No products in the cart.
Sale
ACE-031 (CAS 1621169-52-5) High purity peptide Factory manufactured
Original price was: $48.00.$42.00Current price is: $42.00.
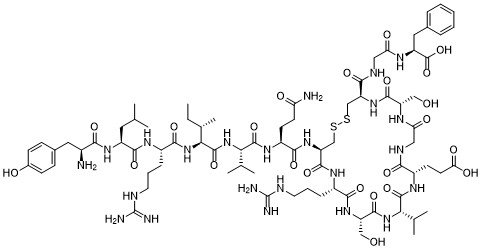
ACE-031 is a recombinant research-grade fusion protein designed for laboratory studies involving myostatin pathway inhibition, muscle-related signaling, and ligand-binding interactions. Manufactured under high-purity conditions, it supports mechanistic, biochemical, and multi-omic research workflows. For research use only.
Description
Product Description
ACE-031 (CAS 1621169-52-5) is a high-purity recombinant fusion protein designed specifically for advanced laboratory research focused on myostatin pathway biology, ligand-receptor interactions, and muscle-associated signaling mechanisms. As a soluble ActRIIB-Fc construct, ACE-031 serves as a highly effective ligand-binding reagent, enabling researchers to study how myostatin and related TGF-β superfamily ligands regulate cellular pathways involved in differentiation, structural remodeling, and protein turnover. Its engineered extracellular receptor domain provides strong affinity for multiple ligands, making it an essential tool for laboratories investigating inhibitory signaling dynamics and cross-talk within complex regulatory networks.
In controlled in-vitro settings, ACE-031 assists researchers in mapping upstream and downstream signaling processes, particularly those associated with SMAD phosphorylation, transcriptional response patterns, and regulatory protein expression. Because the protein binds to multiple members of the myostatin/activin family, it enables the systematic evaluation of pathway attenuation, ligand competition, and compensatory interactions across a wide range of biological models. This allows scientists to explore how cells respond when specific ligands are sequestered or removed from the signaling environment, providing insights into pathway balance, feedback loops, and regulatory hierarchies.
The structural stability and high purity of ACE-031 are especially beneficial for analytical workflows, including SEC, SDS-PAGE, mass spectrometry, and biochemical affinity measurement assays. Consistent lot-to-lot quality supports long-term reproducibility—an essential factor in quantitative signaling studies, binding-kinetics analysis, and multi-omic research designs. Laboratories can use ACE-031 to dissect signaling-environment remodeling, examine molecular interactions at the receptor level, and assess how ligand trapping influences transcriptional and proteomic landscapes in various cultured cell systems.
Additionally, ACE-031 integrates seamlessly into computational and systems-biology modeling workflows, aiding researchers who aim to predict ligand-receptor interaction networks, simulate inhibitory effects, and correlate experimental outcomes with digital pathway reconstructions. Its well-defined structure makes it compatible with docking simulations, structural visualization, and machine-learning-based predictive tools, further expanding its utility across modern mechanistic research.
Manufactured under stringent quality standards with analytical documentation provided for every batch, ACE-031 is ideal for academic, pharmaceutical, and biotech laboratories requiring a reliable, research-grade ActRIIB-Fc fusion protein. This product is intended exclusively for scientific experimentation in controlled laboratory environments. It is not for human or veterinary use, and all handling must follow institutional research safety guidelines.

