM-1, ICAM-1) and inhibit foam cell formation in vascular endothelium. LVGRQLEEFL contributes to these effects by modulating NF-κB signaling, leading to reduced vascular inflammation and improved endothelial health.
Role in Retinal and Neuroprotective Research
LVGRQLEEFL’s incorporation into HM-10/10 confers neuroprotective effects, particularly against oxidative stress in retinal cells. Oxidative stress is a major contributor to retinal degenerative diseases such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD). HM-10/10 peptides containing the LVGRQLEEFL motif protect RPE and photoreceptors by:
Neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS)
Reducing lipid peroxidation
Preserving mitochondrial integrity
Inhibiting apoptotic pathways
These effects establish LVGRQLEEFL as a key sequence for developing apoJ-derived therapeutic mimetics targeting retinal degeneration and vascular oxidative injury.
Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms
LVGRQLEEFL reduces the release of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 from activated macrophages and microglia. It interferes with TLR and NF-κB signaling, suppressing inflammatory cascades while enhancing cell survival pathways such as PI3K/Akt and Nrf2. This dual regulation of oxidative and inflammatory stress makes it a promising peptide for investigating chronic inflammatory pathologies.
Experimental Evidence
Experimental data suggest that G* peptide analogs such as LVGRQLEEFL:
Decrease oxidized lipid accumulation in aortic tissues.
Improve HDL functionality in murine atherosclerosis models.
Protect retinal cells from H₂O₂-induced apoptosis.
Restore mitochondrial function under oxidative stress.
These findings underscore the translational potential of LVGRQLEEFL-based peptides for metabolic, vascular, and ocular research.
Product Specifications
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | LVGRQLEEFL (mouse) |
| CAS Number | 608513-82-2 |
| Synonyms | G* peptide; [113–122] apoJ peptide; Clusterin fragment |
| Origin | Mouse (Mus musculus) |
| Source | Derived from apolipoprotein J sequence |
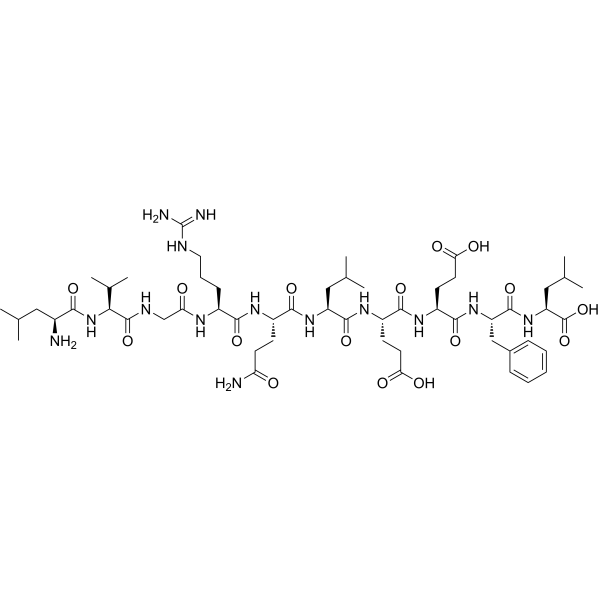
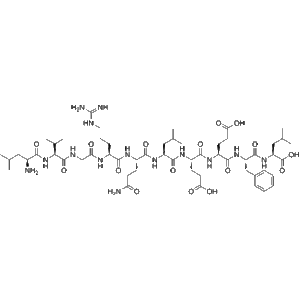
| Sequence | LVGRQLEEFL |
| Length | 10 amino acids |
| Purity | ≥ 99% (HPLC) |
| Molecular Formula | C₅₂H₈₇N₁₅O₁₅ |
| Molecular Weight | ~1140.3 Da |
| Appearance | White lyophilized powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, PBS, or DMSO |
| Storage Conditions | -20°C (desiccated, protect from light) |
| Stability | Stable for ≥24 months under recommended storage |
| Applications | Anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative, HDL mimetic research |
Synonyms
G* peptide
ApoJ fragment (113–122)
Clusterin-derived peptide
HM-10/10 component
Apolipoprotein J mimetic sequence
Mechanism of Action
LVGRQLEEFL (mouse) acts as a bioactive mimetic fragment of apolipoprotein J (apoJ). Its amphipathic α-helical structure enables it to interact with lipid bilayers and apolipoprotein complexes, replicating apoJ’s lipid transport and anti-inflammatory functions.
