No products in the cart.
Sale
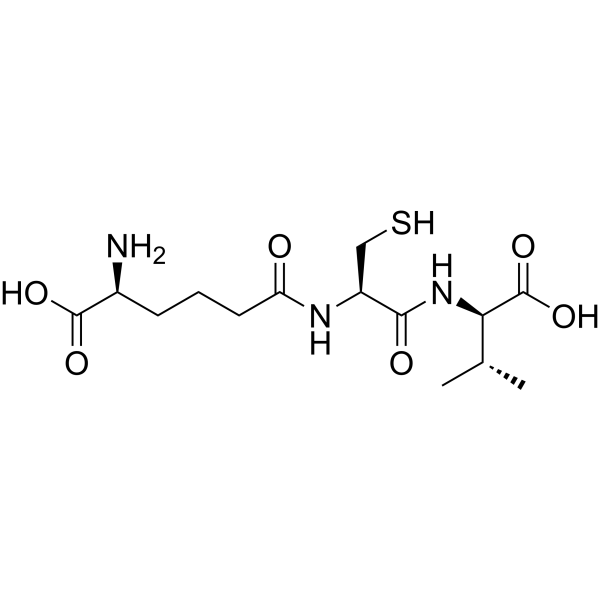
ACV Tripeptide | CAS No. 32467-88-2
Original price was: $28.00.$23.00Current price is: $23.00.
ACV Tripeptide is the essential biosynthetic intermediate for the production of penicillin and cephalosporins in Penicillium chrysogenum and Acremonium chrysogenum. It is formed by the enzyme ACV synthase, a large non-ribosomal peptide synthase encoded by the pchAB gene cluster.
Description
Contents
hide
Product Description
ACV Tripeptide (CAS 32467-88-2) is a non-ribosomal peptide consisting of L-α-aminoadipic acid, L-cysteine, and L-valine (ACV). It is the direct precursor to the β-lactam nucleus, which forms the structural core of penicillin and cephalosporins, two of the most clinically important classes of antibiotics.
Biosynthetic Context
The biosynthesis of ACV Tripeptide occurs in fungi such as Penicillium chrysogenum and Acremonium chrysogenum. This tripeptide is assembled by the enzyme ACV synthase, a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) encoded by the pchAB gene cluster (~11 kb). ACV synthase catalyzes the stepwise condensation of the three amino acids:
L-α-aminoadipic acid
L-cysteine
L-valine
The resulting tripeptide is then cyclized to form isopenicillin N by isopenicillin N synthase (IPNS), a pivotal step in the β-lactam antibiotic pathway.
Significance in β-Lactam Antibiotics
Penicillins: ACV Tripeptide provides the foundation for the thiazolidine and β-lactam rings.
Cephalosporins: Extended biosynthetic steps modify the ACV backbone into cephalosporin precursors.
Industrial fermentation: The regulation of ACV synthase expression directly influences antibiotic yields.
Research Applications
Antibiotic Biosynthesis Research: ACV Tripeptide is central to understanding how fungi synthesize β-lactam antibiotics.
Genetic Engineering: Modifying pchAB genes allows strain optimization for enhanced antibiotic production.
Metabolic Pathway Studies: ACV levels are biomarkers of fungal productivity in penicillin and cephalosporin biosynthesis.
Synthetic Biology: Serves as a model for engineering novel antibiotics by manipulating non-ribosomal peptide synthases.
Importance in Modern Medicine
Since the discovery of penicillin, β-lactam antibiotics have remained the cornerstone of antibacterial therapy. Understanding and manipulating the biosynthesis of ACV Tripeptide has contributed to industrial advances, improving yields and enabling semi-synthetic derivatives with broader activity.
Product Specifications
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | ACV Tripeptide |
| CAS No. | 32467-88-2 |
| Synonyms | δ-(L-α-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine, ACV precursor |
| Molecular Formula | C14H24N4O7S |
| Molecular Weight | 392.43 g/mol |
| Structure | Tripeptide of α-aminoadipic acid, cysteine, valine |
| Source | Biosynthesized in Penicillium and Acremonium spp. |
| Purity | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white lyophilized powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, buffers, DMSO |
| Storage | -20°C, desiccated, away from light |
| Stability | Stable for 12 months under recommended conditions |
| Applications | Penicillin and cephalosporin biosynthesis research, metabolic engineering, antibiotic pathway studies |
Notes
Produced in trace amounts naturally, but can be synthesized chemically for research.