Product Specifications
| Specification | Detailed Information |
|---|---|
| Product Name | ACE-031 |
| CAS Number | 1621169-52-5 |
| Synonyms | ActRIIB-Fc fusion protein, Soluble Activin Receptor Type IIB extracellular domain–Fc construct |
| Molecular Type | Recombinant fusion protein (ActRIIB extracellular domain linked to IgG-Fc) |
| Molecular Weight | Approx. 80–90 kDa (dimeric) depending on glycosylation patterns |
| Biological Target | Myostatin (GDF-8), Activins, and other ActRIIB-binding ligands in TGF-β superfamily |
| Appearance | White to off-white lyophilized powder |
| Form | Freeze-dried research-grade protein, sterile-filtered during manufacture |
| Purity Level | ≥98%, validated by SEC-HPLC, SDS-PAGE, and mass spectrometry |
| Endotoxin Level | < 1.0 EU/µg protein (LAL-tested), suitable for sensitive in-vitro systems |
| Protein Structure | Dimeric Fc-fusion; includes hinge region to support structural stability |
| Expression System | Mammalian expression (commonly CHO or HEK293 for optimal glycosylation) |
| Solubility | Soluble in sterile water, PBS, or appropriate neutral pH buffers |
| Reconstitution Recommendation | Add sterile aqueous buffer slowly to walls of vial; avoid foaming; mix gently |
| Stability (Lyophilized) | Stable for long-term storage when protected from moisture and light |
| Stability (Reconstituted) | Short-term stable at 2–8°C; for longer storage, prepare aliquots and freeze; avoid freeze–thaw cycles |
| Storage Conditions | Store at −20°C or below; keep container tightly sealed |
| Handling Recommendations | Use low-binding tubes and pipette tips; avoid vigorous shaking to preserve structural integrity |
| Analytical Documentation | COA, SEC chromatogram, SDS-PAGE gel image, MS report provided with each batch |
| Quality Assurance | Manufactured under ISO-level laboratory standards with strict QC checkpoints |
| Packaging Options | 0.1 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, and bulk research-pack quantities available |
| OEM & Customization | Custom vialing, labeling, and bulk packaging support available |
| Intended Use | For laboratory research only. Not for human or veterinary use. |
Mechanism of Action
ACE-031 is a recombinant fusion protein designed to act as a high-affinity soluble decoy receptor for myostatin and related TGF-β superfamily ligands, providing a potent inhibitory effect on negative regulators of skeletal muscle growth. Structurally, ACE-031 combines the extracellular domain of Activin Receptor Type IIB (ActRIIB) with the Fc portion of human IgG1, increasing its circulatory half-life, stability, and systemic bioavailability for research applications. The molecule’s engineered configuration allows it to circulate in plasma and selectively bind endogenous ligands before they reach membrane-bound ActRIIB receptors on muscle cells.
1. Ligand Sequestration and Blockade of Catabolic Signaling
Myostatin, Activin A, and other ActRIIB-binding ligands function as key molecular “brakes” on muscle growth, promoting catabolism, inhibiting myoblast differentiation, and suppressing hypertrophic signaling pathways. ACE-031 binds these ligands with high affinity, preventing their interaction with endogenous ActRIIB receptors.
This ligand sequestration disrupts canonical SMAD2/3 phosphorylation, the primary intracellular cascade responsible for transmitting inhibitory growth signals. When SMAD signaling is suppressed, muscle precursor cells experience reduced transcriptional repression, enabling enhanced differentiation, higher myogenic fusion rates, and increased protein synthesis.
2. Promotion of Muscle Fiber Hypertrophy
By blocking myostatin/activin signaling, ACE-031 shifts the intracellular balance toward pro-growth pathways, notably PI3K/Akt/mTOR, which governs protein synthesis, ribosomal biogenesis, and hypertrophic expansion of muscle fibers. Research models consistently observe increases in:
Muscle fiber cross-sectional area
Total lean mass accumulation
Satellite cell activation and fusion events
Reduced proteolytic activity (via ubiquitin–proteasome and autophagy pathways)
These effects collectively demonstrate how ligand neutralization leads to net anabolic remodeling even under catabolic or aging-associated conditions.
3. Enhancement of Muscle Regeneration and Repair Capacity
Preclinical data show that ACE-031 indirectly strengthens skeletal muscle regenerative capacity by promoting satellite cell pool expansion. With fewer inhibitory signals acting on progenitor cells, tissue remodeling after micro-injury becomes more efficient.