Lipid Interaction and HDL Formation
The peptide’s hydrophobic and hydrophilic residues allow integration into phospholipid monolayers, promoting HDL-like nanoparticle assembly. This structural mimicry improves cholesterol efflux and enhances reverse cholesterol transport.Antioxidant Protection
LVGRQLEEFL neutralizes reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibits lipid peroxidation. By scavenging oxidized phospholipids, it prevents the formation of oxidized LDL (oxLDL), a central mediator of atherosclerosis.Inflammation Suppression
The peptide inhibits activation of NF-κB and MAPK pathways, reducing expression of inflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules. It interferes with macrophage activation and vascular endothelial inflammation, mitigating plaque development.Cytoprotection in Retinal Cells
In RPE and photoreceptor cells, LVGRQLEEFL-containing mimetics like HM-10/10 protect against oxidative apoptosis by stabilizing mitochondrial membranes and upregulating antioxidant enzymes (SOD2, HO-1, catalase).Vascular Health and Atheroprotection
LVGRQLEEFL enhances endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activity, improving vascular relaxation and endothelial barrier integrity. This contributes to anti-atherogenic and anti-inflammatory vascular profiles.
Side Effects / Safety Notes
is for research use only and not approved for clinical applications. It has low cytotoxicity in in vitro studies and is considered biologically safe when handled under standard laboratory conditions.
Avoid direct skin or eye contact, inhalation, or ingestion. Use gloves and protective eyewear. Dispose of peptide solutions according to institutional biosafety regulations.
Disclaimer
All information provided about LVGRQLEEFL (mouse) is for scientific research and educational purposes only. The product is not intended for human or veterinary use. It must not be administered to animals or humans. End users are responsible for ensuring proper handling and compliance with biosafety protocols.
Keywords
LVGRQLEEFL peptide, apoJ fragment, clusterin-derived peptide, G* peptide, HM-10/10 peptide, HDL mimetic, anti-inflammatory peptide, anti-atherogenic peptide, oxidative stress modulator, retinal protection peptide, apolipoprotein J mimetic, lipid metabolism regulator, vascular research peptide
Shipping Guarantee
All products are shipped under cold-chain conditions to preserve purity and activity. Each vial is sealed, desiccated, and accompanied by a Certificate of Analysis (COA) confirming identity, purity, and stability.
Transaction Guarantee
Transactions are secured through encrypted payment processing. Products are covered by a 100% delivery guarantee — replacement or refund is provided if damage or quality deviation is confirmed upon receipt.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 56 × 28 × 56 cm |
What is LVGRQLEEFL (mouse)?
A peptide corresponding to amino acids 113–122 of apolipoprotein J (apoJ), known for its anti-inflammatory and anti-atherogenic properties.
What is its biological function?
It modulates lipid transport, inhibits inflammation, and protects cells from oxidative injury.
Can LVGRQLEEFL be used therapeutically?
No, it is for laboratory research only.
How is it related to HM-10/10?
LVGRQLEEFL forms part of HM-10/10, a chimeric HDL mimetic peptide with both apoA-I and apoJ domains.
What diseases is it studied in?
Atherosclerosis, retinal degeneration, oxidative stress disorders, and vascular inflammation.
Is LVGRQLEEFL toxic?
It exhibits minimal cytotoxicity in research concentrations and is safe under standard lab conditions.
How should it be stored?
Store at -20°C, in a tightly sealed, desiccated vial, protected from light.
Can it form HDL-like particles?
Yes, its amphipathic helix enables lipid binding and HDL nanoparticle formation.
What purity level is provided?
≥99% by HPLC, with full analytical certification.
Does it affect macrophage activation?
Yes, it suppresses pro-inflammatory macrophage signaling and reduces cytokine output.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.