No products in the cart.
Sale
Amphomycin – High Purity Lipopeptide Antibiotic for Research
Original price was: $20.00.$16.00Current price is: $16.00.
Amphomycin is a potent lipopeptide antibiotic with 97.28% purity, produced under GMP standards. It blocks peptidoglycan synthesis and bacterial cell wall formation, demonstrating activity against MRSA, VRE, and drug-resistant pathogens. Supplied for laboratory research use only. Wholesale and retail options available.?If you need to place an order or inquire about wholesale product prices, specifications and uses, please contact our staff?
Description
Amphomycin (CAS No. 1402-82-0) is a naturally occurring lipopeptide antibiotic first discovered for its broad-spectrum antibacterial properties. Its chemical structure includes a lipid tail conjugated to a peptide core, allowing it to integrate into bacterial membranes and interfere with cell wall biosynthesis. Amphomycin primarily inhibits the formation of peptidoglycan, a critical polymer that maintains bacterial cell wall integrity, thereby preventing bacterial proliferation and inducing bactericidal effects.
The mode of action of Amphomycin is highly selective for Gram-positive bacteria, particularly those with multi-drug resistance profiles. It demonstrates potent antibacterial activities against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), penicillin-gentamicin-erythromycin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae, and linezolid-quinupristin-dalfopristin-resistant enterococci. This unique spectrum positions Amphomycin as a critical molecule in preclinical antibiotic research and drug development studies.
Amphomycin’s lipopeptide structure facilitates strong membrane interaction, enhancing its antibacterial efficacy while minimizing off-target effects in bacterial research models. The compound is supplied as a lyophilized powder, maintaining stability under controlled storage conditions, ensuring reproducibility and reliability in experimental protocols.
Produced under GMP standards, comes with a certified purity of 97.28%, making it suitable for advanced microbiology, infectious disease, and pharmacology research. Its stability profile allows storage at -20°C under inert atmosphere, with protection from moisture and light. Amphomycin is available for both wholesale and retail, enabling research laboratories and institutions to access high-quality material for in vitro and in vivo investigations.
Laboratory Use Only: is not intended for human or veterinary use. All handling should follow appropriate biosafety and chemical safety protocols.
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Amphomycin |
| Synonyms | Lipopeptide Antibiotic Amphomycin |
| CAS Number | 1402-82-0 |
| Molecular Type | Lipopeptide |
| Purity | 97.28% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Lyophilized powder |
| Stability | Stable at -20°C; protect from light and moisture |
| Storage | Store at -20°C under inert atmosphere |
| GMP Compliance | Produced in GMP-certified facility |
| Application | Laboratory research on antibiotic resistance, bacterial cell wall synthesis, and multi-drug resistant pathogens |
| Availability | Wholesale & retail supply |
Mechanism of Action & Research Applications
Amphomycin is a highly selective lipopeptide antibiotic that exerts its antibacterial effect through inhibition of peptidoglycan biosynthesis. Peptidoglycan, a polymer of sugars and amino acids, provides structural rigidity to bacterial cell walls. By blocking its synthesis, Amphomycin compromises the structural integrity of Gram-positive bacteria, leading to cell lysis.
Mechanism of Action
Peptidoglycan Inhibition: Amphomycin binds to the lipid II intermediate, an essential component in cell wall biosynthesis, preventing incorporation into the growing peptidoglycan chain.
Membrane Interaction: Its lipid tail anchors into bacterial membranes, disrupting membrane-associated processes essential for cell wall assembly.
Bactericidal Activity: Inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis leads to cell wall destabilization, resulting in bacterial death.
Selective Targeting: Amphomycin preferentially targets Gram-positive bacteria and multi-drug resistant strains, while exhibiting minimal interaction with mammalian membranes in controlled experimental models.
Research Applications
Amphomycin is widely applied in preclinical and laboratory research for multiple purposes:
Antibiotic Resistance Studies: Evaluation of mechanisms behind MRSA, VRE, and resistant S. pneumoniae, enabling the development of next-generation antibacterial therapies.
Microbiology and Infectious Disease Models: Amphomycin is used to model bacterial infections and test antimicrobial efficacy in vitro and in vivo.
Cell Wall Biosynthesis Research: Investigations into peptidoglycan assembly, lipid II dynamics, and bacterial membrane processes.
Drug Development: Screening potential derivatives and conjugates to overcome multi-drug resistant bacterial strains.
Synergistic Studies: Evaluating Amphomycin in combination with other antibiotics to study synergistic effects and optimize therapeutic strategies.