The reduction in transforming growth factor–β activity also decreases extracellular matrix stiffening and fibrosis formation—common obstacles to functional regeneration.
4. Modulation of Bone and Metabolic Pathways (Research Observations)
Beyond muscle biology, ActRIIB ligands influence bone density, adipose metabolism, and inflammatory cascades. In various investigative models, ACE-031 has demonstrated:
Increased bone mineral content and trabecular density
Improved insulin sensitivity and glucose utilization
Altered fat distribution and reduced adipocyte size
Downregulation of inflammatory mediators linked to tissue degeneration
These secondary effects emphasize the wide-ranging influence of ActRIIB signaling and provide multiple avenues for research into musculoskeletal, metabolic, and aging-related conditions.
5. Impact on Systemic Growth Factor Networks
ACE-031 does not function as a generalized growth stimulant; rather, it selectively alters ligand–receptor interactions within the TGF-β superfamily. As ligand availability is reduced, compensatory changes can occur in other growth pathways, including BMP signaling, which may become relatively upregulated due to reduced competitive ligand pressure.
This shift can contribute to enhanced anabolic outcomes in both muscle and bone tissues, further demonstrating the mechanistic interplay between negative and positive regulators in the musculoskeletal system.

Applications
ACE-031 is widely applied across advanced research fields due to its highly specific role as a soluble ActRIIB decoy receptor, enabling targeted inhibition of myostatin and activin signaling. Its ability to modulate skeletal muscle mass, fiber regeneration, metabolic pathways, and bone remodeling makes it a versatile tool in mechanistic studies and multi-disciplinary experimental designs.
1. Skeletal Muscle Growth & Atrophy Research
ACE-031 is extensively used to explore the molecular basis of muscle hypertrophy, satellite cell dynamics, and inhibitory SMAD2/3 signaling pathways. Researchers investigate:
Mechanisms underlying age-related sarcopenia
Muscle-wasting associated with cachexia or chronic illness
Recovery and repair following disuse, immobilization, or nerve injury
The interplay between myostatin inhibition and anabolic pathways such as Akt/mTOR
Its ligand-sequestration mechanism makes ACE-031 an ideal reagent for dissecting how negative growth regulators govern myoblast proliferation, maturation, and hypertrophy.
2. Duchenne & Other Muscular Dystrophy Models
Due to its strong inhibitory effect on downstream pathways that restrict muscle formation, ACE-031 is frequently employed in models of:
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)
Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD)
Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD)
Its use helps researchers analyze fibrosis reduction, satellite cell rescue, compensatory regeneration, and modulation of dystrophin-deficiency phenotypes.
3. Bone Biology & Osteogenesis Studies
ActRIIB ligands also influence bone metabolism, making ACE-031 relevant to investigations involving:
Osteoporosis and age-related bone density loss
Trabecular and cortical bone remodeling
BMP versus activin signaling balance
Mechanical loading–induced bone adaptation
By modulating inhibitory ligand pools, ACE-031 helps researchers quantify how bone anabolic pathways respond when myostatin/activin constraints are removed.
4. Metabolic, Endocrine & Adipose Tissue Research
ACE-031 has growing relevance in studies evaluating systemic metabolic regulation. Preclinical models highlight its utility in:
Insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis studies
Brown and white adipose tissue remodeling
Energy expenditure and nutrient partitioning
Investigating cross-talk between muscle and endocrine pathways
Because myokines and adipokines interact extensively, ACE-031 enables exploration of metabolic shifts associated with altered muscle–adipose communication.
5. Regenerative Medicine & Tissue Engineering
Research programs in tissue engineering use ACE-031 to optimize muscle scaffold integration, stem cell differentiation, and regenerative microenvironments. Applications include:
Improving myogenic bioengineered tissue constructs
Optimizing extracellular matrix (ECM) stiffness and fibrosis modulation
Enhancing repair after volumetric muscle loss (VML) in preclinical models
The tool’s ability to modulate TGF-β family dynamics makes it valuable in designing regenerative biomaterials.
