No products in the cart.
Sale
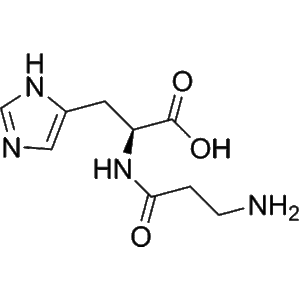
L-Carnosine | CAS 305-84-0 | Endogenous Antioxidant Peptide for Skin Protection and Anti-Aging Research | High Quality Best Price
Original price was: $23.00.$15.00Current price is: $15.00.
L-Carnosine is an endogenous dipeptide composed of β-alanine and L-histidine, widely distributed in human tissues. It exhibits strong antioxidant, anti-glycation, and anti-aging properties, making it a key research molecule in skin protection and cosmetic peptide studies.
Description
Product Description
L-Carnosine (β-alanyl-L-histidine) is a naturally occurring dipeptide composed of β-alanine and L-histidine. As a multifunctional bioactive compound, it plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, particularly in tissues with high oxidative metabolism such as the brain, skeletal muscle, and skin. In cosmetic peptide research, L-Carnosine has become a focal molecule due to its diverse biological functions, including antioxidant activity, anti-glycation effects, metal ion chelation, and anti-aging potential. These combined actions make it an essential reference molecule for studies on dermal protection, collagen preservation, and cellular longevity.
At the molecular level, L-Carnosine acts as a non-enzymatic free radical scavenger, neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), reactive nitrogen species (RNS), and lipid peroxidation byproducts. This antioxidant property helps maintain redox balance within cells, preventing oxidative damage to proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. In dermatological models, oxidative stress is a primary factor contributing to photoaging, wrinkle formation, and barrier dysfunction. Therefore, L-Carnosine’s role as an antioxidant peptide makes it an indispensable research tool in anti-aging and photoprotection studies.
A distinctive feature of L-Carnosine is its anti-glycation ability. Glycation refers to the non-enzymatic reaction between reducing sugars and amino groups in proteins, leading to the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs). These AGEs accumulate in dermal tissues over time, crosslinking collagen and elastin fibers, thereby reducing elasticity and leading to visible skin aging. L-Carnosine interrupts this process by reacting with carbonyl intermediates, thereby preventing the formation of AGEs. Research indicates that carnosine can restore the flexibility and functional properties of collagen fibers in in vitro models, demonstrating its value in cosmetic peptide studies related to skin elasticity and wrinkle prevention.
Furthermore, L-Carnosine’s metal ion chelation property enhances its antioxidant defense capacity. Transition metals such as copper and iron catalyze the Fenton reaction, generating hydroxyl radicals that cause oxidative stress. By chelating these metals, L-Carnosine minimizes radical generation, contributing to cellular stability and anti-aging protection in skin tissue. This metal-binding property also helps protect against environmental pollutants and heavy-metal-induced oxidative damage, which are significant contributors to skin dullness and loss of vitality.
From a biochemical perspective, L-Carnosine modulates intracellular signaling pathways associated with inflammation and stress response. It downregulates pro-inflammatory cytokines (such as IL-6 and TNF-α) and inhibits NF-κB activation, leading to a reduction in oxidative and inflammatory damage. In dermal fibroblast research, carnosine supplementation enhances collagen synthesis, accelerates wound healing, and protects mitochondrial function, all of which are critical factors in maintaining youthful skin physiology.
In addition to its antioxidant and anti-glycation roles, L-Carnosine also functions as a cellular buffer, regulating pH fluctuations in metabolically active tissues. This buffering capacity contributes to the stability of cellular microenvironments, which is particularly beneficial for skin cells exposed to UV radiation and oxidative insults. In experimental dermatology, this property helps simulate protective responses observed in human epidermal keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts.
L-Carnosine’s potential in skin-brightening and tone-evening research is also noteworthy. By mitigating oxidative stress and glycation, it indirectly influences melanin synthesis and reduces the accumulation of dull, glycation-induced chromophores in the skin. When combined with other cosmetic peptides such as glutathione or acetyl hexapeptide derivatives, L-Carnosine exhibits synergistic antioxidant and skin-conditioning effects, making it a versatile tool for cosmetic and dermatological peptide studies.
At the cellular signaling level, L-Carnosine modulates the expression of longevity-associated proteins such as sirtuins and activates antioxidant response elements (ARE) through the Nrf2 pathway. These mechanisms contribute to cellular detoxification and repair processes, thereby reducing oxidative damage accumulation. In vitro studies demonstrate that carnosine-treated fibroblasts show increased resistance to oxidative and carbonyl stress, which translates to improved structural protein integrity and reduced senescence markers.
From a systems biology perspective, L-Carnosine represents a key molecule in redox proteostasis. It maintains protein structure by preventing oxidation and carbonylation of amino acid residues, thereby preserving enzymatic function and structural integrity in skin tissue. This aspect is critical for understanding how peptide-based antioxidants maintain cellular youthfulness in cosmetic and anti-aging research contexts.

