No products in the cart.
Sale
Isariin C | CAS 80111-96-2 | Flavonoid Glycoside for Antioxidant, Angiogenesis, and Insecticidal Research
Original price was: $36.00.$23.00Current price is: $23.00.
Isariin C (CAS 80111-96-2) is a naturally occurring flavonoid glycoside with potent antioxidant and angiogenic properties. It exhibits insecticidal activity and plays a dual role in oxidative stress modulation and vascular development research.
Description
Product Description
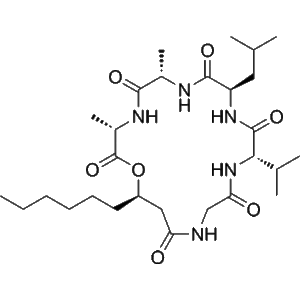
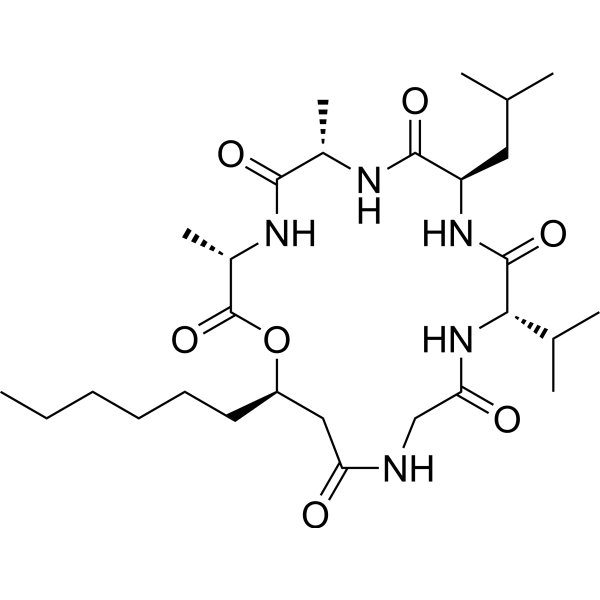
Isariin C is a naturally derived flavonoid glycoside isolated from fungal and plant sources, belonging to the large class of phenolic secondary metabolites. Structurally, it consists of a flavone backbone conjugated to a sugar moiety, typically glucose, which enhances solubility and biological stability. This compound has drawn scientific attention for its multifunctional bioactivities — particularly antioxidant, angiogenic, and insecticidal effects — making it an important biochemical tool in redox biology, vascular development, and ecological defense studies.
Structural Characteristics
As a glycosylated flavonoid, Isariin C features a core flavone structure containing hydroxyl substituents capable of donating hydrogen atoms or electrons to neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS). The glycosidic linkage, generally attached at the 7- or 3-position, contributes to enhanced water solubility and stability in biological systems. Such conjugation facilitates membrane transport, enzymatic recognition, and controlled bioavailability during experimental applications.
Natural Occurrence and Biological Source
Isariin C is primarily isolated from fungi of the Isaria genus — a group of entomopathogenic fungi known for producing bioactive metabolites that regulate oxidative stress and target insect physiology. This dual functionality allows Isariin C to act both as a defensive molecule in nature and a promising research compound for biomedical and entomological studies.
Antioxidant Activity
Flavonoid glycosides like Isariin C serve as free radical scavengers, chelating metal ions and preventing oxidative damage to lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. In vitro assays such as DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging tests consistently demonstrate its ability to suppress ROS accumulation.
In biological models, Isariin C modulates key antioxidant enzymes including superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), thereby reinforcing the cellular defense system against oxidative stress. The compound also inhibits lipid peroxidation and prevents mitochondrial dysfunction, supporting studies in oxidative injury and redox signaling.
Angiogenesis Modulation
Beyond its antioxidant effects, Isariin C has been shown to activate angiogenesis, the physiological process of new blood vessel formation. It enhances endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation via activation of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway.
Mechanistic evidence suggests that Isariin C stimulates PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK signaling cascades, resulting in upregulation of angiogenic genes and nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activity. These actions make it an important compound for investigating the relationship between oxidative balance and vascular growth, as well as potential applications in wound healing or tissue regeneration models.
Insecticidal Properties
Isariin C’s insecticidal function derives from its ability to interfere with insect energy metabolism, oxidative balance, and neural signaling. Entomological research has demonstrated its activity against larvae of several agricultural pests by inducing oxidative stress and apoptosis in target insect tissues.
As part of natural fungal defense systems, Isariin C disrupts mitochondrial respiration in insects, leading to cell death. Its selectivity toward insect species while sparing mammalian cells makes it a valuable natural pesticide research agent and a safer alternative to synthetic insecticides in laboratory screening studies.
Research Applications
Isariin C’s diverse bioactivity allows its use in multiple research fields:
Antioxidant Research: ROS modulation, lipid peroxidation, mitochondrial protection
Angiogenesis Studies: VEGF pathway activation, endothelial proliferation assays
Insecticidal Mechanism Analysis: Oxidative stress induction, mitochondrial disruption
Phytochemical and Mycochemical Profiling: Structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies
Cell Signaling: PI3K/Akt, ERK1/2, and NF-κB pathway modulation
Experimental Utility
Because of its structural stability and broad compatibility, Isariin C is commonly used in:
In vitro cell culture studies of oxidative stress and vascular biology
In vivo insecticidal mechanism exploration
Antioxidant screening assays comparing natural compounds
Vascular endothelial cell migration and wound closure models
Its solubility in organic solvents and partial aqueous systems makes it suitable for biochemical and pharmacological testing across multiple model organisms.
