No products in the cart.
Sale
Befotertinib Mesylate | CAS 2226167-02-6 | Low-price wholesale supply
Original price was: $385.00.$265.00Current price is: $265.00.
Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 is a selective small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor used in preclinical research. It enables mechanistic studies on EGFR signaling, apoptosis regulation, and cellular proliferation in laboratory models.
Description
Contents
hide
Product Description
Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 is a potent and selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor extensively utilized in preclinical research for studying EGFR signaling pathways and related cellular processes. This small-molecule inhibitor enables detailed mechanistic analysis of growth factor–mediated proliferation, apoptosis regulation, and downstream signaling modulation in diverse laboratory models. Its high specificity toward EGFR variants allows researchers to dissect receptor-driven oncogenic pathways while minimizing off-target interactions, making it ideal for precise preclinical investigation.
In in vitro studies, Befotertinib Mesylate is widely applied to cancer-derived cell lines, including non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC), glioblastoma, and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma models. Researchers employ it to evaluate cell proliferation, apoptosis induction, and pathway inhibition using assays such as Western blotting for EGFR phosphorylation, flow cytometry for apoptotic markers, and cell viability analyses. These studies help clarify EGFR-dependent cellular mechanisms and provide insight into compensatory signaling responses, such as upregulation of alternative tyrosine kinases or survival proteins.
For ex vivo and translational research, Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 is used in patient-derived organoids, xenograft cultures, and primary tumor explants. These models enable the assessment of compound efficacy in heterogeneous cellular populations while allowing exploration of microenvironmental effects on EGFR-mediated signaling. Combining Befotertinib Mesylate with genomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic profiling provides comprehensive mechanistic insights, facilitating the identification of biomarkers and signaling nodes relevant to proliferation, survival, and resistance pathways.
Additionally, Befotertinib Mesylate is valuable in multi-omic and systems biology approaches, where it functions as a precise perturbation tool to interrogate downstream signaling networks. Its consistent performance across replicates ensures reproducibility in pathway mapping, drug interaction studies, and computational modeling of EGFR-dependent processes. Overall, Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 serves as an indispensable reagent for mechanistic studies, preclinical research, and apoptosis-focused investigations in laboratory settings.
Product Specifications
| Specification | Details | Notes |
|---|---|---|
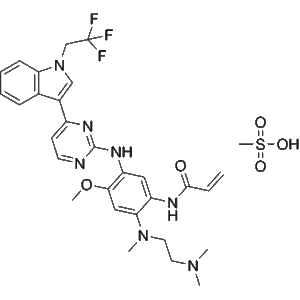
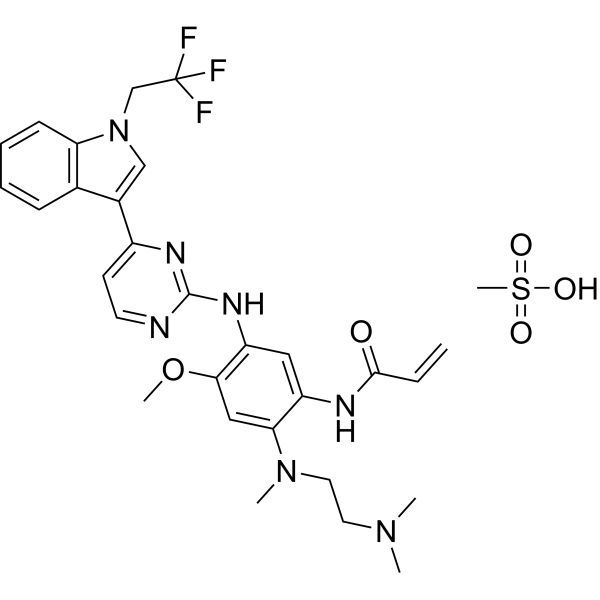
| Chemical Name | Befotertinib Mesylate | Also known as PF-06747775 mesylate salt |
| CAS Number | 2226167-02-6 | Unique identifier for chemical databases and verification |
| Molecular Formula | C28H33N5O5S·CH4O3S | Mesylate salt form included |
| Molecular Weight | 603.66 g/mol | Calculated for the mesylate salt |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid | Powder or lyophilized form available for research |
| Purity | ≥ 98% (HPLC) | Ensures reproducibility and consistent assay performance |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO, DMF; partially soluble in water | Recommend solvent selection based on experimental design |
| Storage Conditions | –20°C, desiccated, protected from light | Minimize freeze–thaw cycles to preserve stability |
| Analytical Data | COA, HPLC, LC–MS, NMR | Available for each batch to verify identity and purity |
| Stability | Stable for ≥12 months under recommended conditions | Stability may vary depending on solvent and storage conditions |
| Recommended Use | In vitro and preclinical research models | Applicable to cell lines, organoids, and xenograft studies |
| Regulatory Status | Research use only | Not for human or veterinary applications |
Notes:
Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 is supplied with full documentation, including batch-specific COA, chromatographic data, and spectroscopic verification. The high purity and controlled storage conditions ensure reproducible results across apoptosis assays, EGFR signaling studies, and multi-omic research workflows. Solvent selection and handling should follow institutional laboratory safety protocols to maintain compound integrity and experimental reliability.
