No products in the cart.
Sale
Biotin-Bradykinin (CAS No. 477319-71-4) | Biotin-Labeled Bioactive Peptide
Original price was: $36.00.$22.00Current price is: $22.00.
Biotin-Bradykinin (CAS No. 477319-71-4) is a biologically active, biotin-labeled peptide derived from Bradykinin. It is widely used in receptor-binding assays, imaging, and molecular interaction studies. Research use only.
Description
Product Description
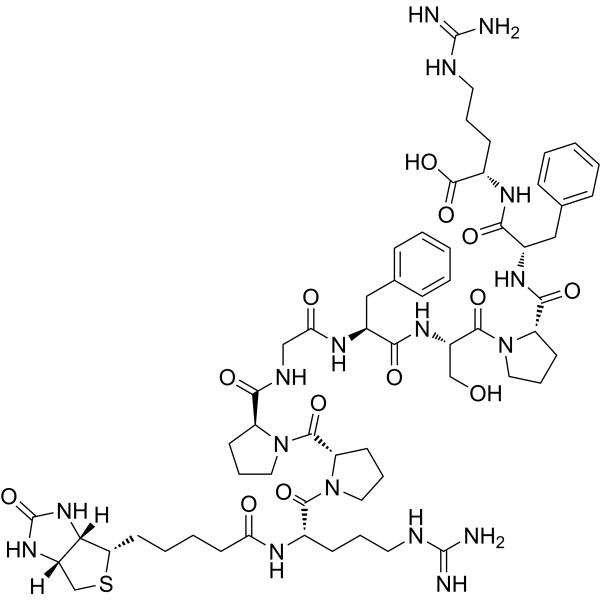
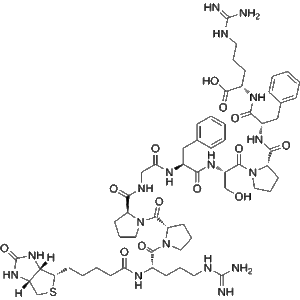
Biotin-Bradykinin (CAS No. 477319-71-4), also referred to as Biotin-HY-P0206, is a synthetic biotin-conjugated derivative of the vasoactive peptide Bradykinin. Bradykinin itself is a well-characterized nonapeptide involved in vasodilation, vascular permeability, pain modulation, and smooth muscle contraction. By conjugating biotin to Bradykinin, researchers gain a powerful molecular tool that combines the bioactivity of the parent peptide with the molecular tracking capability of biotin labeling.
Bradykinin plays a central role in the kallikrein-kinin system, a complex enzymatic cascade responsible for regulating vascular tone, inflammatory responses, and tissue homeostasis. It exerts its effects primarily via B1 and B2 receptors, both of which are G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). The Bradykinin–receptor axis has been linked to physiological processes such as blood pressure regulation, renal function, nociception, and inflammatory signaling. In addition, it has been implicated in pathological conditions ranging from asthma and angioedema to hypertension and cancer.
The biotinylation of Bradykinin represents a key advancement for research methodology. Biotin, a small vitamin (vitamin B7, also known as vitamin H), exhibits high-affinity binding to streptavidin and avidin. This property is widely exploited in biochemical assays, imaging systems, and protein interaction studies. By attaching biotin to Bradykinin, scientists can track peptide–protein interactions, perform receptor localization experiments, and integrate Bradykinin into high-sensitivity detection platforms.
Applications in Research Methodologies
Biotin-Bradykinin serves as a hybrid tool with dual roles: it retains the biological activity of Bradykinin and adds the biotin handle for biochemical manipulation. This makes it particularly valuable in the following contexts:
Receptor-binding assays: Biotin-Bradykinin can be used to study B1 and B2 receptor distribution and binding affinity in different tissues.
Pull-down experiments: The biotin tag allows immobilization of Bradykinin for identifying receptor complexes or interacting proteins.
Imaging and localization studies: When paired with fluorescently labeled streptavidin, Biotin-Bradykinin can be visualized in cellular or tissue environments.
Drug screening platforms: Biotinylated peptides help evaluate antagonists and agonists targeting the Bradykinin pathway.