6. Aging & Longevity Studies
Age-associated muscle decline is tightly linked to chronic elevation of myostatin and inflammatory cytokines. ACE-031 is used to examine:
Muscle functional decline in geriatric models
Reversal of age-related satellite cell quiescence
Interaction between inflammation, SMAD3, and anabolic signaling
Whole-body metabolic changes associated with anti-catabolic pathways
These investigations help characterize the molecular drivers of aging phenotypes.
7. Neuromuscular & Motor Function Research
Because muscle strength and contractility influence neuromuscular stability, ACE-031 is incorporated in:
Denervation and reinnervation studies
Peripheral nerve injury models
Motor coordination and locomotor adaptation research
Synaptic plasticity analysis at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
Modulation of muscle volume provides a controlled variable for linking tissue strength with neural adaptation.
8. Comparative Physiology & Veterinary Research Models
ACE-031 is used in multiple species to evaluate how conserved ActRIIB pathways operate in:
Rodents (primary mechanistic studies)
Large-animal translational models
Preclinical functional performance assays
Cross-species muscle and bone physiology comparisons
The broad conservation of myostatin/activin signaling allows ACE-031 to serve as a universal investigative tool across mammalian models.
9. Multi-Organ Interaction & Systems Biology Studies
Because myostatin pathway modulation influences muscle, bone, fat, liver, and immune processes, ACE-031 is used to study:
Whole-body signaling networks
Myokine-driven endocrine regulation
Metabolic flux and nutrient redistribution
System-level adaptations following ligand inhibition
This makes ACE-031 valuable in systems biology, omics-based modeling, and integrative pathway analysis.

Research Models
ACE-031 is widely incorporated into diverse preclinical research models due to its precise activity as a soluble ActRIIB ligand trap capable of modulating myostatin/activin signaling. Its versatility allows researchers to examine muscle growth, bone remodeling, metabolic shifts, neuromuscular adaptation, and cross-organ communication under controlled experimental conditions. The following model systems represent the most common and scientifically validated applications.
1. Rodent Models for Skeletal Muscle Research
Murine and rat models remain the primary platforms for evaluating ACE-031 due to their well-characterized myostatin/activin pathways. Researchers utilize:
Wild-type rodents to establish baseline hypertrophic responses and fiber-type transitions.
Sarcopenia models induced by aging, immobilization, or hindlimb unloading to investigate anti-catabolic effects.
Denervation or nerve-crush models to observe relationships among neuromuscular signaling, atrophy rescue, and satellite cell activation.
These systems allow precise quantification of muscle volume, contractile force, SMAD2/3 phosphorylation, and associated transcriptional changes.
2. Muscular Dystrophy Models
ACE-031 is extensively used in dystrophic animal models to assess how ActRIIB inhibition influences regenerative deficits. Key models include:
mdx mice (Duchenne muscular dystrophy) for fibrosis profiling, satellite cell regeneration, and muscle membrane stability analysis.
Sgca-null and Dysf-null models to study broader dystrophy phenotypes, inflammation, and ECM remodeling.
LGMD variants for examining compensatory hypertrophy and phenotypic rescue mechanisms.
These models help researchers map the relationship between myostatin suppression and dystrophin-associated pathology.
3. Bone Density, Osteoporosis & Orthopedic Models
Because activin signaling plays a central role in skeletal homeostasis, ACE-031 is incorporated into bone-focused studies such as:
Ovariectomized rodent osteoporosis models to evaluate trabecular and cortical bone restoration.
Mechanical unloading or microgravity simulation models to examine mechanotransduction and bone resorption patterns.
Fracture healing and bone defect models to observe changes in osteoblast–osteoclast balance.
These systems are valuable for mapping BMP/activin interactions, bone microstructure, mineralization, and anabolic responses following ligand sequestration.
