No products in the cart.
Sale
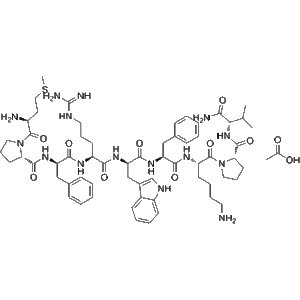
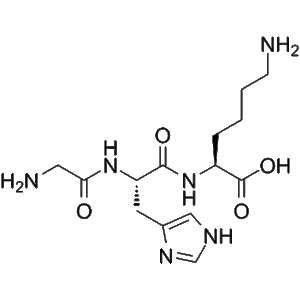
B7-33 | CAS 1818415-56-3 | RXFP1 Agonist and Anti-Fibrotic Relaxin Mimetic
Original price was: $46.00.$28.00Current price is: $28.00.
B7-33 is a selective relaxin receptor 1 (RXFP1) agonist that mimics the endogenous hormone relaxin. As a novel anti-fibrotic peptide, B7-33 activates pERK signaling and offers cardioprotective and anti-fibrotic effects.
Description
Contents
hide
Product Description
B7-33 is a single-chain relaxin mimetic peptide that functions as a selective agonist of the relaxin family peptide receptor 1 (RXFP1). It was rationally designed to mimic the biological actions of human relaxin-2 (H2 relaxin), a peptide hormone known for its potent anti-fibrotic, vasodilatory, and cardioprotective properties.
Unlike natural H2 relaxin, which is a two-chain peptide connected by disulfide bridges, B7-33 adopts a simplified single-chain structure. This modification enhances its synthetic stability, cost-efficiency, and bioavailability, while maintaining receptor selectivity.
Structural and Functional Background
Relaxin signaling through RXFP1 regulates fibrosis, inflammation, and tissue remodeling. The B7-33 peptide was developed to retain the beneficial effects of relaxin but minimize its complexity and off-target effects. By selectively activating the pERK1/2 pathway instead of the canonical cAMP pathway, B7-33 achieves targeted anti-fibrotic outcomes without triggering hormonal side effects.
B7-33 has demonstrated efficacy in reducing fibrosis, improving cardiac function, and promoting endothelial repair across several preclinical models.
Key Research Applications
Anti-Fibrotic Studies: Inhibits myofibroblast differentiation, decreases collagen synthesis, and reverses established fibrosis.
Cardioprotection: Enhances myocardial recovery following ischemic injury, attenuates remodeling, and reduces cardiac hypertrophy.
Vascular Research: Promotes endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activation, improving vascular tone and compliance.
Inflammation Modulation: Reduces inflammatory cytokine release and oxidative stress markers in fibrotic tissues.
B7-33 represents a next-generation relaxin analog that combines molecular simplicity with pharmacological potency, providing researchers with a valuable tool for investigating fibrosis, cardiovascular dysfunction, and tissue regeneration.
Product Specifications
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Name | B7-33 |
| CAS Number | 1818415-56-3 |
| Synonyms | Relaxin mimetic B7-33, RXFP1 agonist peptide, Single-chain relaxin analog |
| Chemical Class | Peptide hormone mimetic |
| Molecular Target | RXFP1 (Relaxin receptor 1) |
| Mechanism | Selective pERK pathway activation via RXFP1 |
| Molecular Formula | Peptide (sequence-based) |
| Molecular Weight | Approx. 3–4 kDa |
| Appearance | White lyophilized powder |
| Purity | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, PBS, or DMSO |
| Storage Conditions | –20°C, desiccated and light-protected |
| Stability | Stable ≥2 years under recommended conditions |
| Applications | Fibrosis, cardiac injury, vascular research |
| Safety Level | For research use only |
| QC Verification | HPLC, Mass spectrometry, peptide mapping |
Mechanism of Action
1. RXFP1 Receptor Activation
B7-33 is a selective agonist of the relaxin family peptide receptor 1 (RXFP1), a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) expressed in fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and cardiomyocytes. Unlike native relaxin, which robustly activates adenylyl cyclase and increases cAMP, B7-33 preferentially activates ERK1/2 signaling with minimal cAMP involvement.
This biased agonism allows pathway-specific pharmacology: B7-33 triggers the pERK–NO–MMP axis, which mediates antifibrotic and vasoprotective effects, while avoiding unnecessary hormonal or reproductive effects associated with traditional relaxins.