Product Specifications
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Name | L-Carnosine |
| CAS Number | 305-84-0 |
| Synonyms | β-Alanyl-L-histidine; Carnosine |
| Molecular Formula | C9H14N4O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 226.23 g/mol |
| Purity | ≥99% |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in water |
| Storage | Store at −20°C, protected from light and moisture |
| Category | Cosmetic peptide; Antioxidant peptide |
| Applications | Anti-aging research, skin protection, anti-glycation, oxidative stress studies |
| Research Area | Dermatology, redox biology, collagen preservation, cosmetic science |
| Supplier Type | Research use only reagent |
| Intended Use | For laboratory research use only |
Mechanism of Action
The biological action of L-Carnosine centers on its ability to scavenge free radicals, chelate metal ions, and inhibit glycation. Its imidazole ring in the histidine residue provides proton-donating capacity, enabling it to neutralize ROS such as hydroxyl radicals, superoxide anions, and peroxynitrite. This reaction prevents oxidative degradation of cell membranes and structural proteins.
In anti-glycation research, L-Carnosine intercepts reactive carbonyl intermediates derived from sugar metabolism, such as methylglyoxal and glyoxal. By forming adducts with these intermediates, carnosine prevents them from reacting with lysine and arginine residues in collagen, thereby reducing AGE formation. This mechanism helps maintain the suppleness and elasticity of the dermal matrix in long-term anti-aging studies.
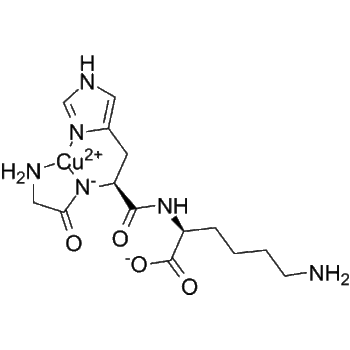
L-Carnosine’s chelation activity adds another layer of defense. It forms complexes with divalent cations like Cu²⁺ and Fe²⁺, preventing them from catalyzing free radical formation via Fenton and Haber–Weiss reactions. As a result, cellular oxidative burden decreases, and antioxidant enzymes such as SOD and catalase are preserved from oxidative deactivation.
Another major mechanism is the modulation of intracellular redox signaling. Carnosine stabilizes NAD⁺/NADH and GSH/GSSG ratios, essential for maintaining oxidative equilibrium. It also interacts with molecular chaperones and proteasomal pathways to prevent the accumulation of misfolded proteins under stress conditions—a process particularly relevant to cellular longevity studies.
Side Effects
Under laboratory conditions, L-Carnosine exhibits a favorable safety profile and high biocompatibility. It is an endogenous molecule naturally found in mammalian tissues, making it suitable for in vitro and biochemical research models. However, excessive concentrations may alter redox signaling or interfere with controlled oxidative assays. Researchers are advised to optimize concentrations based on assay design and cell type.
This compound is not intended for human or cosmetic application. It should be handled under appropriate laboratory safety standards, with protective equipment and good cell culture practices to avoid contamination or cross-reactivity in sensitive analytical systems.

Keywords
L-Carnosine, CAS 305-84-0, antioxidant peptide, anti-aging research, anti-glycation peptide, oxidative stress, skin protection, collagen preservation, cosmetic peptide, redox regulation
Shipping Guarantee
All shipments are handled using validated cold-chain logistics to preserve peptide integrity. Each package is sealed in moisture-proof containers with secondary protective wrapping and continuous temperature monitoring. Products are shipped via express international couriers with full tracking and insurance coverage.
Trade Assurance
We ensure product authenticity, verified ≥99% purity, and compliance with analytical standards (HPLC, MS, and NMR). Each batch is supplied with a Certificate of Analysis (CoA). Our trade assurance policy guarantees replacement or refund for any deviation from listed specifications.
Payment Support
We provide flexible and secure global payment options to support international research transactions. Accepted payment methods include PayPal, major credit cards (Visa, MasterCard, American Express), telegraphic transfer (T/T), and cryptocurrencies (USDT, Bitcoin, Ethereum). All transactions are protected by industry-standard encryption and verified payment gateways to ensure confidentiality and fund security.
Disclaimer
All products listed are intended for laboratory research use only and not for human or veterinary use. They are not drugs, medical devices, or diagnostics and should not be administered to humans or animals. Researchers must handle all materials in accordance with institutional biosafety and chemical safety guidelines. The information provided is for scientific reference only and does not imply therapeutic efficacy, safety, or regulatory approval.
Additional information
| Weight | 1.2 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 53 × 46 × 53 cm |
What is L-Carnosine used for in research?
It is used in anti-aging, skin protection, antioxidant, and anti-glycation research studies.
What makes L-Carnosine a cosmetic peptide of interest?
Its strong antioxidant and anti-glycation properties make it ideal for studying mechanisms of dermal aging.
Is L-Carnosine safe for cell culture research?
Yes, it is an endogenous molecule generally well-tolerated in in vitro models.
Can it prevent protein glycation in collagen studies?
Yes, it effectively inhibits AGE formation and collagen crosslinking in biochemical assays.
What are the solubility characteristics of L-Carnosine?
It is readily soluble in water.
Does it have synergistic effects with other antioxidants?
Yes, studies show synergism with glutathione, vitamin C, and coenzyme Q10.
Is it stable during storage?
When stored at −20°C and protected from light, L-Carnosine maintains long-term stability.
Can it be used for pigmentation research?
Yes, it helps reduce oxidative and glycation-related dullness in skin models.
Does it chelate metal ions?
Yes, it binds copper and iron, reducing oxidative radical formation.
Is it approved for human cosmetic use?
No. It is intended strictly for laboratory and in vitro research only.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.