4. Metabolic & Endocrine Research Models
ACE-031 is used in metabolic studies to clarify how altering myokine signaling affects whole-body energy regulation. Common models include:
Diet-induced obesity (DIO) models for tracking adipose remodeling, insulin sensitivity, and glucose clearance.
Hyperglycemia or insulin-resistance models to examine cross-talk between muscle hypertrophy and endocrine signaling.
Brown and white fat differentiation models to evaluate shifts in thermogenesis, lipolysis, and nutrient partitioning.
These systems support multi-organ profiling of systemic metabolic adaptations.
5. Aging & Longevity Models
Age-related muscle degeneration is a major research theme where ACE-031 is frequently deployed. Aging-related models include:
Naturally aged rodents for sarcopenia progression tracking.
Progeroid models to accelerate the study of mitochondrial decline, inflammatory cytokine activity, and anabolic resistance.
Longitudinal muscle function assays measuring gait, grip strength, and endurance metrics.
These models help researchers define the molecular underpinnings of age-associated frailty and muscle loss.
6. Neuromuscular & Motor Function Models
Due to its ability to induce significant hypertrophic responses, ACE-031 is used to dissect neuromuscular interactions in:
Peripheral nerve injury models, including crush and transection paradigms.
Motor coordination tests such as rotarod, treadmill performance, and locomotion tracking.
Neuromuscular junction (NMJ) studies to evaluate synaptic plasticity under altered muscle loading conditions.
This provides insight into how muscle mass influences neural regeneration and motor output.
7. Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Biology Models
ACE-031 is incorporated into biomaterial and regenerative medicine studies including:
Engineered skeletal muscle constructs for enhanced contractility and structural maturation.
Volumetric muscle loss (VML) models to evaluate scaffold performance, fibrosis reduction, and myogenic integration.
Stem cell differentiation assays, particularly involving mesenchymal or muscle progenitor cells.
These models highlight the regenerative benefits of modulating TGF-β superfamily signaling.
8. Comparative Physiology & Cross-Species Studies
Researchers utilize ACE-031 across multiple species to understand conserved ActRIIB regulatory pathways. Applications include:
Rodent baseline studies
Large animal translational models such as canines, pigs, or sheep
Comparative muscle physiology to evaluate interspecies differences in myostatin/activin responsiveness
These models are essential for multi-species validation of pathway modulation.
9. Systems Biology & Multi-Organ Integration Models
Given the central metabolic role of skeletal muscle, ACE-031 is used in integrated model systems such as:
Multi-organ metabolic flux experiments
Cytokine and myokine interaction studies
Whole-body omics mapping (transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics)
Computational modeling validation datasets
These approaches help create predictive frameworks describing the systems-level consequences of inhibiting ActRIIB ligands.

Experimental Design Considerations
When designing experiments with ACE-031, researchers should consider ligand concentration, buffer composition, incubation time, and pathway-specific readouts. Optimal controls may include untreated models, competing ligands, or receptor domain fragments to validate specificity.
Avoid repeated freeze–thawing of reconstituted protein stocks, and always use low-binding consumables to maintain consistent recovery. For quantitative proteomic or transcriptomic workflows, ensure that sample preparation, replication, and batch normalization are carefully controlled.
Laboratory Safety & Handling Guidelines
Handle ACE-031 under standard laboratory safety procedures, including gloves, eye protection, and use of designated workspaces. Protect protein samples from contamination and moisture, and avoid aerosol formation.
All waste materials must be disposed of according to institutional chemical and biological safety protocols. This product should never be used outside laboratory environments.

Integration with Multi-Omic & Computational Studies
ACE-031 integrates effectively with transcriptomics, proteomics, phospho-proteomics, lipidomics, and computational systems biology. Researchers often use it to examine pathway remodeling, ligand-receptor interaction networks, and regulatory feedback loops.
Computational modeling tools, including docking simulations and pathway prediction algorithms, can complement wet-lab assays, enhancing understanding of ACE-031’s interaction landscape.
