No products in the cart.
Sale
Thymocartin | CAS 85466-18-8 | Thymopoietin Fragment for Immune Function Research | low price wholesale
Original price was: $32.00.$19.00Current price is: $19.00.
Thymocartin (CAS 85466-18-8) is a synthetic thymopoietin II (32–35) fragment peptide that promotes T-cell differentiation and supports immunomodulatory research in cellular and molecular immunology.
Description
Product Description
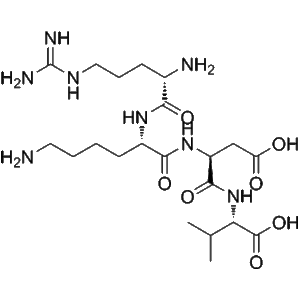
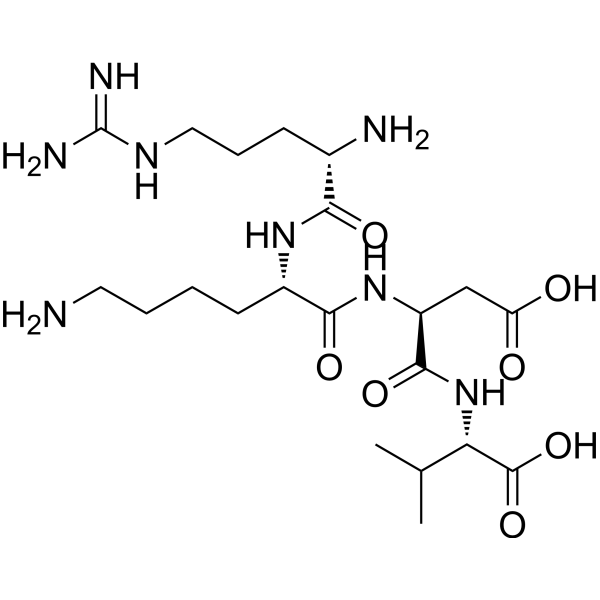
Thymocartin, also known as Thymopoietin II (32–35), is a synthetic tetrapeptide fragment derived from the larger thymopoietin molecule, a thymic hormone essential for T-cell differentiation and maturation. This biologically active peptide represents the minimal sequence necessary to reproduce the immunoregulatory functions of thymopoietin, making it a valuable research tool for studying thymic peptide signaling, T-lymphocyte activation, and immune system modulation.
As a short-chain peptide, Thymocartin plays an integral role in mimicking thymopoietin’s activity on lymphoid precursor cells. Its structure enables it to bind specific thymic peptide receptors on T-cells, triggering intracellular cascades that modulate immune responsiveness. In immunological studies, Thymocartin has been shown to restore or enhance the activity of immunocompromised cells, making it particularly useful in models of immunodeficiency and immune reconstitution.
Research involving Thymocartin spans multiple immunological domains — from fundamental studies on thymus-derived peptides to applied investigations in immune regeneration. Because it represents a specific and biologically conserved fragment, Thymocartin’s actions are highly selective, reducing off-target effects and simplifying interpretation of results in cell-based assays.
Thymocartin’s structure, composed of four amino acid residues corresponding to positions 32–35 of thymopoietin II, exhibits stability under standard laboratory conditions. The peptide retains its biological activity when stored appropriately at low temperatures, making it suitable for both in vitro and ex vivo applications.
Role in Thymic Function
In thymic physiology, thymopoietin and its derived peptides govern the differentiation of immature thymocytes into functional T-cells, a process critical for adaptive immunity. Thymocartin reproduces this action at a molecular level, promoting T-cell receptor expression and enhancing the signaling necessary for immune competence. Its application in cellular assays provides a mechanistic window into the molecular triggers of thymic peptide-mediated immunity.
Applications in Immunodeficiency Research
Thymocartin is widely used in immunodeficiency-related studies, where it serves as a prototype compound for examining how thymic peptides can restore impaired immune function. Experimental models using Thymocartin demonstrate increased T-cell output, elevated lymphocyte proliferation rates, and improved cytokine secretion profiles. These outcomes make it a cornerstone reagent for exploring immune system recovery after suppression or depletion.
Relevance in Cytokine Modulation Studies
In addition to its effects on T-cell maturation, Thymocartin influences cytokine balance, particularly interleukin-2 (IL-2) and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), which are critical mediators of cell-mediated immunity. Through these pathways, Thymocartin helps researchers understand how thymic peptides regulate communication between immune cells and maintain immune homeostasis.
Stability and Handling
Thymocartin exhibits high chemical stability and predictable degradation kinetics under controlled conditions. It can be dissolved in sterile aqueous buffers or dilute acids and is compatible with a variety of cell culture systems. Standard peptide handling practices, including the use of low-protein binding vials and cold-chain preservation, are recommended to maintain activity.
From an experimental perspective, Thymocartin provides a reproducible and well-characterized model for understanding thymic peptide biology. Because of its short chain length and defined sequence, it is easily synthesized and purified to ≥99% purity, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency for quantitative immunological experiments.

Product Specifications
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Thymocartin |
| CAS Number | 85466-18-8 |
| Synonyms | Thymopoietin II (32–35), Thymic peptide fragment |
| Molecular Formula | C₁₈H₂₉N₅O₇ |
| Molecular Weight | 443.45 g/mol |
| Purity | ≥99% |
| Appearance | White to off-white lyophilized powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, DMSO, or mild acidic buffer |
| Storage Conditions | -20°C, desiccated, protected from light |
| Applications | Immune modulation research, T-cell differentiation assays, immunodeficiency modeling, thymic peptide signaling studies |
Mechanism of Action
Thymocartin exerts its biological effects by mimicking the natural activity of thymopoietin, a thymic hormone responsible for the development and regulation of T-lymphocytes. Thymopoietin interacts with thymic epithelial and lymphoid cells to promote the differentiation of immature thymocytes into mature, functional T-cells capable of antigen recognition and immune response coordination.