2. Anti-Fibrotic Signaling
Through RXFP1 activation, B7-33 suppresses TGF-β1–induced myofibroblast differentiation and collagen type I/III synthesis, key drivers of fibrosis. The peptide enhances matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) expression, particularly MMP-2 and MMP-9, which promote extracellular matrix degradation.
In cardiac and pulmonary fibroblast models, B7-33 reduces α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expression, restoring tissue elasticity and preventing scar tissue formation.
3. Cardioprotective Pathways
In ischemia–reperfusion injury models, B7-33 improves myocardial relaxation, reduces infarct size, and enhances left ventricular ejection fraction. Mechanistically, this is achieved through ERK-mediated eNOS activation, resulting in nitric oxide (NO) generation, vasodilation, and oxidative stress reduction.
B7-33 also mitigates cardiac hypertrophy by regulating connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) and collagen turnover genes, leading to improved cardiac compliance.
4. Anti-Inflammatory and Cytoprotective Mechanisms
B7-33 inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and MCP-1, while promoting anti-inflammatory mediators like IL-10. Additionally, it stabilizes mitochondrial function under oxidative conditions, protecting cardiomyocytes from apoptosis.
5. Signal Bias and Selectivity
The hallmark of B7-33 is its biased agonism—it selectively triggers pERK1/2 phosphorylation without robustly activating cAMP or PI3K-AKT pathways. This makes it an ideal research probe to study GPCR signal bias, fibrosis regulation, and tissue remodeling mechanisms.
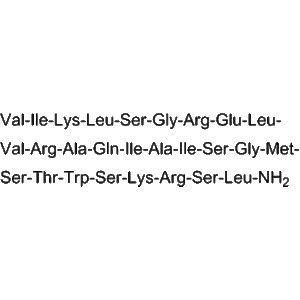
Side Effects
B7-33 is used exclusively in research settings, but based on mechanistic and animal model data, several potential effects have been observed:
Vasodilation: Due to enhanced NO signaling, transient decreases in vascular resistance may occur in vivo.
Hypotension: Observed at supraphysiological doses in preclinical models.
Hormone Cross-Activity: Minimal cross-reactivity with other relaxin receptors (e.g., RXFP2) has been reported, but remains minor.
Mild Edema: Linked to increased vascular permeability in isolated cases.
Reduced Collagen Deposition: A desired antifibrotic effect but may alter tissue stiffness in long-term cultures.
Researchers are advised to titrate concentrations based on target cell type and signaling readouts.
Disclaimer
For research use only. Not for human or veterinary use, diagnosis, or treatment.
Keywords
CAS No 1818415-56-3, Relaxin mimetic, RXFP1 agonist, ERK pathway activator, anti-fibrotic peptide, cardioprotective agent, biased agonist, fibrosis research, vascular protection, peptide hormone analog.
Shipping Guarantee
All products are shipped with full insurance coverage against loss or damage, and customs clearance support is included.
Transaction Guarantee
We provide secure payment options including T/T, PayPal, and cryptocurrency. Contact our support team for details.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.7 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 58 × 48 × 58 cm |
What is B7-33?
B7-33 is a single-chain relaxin mimetic that acts as a selective RXFP1 agonist with anti-fibrotic and cardioprotective functions.
What is the CAS number for B7-33?
CAS No. 1818415-56-3.
How does B7-33 differ from human relaxin?
B7-33 is a simplified single-chain analog that preferentially activates pERK rather than cAMP signaling.
What are the main applications of B7-33?
Fibrosis, cardiovascular injury, endothelial repair, and GPCR signaling research.
What is its mechanism of action?
B7-33 binds to RXFP1 and selectively triggers the pERK–NO–MMP signaling axis.
Is B7-33 a natural peptide?
No, it is a synthetic analog designed to mimic relaxin activity.
What diseases can it be used to model?
Heart failure, pulmonary fibrosis, hepatic fibrosis, and vascular disorders.
What is the molecular target of B7-33?
The relaxin receptor RXFP1.
How should B7-33 be stored?
At –20°C, desiccated, and protected from light.
What solvents are suitable?
Water, PBS, or DMSO.
Does it have hormonal side effects?
Minimal; it avoids reproductive effects typically associated with relaxin.
Is it suitable for clinical use?
No, it is strictly for research use only.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.