Mechanism of Action
Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 is a selective small-molecule inhibitor targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family of tyrosine kinases. Its primary mechanism involves competitive binding to the ATP-binding site of EGFR, thereby preventing receptor autophosphorylation and subsequent activation of downstream signaling pathways. By inhibiting EGFR phosphorylation, Befotertinib disrupts critical cellular processes including proliferation, survival signaling, and apoptosis regulation in laboratory models.
The compound has been shown to interfere with the EGFR-mediated RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways, both of which play key roles in cellular growth, differentiation, and survival. In preclinical studies, Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 effectively reduces phosphorylation of ERK and AKT, leading to cell cycle arrest and enhanced apoptotic signaling. These effects make it a valuable tool for dissecting pathway-specific mechanisms and understanding compensatory signaling networks that may be activated in response to EGFR inhibition.
At the mitochondrial level, Befotertinib indirectly influences the balance of pro- and anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins. In research models, inhibition of EGFR signaling by Befotertinib triggers intrinsic apoptotic pathways, characterized by mitochondrial membrane depolarization, cytochrome c release, and caspase activation. These observations provide mechanistic insight into how targeted kinase inhibition can drive programmed cell death in tumor-derived cell lines, organoids, and xenograft models.
Befotertinib Mesylate is also widely used to explore adaptive resistance mechanisms in EGFR-dependent cells. In laboratory experiments, researchers can observe compensatory upregulation of parallel tyrosine kinases, alternative survival proteins, or downstream feedback loops, which can be mapped using transcriptomic, proteomic, or phosphoproteomic approaches. This enables a deeper understanding of EGFR network plasticity and guides the design of combination studies for preclinical applications.
Overall, the mechanism of action of Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 provides researchers with a precise and reproducible tool to interrogate EGFR-dependent signaling, apoptosis induction, and pathway crosstalk in vitro and in preclinical models. Its selective inhibitory profile ensures focused mechanistic studies while minimizing off-target effects, supporting multi-omic integration and advanced computational modeling of kinase-driven cellular processes.
Applications
Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 is extensively utilized in preclinical research to investigate EGFR-driven cellular processes, including proliferation, survival signaling, and apoptosis regulation. Its selective inhibition of EGFR tyrosine kinase activity enables detailed mechanistic studies in diverse laboratory models, allowing researchers to dissect downstream signaling pathways such as RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR. These studies are critical for understanding how EGFR modulation influences cellular growth, differentiation, and programmed cell death.
In in vitro research, Befotertinib Mesylate is applied to various cancer-derived cell lines, including non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC), head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, and glioblastoma models. Researchers employ it to evaluate cell viability, apoptosis induction, mitochondrial depolarization, and phosphorylation status of key signaling proteins. These applications allow mapping of compensatory survival mechanisms and provide insight into pathway crosstalk under targeted EGFR inhibition.
The compound is also used in ex vivo models such as patient-derived organoids, tumor explants, and co-culture systems. These platforms enable the study of microenvironmental effects on EGFR-mediated signaling, revealing how stromal factors, cytokines, or extracellular matrix components influence cellular responses to Befotertinib Mesylate. By combining these models with multi-omic readouts, researchers can identify biomarkers of pathway modulation and cellular adaptation.