Keywords
ACE-031, ActRIIB-Fc, myostatin research protein, TGF-β ligand trap, high-purity fusion protein, muscle signaling research, recombinant laboratory protein, wholesale ACE-031, factory-direct peptide fusion protein, CAS 1621169-52-5.
Shipping Guarantee
Temperature-controlled packaging preserves the structural stability of ACE-031 during transit, ensuring that sensitive protein configurations remain uncompromised. Tamper-proof sealing provides an added layer of protection, helping researchers confirm that the shipment remained secure throughout the logistics chain. Global logistics partners are selected for their reliability in handling temperature-sensitive scientific materials. Bulk and institutional packaging options are available for laboratories requiring high-volume, continuous-supply workflows. Additional documentation such as batch release forms can be provided upon request.
Trade Assurance
Factory-direct sourcing ensures batch-to-batch authenticity, purity, and manufacturing traceability from controlled production environments. Each shipment includes validated analytical documents such as COA, HPLC profiles, and SDS-PAGE results that confirm identity and quality. Consistent supply chain management supports long-term research schedules without unexpected variability. OEM labeling, custom packaging, and bulk configuration services are available to match institutional procurement requirements. Dedicated support is provided for laboratories needing recurring or contract-based sourcing.
Payment Support
Multiple payment channels are available—including bank transfer, PayPal, major credit cards, and corporate procurement systems—to accommodate global institutional purchasing. Flexible invoicing solutions help simplify acquisition for organizations operating under grant-based or multi-department funding structures. For recurring research orders, scheduled billing or consolidated invoicing can be arranged. International buyers benefit from currency-adaptive payment options that reduce administrative complexity. Support teams are available to help navigate compliance documentation, purchase approvals, or procurement-specific needs.
Disclaimer
ACE-031 is supplied strictly for research use only and is not intended for human or veterinary applications under any circumstances. All laboratory work must follow institutional biosafety, chemical handling, and experimental procedure guidelines. Researchers are responsible for ensuring proper storage, waste disposal, and containment practices as mandated by their facility. The product should only be handled by trained personnel familiar with peptide-based research materials. No therapeutic, diagnostic, or clinical claims are made or implied.
References
Cadena, S. M., et al. (2010). Administration of a soluble activin type IIB receptor increases skeletal muscle mass in mice. PLoS ONE, 5(6), e10809. PMC Link
Rodgers, B. D., et al. (2022). Myostatin and Activin Receptor Ligands in Muscle and the Musculoskeletal System. Endocrine Reviews, 43(2), 329–353. Oxford Academic Link
Attie, K. M., et al. (2013). A single ascending-dose study of muscle regulator ACE-031 in healthy volunteers. Muscle & Nerve, 47(3), 416–423. PubMed Link
Bialek, P., et al. (2014). ActRIIB-Fc increases bone mass in mice: dual effects on muscle and bone. Bone, 66, 215–222. ScienceDirect Link
Lee, S. J. (2023). Challenges and future prospects of targeting the myostatin/ActRIIB pathway. The Journals of Gerontology: Series A, 78(Suppl_1), 32–45. Oxford Academic Link
Lach-Trifilieff, E., et al. (2014). An antibody blocking activin type II receptors induces strong skeletal muscle hypertrophy and protects from atrophy. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 34(4), 606–618. PMC Link
Winbanks, C. E., et al. (2012). Follistatin-mediated skeletal muscle hypertrophy is regulated by Smad3 and mTOR independently of myostatin. Journal of Physiology, 590(24), 6039–6054. PubMed Link
Murphy, K. T., et al. (2010). Myostatin and ActRIIB signaling in skeletal muscle: implications for muscle-wasting disorders. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition & Metabolic Care, 13(3), 245–251. PubMed Link
Additional information
| Weight | 1.2 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 36 × 48 × 36 cm |
1. What is ACE-031 used for in laboratory research?
ACE-031 is utilized as a soluble ActRIIB ligand trap to investigate how myostatin and activin pathway inhibition affects muscle and bone biology. Researchers employ it to study hypertrophy mechanisms, SMAD signaling dynamics, and tissue remodeling responses. It is reserved strictly for controlled laboratory experiments and is not intended for any clinical or in vivo administration.