Analytical validation: confirmed by HPLC and MS.
Critical intermediate in antibiotic fermentation industry.
Mechanism of Action
ACV Tripeptide itself is a biosynthetic intermediate rather than a pharmacologically active compound. Its mechanism of action relates to its role as a precursor molecule in fungal biosynthetic pathways.
Stepwise Role in β-Lactam Biosynthesis
Non-ribosomal synthesis
ACV synthase activates and links aminoadipic acid, cysteine, and valine in an ATP-dependent process.
This reaction bypasses ribosomal machinery, using NRPS enzyme modules.
Formation of ACV Tripeptide
The enzyme arranges the peptide in a specific order, ensuring the correct stereochemistry.
Cyclization to Isopenicillin N
Isopenicillin N synthase (IPNS) catalyzes oxidative cyclization, generating the β-lactam and thiazolidine rings.
Branching Pathways
In penicillin biosynthesis, isopenicillin N is modified to penicillin G or V.
In cephalosporin biosynthesis, additional enzymes (expandase, hydroxylase) convert it into cephalosporins.
Research Impact
Metabolic Bottleneck: ACV availability is often the rate-limiting step in penicillin production.
Genetic Engineering: Overexpression of pchAB enhances ACV levels and increases antibiotic yields.
Synthetic Analogs: Modified tripeptides can alter antibiotic activity profiles.

Side Effects
Since ACV Tripeptide is not used clinically but only in laboratory research, its safety profile is largely experimental.
Observed in Research
Stable and non-toxic under standard laboratory conditions.
Does not show pharmacological activity in mammalian cells.
Potential Risks
May act as an irritant if inhaled or exposed to skin/eyes.
Handling requires gloves and protective equipment.
Long-term effects are not established as it is not intended for human administration.
Laboratory Safety Notes
Classified as for research use only.
Avoid ingestion or injection.
Dispose of according to institutional chemical waste protocols.
Disclaimer
This product is intended for research purposes only. ACV Tripeptide is not approved for clinical use in humans or animals.
Keywords
ACV Tripeptide, CAS 32467-88-2, penicillin biosynthesis precursor, cephalosporin biosynthesis, ACV synthase, pchAB gene, β-lactam antibiotics research, non-ribosomal peptide synthesis, fungal secondary metabolism, antibiotic precursor peptide.
Shipping Guarantee
We provide secure international delivery:
Customs-Cleared & Tax-Inclusive shipping available.
100% Compensation for transit damage or loss.
Trackable and Efficient Delivery worldwide.
Transaction Guarantee
We support multiple safe payment methods:
T/T bank transfer
PayPal
Cryptocurrency (BTC, ETH, USDT, etc.)
More available on request
Ensuring a safe, transparent, and convenient procurement process.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 56 × 23 × 56 cm |
1 review for ACV Tripeptide | CAS No. 32467-88-2
What is ACV Tripeptide?
It is a tripeptide composed of aminoadipic acid, cysteine, and valine, and the key biosynthetic precursor of penicillin and cephalosporins.
What is its CAS number?
32467-88-2.
Where is ACV Tripeptide found?
In fungi such as Penicillium chrysogenum and Acremonium chrysogenum.
Which enzyme synthesizes ACV Tripeptide?
ACV synthase, encoded by the pchAB gene.
Why is ACV Tripeptide important?
It is the central intermediate in the biosynthesis of β-lactam antibiotics.
Is ACV Tripeptide active as a drug?
No, it is a biosynthetic precursor used in research.
How is it analyzed?
By HPLC and mass spectrometry validation.
What are its applications?
Metabolic engineering, antibiotic research, fungal genetics, synthetic biology.
Is it stable?
Yes, stable for 12 months at -20°C.
Is it toxic?
No significant toxicity has been reported; research use only.
Can it be synthesized artificially?
Yes, it can be chemically synthesized for laboratory studies.















Giolou –
the packaging was secure and professionally