This compound’s unique lipopeptide structure offers insight into novel antibacterial mechanisms and has inspired design of structurally related synthetic antibiotics for resistant pathogens.
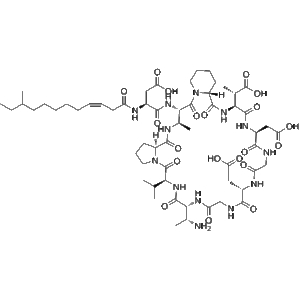
Side Effects (For Reference in Models)
In experimental models, Amphomycin demonstrates specific biological effects tied to its mechanism of action:
Membrane Interaction: Potential for disruption of bacterial membranes, which is desired for antibacterial research but requires caution in model selection.
Cytotoxicity Assessment: Amphomycin may affect bacterial cell viability rapidly; dose-dependent cytotoxicity should be carefully monitored in culture studies.
Resistance Selection Pressure: Prolonged exposure in microbial cultures can lead to selection of resistant strains, which is a key factor in experimental design.
Off-Target Effects: Minimal in mammalian cells under controlled laboratory conditions, but careful in vitro testing is recommended.
Researchers should follow standard laboratory safety procedures, use appropriate containment, and avoid any human or veterinary administration.
Disclaimer
is supplied exclusively for laboratory research use. It is not intended for human or veterinary consumption. All experiments should be conducted under appropriate biosafety protocols.
Keywords
Lipopeptide antibiotic research
VRE research compound
Multi-drug resistant bacteria research
Buy Amphomycin wholesale
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 26 × 85 × 26 cm |
1 review for Amphomycin – High Purity Lipopeptide Antibiotic for Research
What is Amphomycin?
Amphomycin is a lipopeptide antibiotic that inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis and disrupts bacterial cell wall development, widely used in laboratory research on resistant Gram-positive bacteria.
What is the CAS number of Amphomycin?
The CAS number for Amphomycin is 1402-82-0.
What is the purity of Amphomycin?
Amphomycin is supplied with a high purity of 97.28%, verified through HPLC analysis, ensuring consistent performance in experimental studies.
Which bacteria is Amphomycin effective against?
Amphomycin exhibits potent activity against MRSA, VRE, resistant S. pneumoniae, and enterococci resistant to linezolid and quinupristin-dalfopristin.
How does Amphomycin work?
Amphomycin blocks peptidoglycan synthesis and disrupts bacterial cell wall formation, leading to cell death, particularly in Gram-positive bacteria.
Can Amphomycin be used for human treatment?
No. Amphomycin is provided strictly for laboratory research purposes and is not intended for clinical use.
Is Amphomycin manufactured under GMP standards?
Yes. Amphomycin is produced in a GMP-certified facility to ensure quality, purity, and reproducibility.
How should Amphomycin be stored?
Store Amphomycin at -20°C under an inert atmosphere, protected from light and moisture, to maintain stability and activity.
Is Amphomycin available for wholesale supply?
Yes, Amphomycin is available in both wholesale and retail quantities for research laboratories and academic institutions.
What experimental applications is Amphomycin suitable for?
Amphomycin is suitable for studies on multi-drug-resistant bacteria, bacterial cell wall biosynthesis, synergistic antibiotic research, and preclinical infectious disease models.

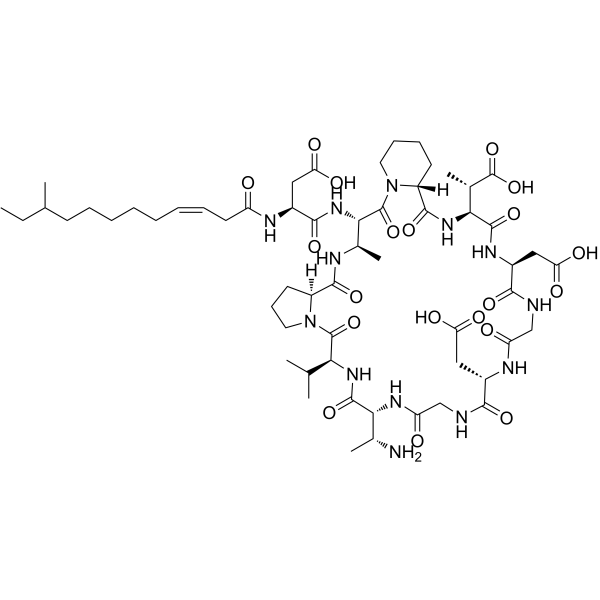












Fancy –
This touched me,thanks