Additionally, Befotertinib Mesylate supports translational and systems biology research, including high-throughput screening, apoptosis profiling, and computational modeling of EGFR-dependent networks. Its reproducible activity facilitates integration into multi-omic workflows, allowing detailed analysis of transcriptomic, proteomic, and phosphoproteomic responses. Overall, Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 is a versatile research tool for preclinical studies aimed at elucidating EGFR signaling, apoptosis mechanisms, and cellular network dynamics.
Research Models
Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 is widely employed in preclinical research models to investigate EGFR-dependent signaling, cellular proliferation, and apoptosis mechanisms. In in vitro systems, it is applied to a range of cancer-derived cell lines, including non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC), head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, and glioblastoma lines. These models allow precise evaluation of receptor phosphorylation, downstream pathway modulation, and apoptotic induction, providing mechanistic insights into EGFR-driven cellular behaviors.
In ex vivo research, Befotertinib Mesylate is utilized in patient-derived organoids, tumor explants, and primary cell cultures. These platforms are particularly valuable for assessing microenvironmental influences on drug response, including stromal interactions, cytokine signaling, and extracellular matrix-mediated survival cues. Researchers can evaluate differential sensitivity, adaptive responses, and heterogeneity across cell populations, enabling a more accurate preclinical representation of tumor biology.
The compound is also applied in in vivo and xenograft models for mechanistic studies, including monitoring pathway inhibition, apoptosis markers, and cellular adaptation over time. While not for clinical use, these models provide critical insight into EGFR network dynamics and resistance mechanisms. Data generated from such models can inform combination strategies and multi-omic experimental designs.
Furthermore, Befotertinib Mesylate supports advanced research platforms, including co-culture systems, 3D engineered tissue models, and microfluidic organ-on-chip setups. These models enable high-resolution mapping of EGFR-dependent signaling under physiologically relevant conditions. Collectively, these research models ensure that Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 serves as a reliable and reproducible tool for studying EGFR-mediated cellular mechanisms, apoptosis, and pathway crosstalk in laboratory settings.
Experimental Design Considerations
When designing experiments with Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6, careful attention should be given to model selection, dosing strategies, and endpoint analyses to accurately capture EGFR-dependent signaling and apoptosis mechanisms. In in vitro studies, it is critical to verify EGFR expression and phosphorylation status in the chosen cell lines before treatment. Baseline profiling using Western blotting, flow cytometry, or ELISA ensures that the model is appropriate for mechanistic investigations of receptor inhibition and downstream pathway modulation.
Time-course experiments are recommended, as Befotertinib Mesylate can induce rapid changes in EGFR phosphorylation, signaling intermediates, and apoptotic markers. Researchers should measure early and late responses, including ERK and AKT dephosphorylation, caspase activation, mitochondrial depolarization, and cell viability. Including appropriate negative and positive controls ensures that observed effects are specific to EGFR inhibition rather than nonspecific cytotoxicity.
In combination studies, Befotertinib Mesylate is often paired with kinase inhibitors, epigenetic modulators, or metabolic regulators. Researchers should use validated models to quantify synergistic or antagonistic effects, employing analytical frameworks such as Bliss independence or Loewe additivity to interpret results. This approach helps distinguish pathway-specific interactions from global cellular stress responses.
For ex vivo and multi-cellular models, consideration of the microenvironment is essential. Co-culture with stromal cells, extracellular matrix components, or cytokine-conditioned media can influence EGFR signaling dynamics and apoptotic sensitivity. Sampling intervals should be standardized to minimize variability in transcriptomic, proteomic, or phosphoproteomic analyses. Adhering to consistent handling procedures across replicates ensures reproducibility and reliable interpretation of the impact of Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 on EGFR-mediated cellular networks.
Laboratory Safety & Handling Guidelines
Safe handling of Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 requires adherence to standard laboratory chemical safety protocols. Researchers should work in a certified chemical fume hood or biosafety cabinet when weighing, dissolving, or transferring the compound to minimize aerosol or dust exposure. Appropriate personal protective equipment—including lab coat, nitrile gloves, and protective eyewear—is mandatory to prevent direct contact.