The minimal active domain of thymopoietin resides within the amino acid sequence 32–35, represented by Thymocartin. This short peptide retains the capacity to engage thymic peptide receptors, initiating a cascade of intracellular signaling events that drive T-cell maturation. Upon receptor binding, Thymocartin activates protein kinase C (PKC)-dependent pathways and enhances transcriptional activity associated with T-cell receptor gene expression.
T-Cell Activation and Differentiation
Thymocartin’s action is particularly evident in early thymocyte cultures, where it accelerates the transition from double-negative (CD4⁻CD8⁻) to double-positive (CD4⁺CD8⁺) phenotypes, a hallmark of functional maturation. This process is mediated through calcium-dependent signaling and subsequent transcriptional activation of IL-2 and other cytokine genes.
Immune Modulation via Cytokine Regulation
Thymocartin’s ability to influence cytokine production allows it to modulate the balance between helper and suppressor T-cell subsets. By increasing IL-2 and IFN-γ synthesis while stabilizing IL-10 levels, the peptide fosters a balanced immune response that is neither hyperactive nor suppressed.
Molecular Interaction with Receptors
Studies indicate that Thymocartin binds to membrane-associated thymic peptide receptors, inducing conformational changes that initiate secondary messenger cascades. These cascades promote gene expression related to T-cell survival, cytoskeletal reorganization, and immune synapse formation.
Cross-Talk with Hormonal and Neuroimmune Axes
Interestingly, thymic peptides such as Thymocartin also interact with the neuroendocrine system, reflecting the thymus’s role as both an immune and endocrine organ. Thymocartin’s structural similarity to endogenous thymopoietin fragments enables it to engage cholinergic receptors, thereby linking immune signaling to neuropeptide pathways — a key focus in modern neuroimmunology.
Through these interconnected mechanisms, Thymocartin provides researchers with a molecular handle to dissect thymus-driven immune maturation and regulatory feedback within the immune network. Its short sequence, stability, and reproducibility make it an ideal experimental tool for mapping peptide-based signaling in immunological systems.
Side Effects
When used under standard research conditions, Thymocartin exhibits minimal cytotoxicity and high selectivity for immune cell targets. Nevertheless, excessive concentrations or prolonged exposure may result in overstimulation of T-cell populations, leading to altered cytokine expression profiles or potential apoptosis in sensitive cell subsets.
In in vitro settings, transient increases in IL-2 and IFN-γ levels have been observed, reflecting heightened immune activation. Researchers should monitor these responses to ensure experimental consistency.
As with other bioactive peptides, potential degradation or oxidation during handling can modify activity; therefore, peptides should be prepared fresh or stored under inert gas to maintain stability.
No data suggest any direct genotoxic or mutagenic effects under laboratory conditions. Thymocartin remains safe for standard immunological research applications when handled following biosafety and peptide-handling guidelines.
Keywords
Thymocartin, Thymopoietin II (32–35), Thymic peptide fragment, immune modulation peptide, T-cell differentiation, thymic hormone analog, immunodeficiency research, cytokine regulation, adaptive immunity, immunological signaling
Shipping Guarantee
All shipments are handled using validated cold-chain logistics to preserve peptide integrity. Each package is sealed in moisture-proof containers with secondary protective wrapping and continuous temperature monitoring. Products are shipped via express international couriers with full tracking and insurance coverage.
Trade Assurance
We ensure product authenticity, verified ≥99% purity, and compliance with analytical standards (HPLC, MS, and NMR). Each batch is supplied with a Certificate of Analysis (CoA). Our trade assurance policy guarantees replacement or refund for any deviation from listed specifications.
Payment Support
We provide flexible and secure global payment options to support international research transactions. Accepted payment methods include PayPal, major credit cards (Visa, MasterCard, American Express), telegraphic transfer (T/T), and cryptocurrencies (USDT, Bitcoin, Ethereum). All transactions are protected by industry-standard encryption and verified payment gateways to ensure confidentiality and fund security.
Disclaimer
All products listed are intended for laboratory research use only and not for human or veterinary use. They are not drugs, medical devices, or diagnostics and should not be administered to humans or animals. Researchers must handle all materials in accordance with institutional biosafety and chemical safety guidelines. The information provided is for scientific reference only and does not imply therapeutic efficacy, safety, or regulatory approval.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.9 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 86 × 59 × 86 cm |
What is Thymocartin?
Thymocartin is a synthetic peptide fragment of thymopoietin II (32–35) that supports T-cell differentiation and immune modulation research.
What is the CAS number of Thymocartin?
The CAS number is 85466-18-8.
What is the purity of Thymocartin?
Purity is guaranteed to be ≥99%.
What are the main research applications of Thymocartin?
Studies on immune modulation, T-cell development, cytokine signaling, and immunodeficiency modeling.
Is Thymocartin soluble in water?
Yes, it is soluble in water and DMSO.
What are the synonyms of Thymocartin?
Thymopoietin II (32–35) and Thymic peptide fragment.
Does Thymocartin influence cytokine production?
Yes, it modulates IL-2 and IFN-γ levels, affecting immune balance.
Can Thymocartin be used for in vivo studies?
It is designed for in vitro and ex vivo research use only.
How should Thymocartin be stored?
Store at -20°C, protected from light and moisture.
Is Thymocartin intended for human use?
No, it is strictly for laboratory research use only.
















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.