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Isariin C |
| CAS Number | 80111-96-2 |
| Synonyms | Isariin-C, Isaria flavonoid glycoside, Isaria-derived polyphenol |
| Molecular Formula | C₂₁H₂₀O₁₀ |
| Molecular Weight | 432.38 g/mol |
| Purity | ≥99% |
| Appearance | Yellowish to pale brown powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol, ethanol, DMSO; limited aqueous solubility |
| Storage Conditions | Store at −20 °C, desiccated, protected from light |
| Applications | Antioxidant, angiogenesis, insecticidal activity, oxidative stress studies |
Mechanism of Action
1. Antioxidant Pathway
Isariin C exhibits antioxidant action primarily through ROS scavenging and enzyme modulation.
ROS Scavenging: Hydroxyl and methoxy substituents on its flavonoid core donate hydrogen atoms to neutralize free radicals.
Metal Chelation: The catechol moiety binds redox-active metals (Fe²⁺, Cu²⁺), inhibiting Fenton reaction–mediated hydroxyl radical formation.
Enzyme Regulation: Upregulates antioxidant enzymes (SOD, CAT, GPx) via activation of the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway, which promotes transcription of antioxidant response elements.
Through these processes, Isariin C reduces oxidative stress–induced damage in cellular systems, making it a benchmark compound for redox biology studies.
2. Angiogenic Mechanism
Isariin C stimulates angiogenesis through activation of the VEGF-A/VEGFR2 axis. The downstream signaling involves:
PI3K/Akt Activation: Enhancing eNOS phosphorylation and nitric oxide release to promote endothelial cell survival and vasodilation.
MAPK/ERK Signaling: Driving endothelial cell proliferation and migration.
HIF-1α Stabilization: Inducing expression of hypoxia-response genes that facilitate new vessel formation under low-oxygen conditions.
These pathways collectively contribute to capillary tube formation, increased vascular permeability, and remodeling processes.
3. Insecticidal Mechanism
Isariin C’s insecticidal action arises from disruption of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in insect cells:
Induces mitochondrial depolarization and ROS overproduction.
Inhibits key metabolic enzymes like NADH dehydrogenase and ATP synthase.
Activates caspase-dependent apoptosis in insect larvae and pupae.
By targeting oxidative homeostasis, it causes oxidative collapse in insect cells, leading to cell death while maintaining selectivity against vertebrates.
4. Cross-Linked Pathways
Interestingly, the same redox-sensitive mechanisms responsible for antioxidant and angiogenic effects contribute to its insecticidal behavior in oxidative imbalance conditions. This dual functionality highlights Isariin C’s unique position as a multi-target bioactive glycoside, bridging plant biochemistry and applied life science research.
Side Effects
In laboratory research settings, Isariin C demonstrates low toxicity and excellent biocompatibility. At standard experimental concentrations, it shows no mutagenic or genotoxic properties. However, due to its redox activity, excessive concentrations may:
Cause mild oxidative stress in cell cultures.
Interfere with mitochondrial electron transport if used at supra-physiological levels.
Exhibit mild pro-oxidant behavior in iron-rich environments.
Handling should follow standard laboratory practices, with use of gloves and protective eyewear to avoid contamination or light-induced degradation. The compound is not suitable for therapeutic or agricultural use outside controlled research environments.
Keywords
Isariin C, flavonoid glycoside, antioxidant compound, angiogenesis activator, insecticidal natural product, oxidative stress research, VEGF signaling, redox biology, fungal secondary metabolite, natural pesticide analog
Shipping Guarantee
All shipments are handled using validated cold-chain logistics to preserve compound integrity. Each package is sealed in moisture-proof containers with secondary protective wrapping and continuous temperature monitoring. Products are shipped via express international couriers with full tracking and insurance coverage.
Trade Assurance
We ensure product authenticity, verified ≥99% purity, and compliance with analytical standards (HPLC, MS, and NMR). Each batch is supplied with a Certificate of Analysis (CoA). Our trade assurance policy guarantees replacement or refund for any deviation from listed specifications.
Payment Support
We provide flexible and secure global payment options to support international research transactions. Accepted payment methods include PayPal, major credit cards (Visa, MasterCard, American Express), telegraphic transfer (T/T), and cryptocurrencies (USDT, Bitcoin, Ethereum). All transactions are protected by industry-standard encryption and verified payment gateways to ensure confidentiality and fund security.
Disclaimer
All products listed are intended for laboratory research use only and not for human or veterinary use. They are not drugs, medical devices, or diagnostics and should not be administered to humans or animals. Researchers must handle all materials in accordance with institutional biosafety and chemical safety guidelines. The information provided is for scientific reference only and does not imply therapeutic efficacy, safety, or regulatory approval.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 65 × 26 × 65 cm |
What is Isariin C?
Isariin C is a naturally occurring flavonoid glycoside with antioxidant, angiogenic, and insecticidal properties.
What is the CAS number of Isariin C?
CAS 80111-96-2.
What are the main biological activities of Isariin C?
It exhibits strong antioxidant activity, promotes angiogenesis, and acts as an insecticidal compound.
What signaling pathways are involved?
Primarily Nrf2/ARE for antioxidant defense, and VEGF/PI3K/Akt/ERK for angiogenesis.
What is its purity?
Verified ≥99% purity.
Is Isariin C toxic?
It shows low toxicity under research conditions; excessive doses may induce mild oxidative stress.
Can it be used as a pesticide?
It exhibits insecticidal activity but is supplied strictly for research purposes.
How should it be stored?
Store at −20 °C, dry, and protected from light.
Is it water soluble?
Partially; better solubility in methanol, ethanol, or DMSO.
Is it suitable for therapeutic or agricultural application?
No, it is intended for laboratory research use only.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.