2. How should ACE-031 be stored for optimal stability?
ACE-031 is typically stored at −20°C or lower to maintain structural integrity over extended research periods. Short-term handling at controlled laboratory conditions is acceptable when preparing experimental solutions. Repeated freeze–thaw cycles should be avoided to prevent degradation and variability in results.
3. Does ACE-031 require sterile handling procedures?
While sterility specifications depend on the experimental design, peptide-based research materials are commonly handled in sterile environments to prevent contamination. Researchers often use biosafety cabinets and sterile filtration to ensure sample consistency. Following institutional laboratory protocols is essential.
4. What documentation is provided with each batch?
Ships with analytical documentation such as COA, purity verification, and identity confirmation data. HPLC and SDS-PAGE results are included when applicable to allow researchers to validate material suitability. Additional technical documents may be provided depending on procurement requirements.
5. Can ACE-031 be reconstituted multiple times?
Reconstitution is typically performed once to maintain experimental consistency. Preparing aliquots immediately after reconstitution helps prevent repeated freeze–thaw cycles. Laboratories often adjust solvent volumes based on planned experimental throughput.
6. What solvents are commonly used for reconstitution?
Solvent selection depends on the experimental framework, but researchers frequently use sterile aqueous buffers compatible with protein-based materials. pH-adjusted solutions may improve solubility depending on specific laboratory protocols. All solvent handling must follow institutional safety guidelines.
7. How do researchers verify ACE-031 integrity after delivery?
Visual inspection of tamper-proof packaging and review of analytical documents are standard steps. Some laboratories perform additional in-house assays such as SDS-PAGE or mass spectrometry to confirm identity. Proper storage immediately upon arrival helps maintain stability.
8. What experimental endpoints are commonly examined with ACE-031?
Researchers may evaluate hypertrophic signaling pathways, SMAD phosphorylation, muscle-fiber architecture, and bone remodeling markers. Gene and protein expression profiling is also frequently integrated. Multi-omics approaches allow for broader pathway interpretation.
9. Is ACE-031 compatible with multi-omics workflows?
Yes—ACE-031 is often incorporated into studies involving transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics. These workflows help quantify systemic effects of ActRIIB ligand sequestration across multiple biological layers. It is especially useful for pathway-mapping and network-level analyses.
10. How does ACE-031 compare with other ActRIIB ligands or inhibitors?
ACE-031 is engineered as a fusion protein combining the extracellular domain of ActRIIB with an Fc fragment, giving it higher stability and broader ligand-binding capacity compared to smaller inhibitors. Its design allows for efficient sequestration of multiple TGF-β superfamily ligands. Researchers select it for its comprehensive pathway-modulation characteristics.
11. Are custom packaging or bulk orders available?
Yes—bulk, OEM, and institutional packaging options are available for laboratories engaged in long-term research. Such configurations help streamline procurement and ensure consistency between experimental batches. Dedicated support teams can arrange special documentation or labeling needs.
12. Can ACE-031 be used in high-throughput experiments?
It can be incorporated into automated screening workflows, provided proper aliquoting and plate-handling procedures are followed. High-throughput platforms often integrate ACE-031 into pathway screening, biomarker profiling, or interaction assays. Stability and handling parameters must still be observed.
13. What quality controls are performed before release?
Each batch undergoes purity testing, identity confirmation, and functional verification assays when applicable. Standard analytical methods include HPLC, SDS-PAGE, and structural confirmation. These measures ensure consistent research-grade reliability.
14. How long can reconstituted ACE-031 remain stable?
Stability after reconstitution depends on buffer composition and storage conditions. Many laboratories maintain aliquots at −20°C to preserve activity for short- to mid-term usage. Stability should always be validated according to internal laboratory practices.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.