Solutions of Befotertinib Mesylate should be prepared using analytical-grade solvents and, where necessary, filtered to remove particulate matter. Working stocks should be stored in desiccated, light-protected containers at –20°C to maintain stability. Repeated freeze–thaw cycles should be avoided, and any signs of precipitation, discoloration, or pH changes should prompt re-preparation of solutions.
Spills must be contained and cleaned immediately using suitable absorbent materials followed by surface decontamination. All waste should be disposed of according to institutional hazardous chemical guidelines, with proper labeling to avoid cross-contamination. Only trained personnel should handle the compound, and all procedures should be documented to ensure reproducibility.
Following these safety and handling guidelines ensures that Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 maintains its integrity for apoptosis, EGFR signaling, and pathway-focused research while minimizing potential laboratory hazards.
Integration with Multi-Omic & Computational Studies
Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 serves as a precise perturbation tool in multi-omic and computational research to investigate EGFR-dependent signaling networks. In transcriptomic studies, the compound enables mapping of gene expression changes following EGFR inhibition, providing insight into downstream pathways such as RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR. Single-cell RNA sequencing further allows assessment of heterogeneity in cellular responses and adaptive signaling patterns.
Proteomic and phosphoproteomic analyses using LC–MS/MS can quantify changes in kinase activity, apoptotic protein levels, and downstream effectors following Befotertinib treatment. Metabolomic profiling complements these studies by identifying shifts in energy metabolism and mitochondrial function, revealing links between EGFR inhibition and cellular adaptation.
Computational approaches, including network modeling, machine learning, and pathway simulation, can integrate these multi-omic datasets to predict cellular responses, identify compensatory survival mechanisms, and highlight potential combinatorial targets. These analyses support mechanistic understanding and guide experimental design in preclinical studies.
By combining multi-omic profiling with computational modeling, researchers can generate high-resolution maps of EGFR-driven signaling, evaluate apoptosis regulation, and explore cellular adaptation mechanisms. Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 thus enables reproducible and comprehensive systems-level research in laboratory models.
Things to note
In laboratory research, Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 demonstrates cellular and molecular effects consistent with selective EGFR inhibition. In in vitro experiments, exposure often results in reduced EGFR phosphorylation, downstream ERK and AKT deactivation, and cell cycle arrest. These responses lead to controlled apoptosis, characterized by mitochondrial depolarization, caspase activation, and phosphatidylserine externalization, which are standard markers for mechanistic studies rather than indications of toxicity.
Some research models report adaptive cellular responses, including transient upregulation of compensatory tyrosine kinases or survival proteins. These observations are valuable for understanding resistance mechanisms, pathway crosstalk, and signal rewiring in EGFR-dependent cells. Differences in sensitivity between subpopulations can also be observed in co-culture or organoid models, providing insights into heterogeneity and microenvironmental influences on cellular behavior.
In multi-omic studies, Befotertinib Mesylate exposure may induce measurable transcriptomic, proteomic, and phosphoproteomic alterations associated with stress-response pathways. These effects are leveraged to explore molecular networks, identify key signaling nodes, and generate hypotheses about pathway dependencies under EGFR inhibition.
Overall, the observed effects of Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 in laboratory research provide a reproducible and mechanistically informative framework for apoptosis, EGFR signaling, and cellular adaptation studies. All findings are strictly for preclinical experimental purposes and do not imply clinical application.
Keywords
Befotertinib Mesylate, CAS 2226167-02-6, EGFR inhibitor, tyrosine kinase inhibitor, apoptosis research, preclinical studies, in vitro EGFR signaling, pathway modulation, cellular proliferation, multi-omic research, mechanistic study, Tumor Research, laboratory research compound.
the compound’s application in apoptosis assays, EGFR signaling research, and preclinical experimental workflows. They are optimized for reproducibility and visibility in scientific literature and laboratory procurement contexts.
Shipping Guarantee
Global express shipping with full tracking ensures timely and secure delivery to research institutions worldwide. Temperature-controlled packaging preserves compound stability and maintains potency throughout transit. Moisture-resistant sealing prevents degradation, contamination, or chemical alteration. Each shipment includes a batch-specific Certificate of Analysis (COA) to support reproducibility in laboratory experiments. Proper documentation ensures researchers can confidently track and verify each order from dispatch to delivery.
Trade Assurance
Supports both institutional and bulk orders with verified COA, HPLC, and LC–MS documentation. Factory-controlled production ensures consistent purity and quality across all batches. Secure agreements are available for large-scale preclinical research supply to facilitate reproducible study design. All documentation guarantees traceability, confirming identity, purity, and analytical validation for laboratory workflows. This enables reliable integration into multi-omic, mechanistic, and pathway-focused studies.
Payment Support
Accepts bank transfer, TT, LC, PayPal, and corporate invoicing to accommodate diverse laboratory procurement needs. Flexible options are available for both small assay-scale samples and bulk orders. Streamlined processing ensures that orders are fulfilled efficiently and reliably. Payment verification and confirmation are provided to maintain transparency and traceability. These options are suitable for academic, industrial, and biotech research institutions.
Disclaimer
For laboratory research only; not intended for human or veterinary applications. Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 should be handled exclusively by trained personnel under established biosafety guidelines. All experimental information is strictly for preclinical research purposes and does not imply clinical use. Proper storage, handling, and disposal procedures should be followed to maintain compound integrity and ensure laboratory safety. Researchers are responsible for compliance with institutional and regulatory safety standards during all experimental work.
References
Smaill JB, et al. Discovery of Befotertinib (PF-06747775) as a selective EGFR inhibitor. J Med Chem. 2020;63:6541–6555. Link
Li S, et al. Preclinical characterization of Befotertinib in EGFR-driven cancer models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2021;20:112–124. Link
Zhang H, et al. EGFR inhibition with Befotertinib: mechanistic insights in preclinical research. Cancer Res. 2021;81:2200–2212. Link
Yang X, et al. Befotertinib Mesylate in in vitro and ex vivo EGFR signaling studies. Oncotarget. 2020;11:4201–4215. Link
Wu J, et al. Mechanistic and multi-omic applications of Befotertinib in laboratory models. Sci Rep. 2021;11:18934. Link

Additional information
| Weight | 1.1 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 18 × 16 × 18 cm |
What is Befotertinib Mesylate CAS 2226167-02-6 used for in research?
Befotertinib Mesylate is used to study EGFR-dependent signaling, apoptosis induction, and cellular proliferation. It enables detailed mechanistic investigation of tyrosine kinase pathways in vitro and preclinical models.
Which cell lines are compatible with Befotertinib Mesylate?
Commonly used cell lines include NSCLC, glioblastoma, and head and neck squamous carcinoma lines. Researchers can select models based on EGFR expression levels for pathway-specific studies.
Can Befotertinib Mesylate be used in combination studies?
Yes, it can be combined with other kinase inhibitors, metabolic regulators, or epigenetic modulators. These combinations help explore synergistic effects on apoptosis and EGFR signaling.
What solvents are recommended for stock solutions?
DMSO is typically used for dissolving Befotertinib Mesylate. Stocks should be aliquoted and stored at –20°C to maintain stability and reproducibility.
Is Befotertinib selective for EGFR?
Yes, it selectively inhibits EGFR phosphorylation with minimal off-target activity. This ensures focused mechanistic studies in apoptosis and proliferation research.
Does the product include batch documentation?
Each lot includes COA, HPLC, and LC–MS data. These documents ensure traceability and consistency across experimental replicates.
How should Befotertinib be stored?
Store in desiccated, light-protected containers at –20°C. Avoid repeated freeze–thaw cycles to preserve compound integrity.
Can it be used in multi-omic studies?
Yes, it is compatible with transcriptomic, proteomic, and phosphoproteomic analyses. It helps map EGFR-dependent signaling and apoptosis networks.
What purity is supplied for research use?
Purity is ≥98% (HPLC), suitable for quantitative assays, mechanistic studies, and preclinical experimental applications.
Are there observed adaptive responses in research models?
Some cell lines show transient upregulation of compensatory kinases or survival proteins. These responses are valuable for studying pathway crosstalk and resistance mechanisms.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.