The peptide’s dual function makes it an attractive tool in pharmacological research, particularly in studying diseases where Bradykinin signaling is dysregulated. For instance, angioedema—a condition associated with excessive Bradykinin activity—can be better understood through receptor visualization and tracking experiments. Similarly, hypertension and pain modulation research benefit from real-time monitoring of receptor–ligand interactions.
Advantages Over Native Bradykinin
While native Bradykinin is biologically potent, its small size and rapid degradation by kininases (such as angiotensin-converting enzyme, ACE) limit its experimental utility. The biotinylated version provides the same receptor-binding capacity but introduces a stable and versatile molecular tag. This not only facilitates detection but also enables integration into diverse bioanalytical platforms.
In addition, biotinylation does not significantly impair Bradykinin’s biological activity. Depending on the site of biotin conjugation, the peptide retains high affinity for its receptors while remaining detectable in complex environments such as serum, tissue lysates, or cell culture systems.
Broader Research Context
The development of biotin-labeled peptides like Biotin-Bradykinin reflects the broader trend in peptide research: enhancing biological molecules with chemical modifications that expand their utility. From fluorophore conjugates to isotope labeling, such modifications enable researchers to probe deeper into cellular and molecular mechanisms.
In this sense, Biotin-Bradykinin is not only a bioactive peptide but also a biochemical probe, bridging pharmacology and molecular biology. Its relevance extends to drug discovery, receptor pharmacology, cardiovascular research, and inflammatory disease modeling.
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Biotin-Bradykinin |
| CAS Number | 477319-71-4 |
| Synonyms | Biotin-HY-P0206 |
| Category | Biotinylated peptide derivative |
| Molecular Formula | C66H101N19O15S |
| Molecular Weight | 1384.7 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to off-white lyophilized powder |
| Purity | ≥95% (HPLC confirmed) |
| Sequence | Bradykinin sequence with biotin conjugation |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, PBS, and aqueous buffers |
| Stability | Stable for months in lyophilized form at -20°C |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C; avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles |
| Applications | Receptor-binding assays, imaging, protein–peptide interaction studies |
| Labeling | Biotin tag for streptavidin/avidin-based detection |
| Availability | Research grade; available in bulk quantities for laboratories |
Extended Commentary on Specifications
The molecular formula reflects the presence of sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen-rich moieties, consistent with both peptide and biotin structures. The high molecular weight relative to unmodified Bradykinin indicates the successful conjugation of the biotin group.
Its purity (≥95%) is a crucial parameter for reproducible results in sensitive receptor studies. High purity ensures minimal background noise in biochemical assays, especially in pull-down experiments where contaminants can interfere with protein–ligand binding.
The lyophilized powder form enhances stability and shipping efficiency. Researchers can reconstitute Biotin-Bradykinin in aqueous buffers, and its solubility ensures compatibility with a wide range of in vitro and ex vivo assays.
Mechanism of Action & Research Applications
Mechanism of Action
Biotin-Bradykinin exerts its biological effects by binding to B2 receptors under normal physiological conditions and B1 receptors under pathological conditions (such as tissue injury and inflammation). Both receptors are GPCRs, initiating signaling cascades that influence vascular permeability, vasodilation, and nociception.
B2 receptor signaling: Ubiquitously expressed, mediates vasodilation, smooth muscle contraction, and pain sensation.
B1 receptor signaling: Induced during inflammation, associated with chronic pain and immune responses.
The addition of the biotin tag allows researchers to track and quantify these interactions in real time. For instance, streptavidin-based fluorescence can be used to visualize receptor localization, internalization, and recycling upon Bradykinin stimulation.
Research Applications
Cardiovascular Research
Biotin-Bradykinin is invaluable in the study of blood pressure regulation, endothelial function, and vascular permeability. By tracking receptor distribution in blood vessels, researchers gain insights into hypertension and vasodilatory disorders.Inflammatory Diseases
Since Bradykinin is a key mediator of inflammation, the biotinylated version is used to explore pathways in asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and rheumatoid arthritis.Pain Mechanisms
Pain modulation is one of Bradykinin’s hallmark effects. Biotin-Bradykinin enables localization studies of pain receptors and their role in hyperalgesia and allodynia.Oncology Research
Elevated Bradykinin signaling has been implicated in tumor microenvironments, particularly in angiogenesis and tumor-associated inflammation. Biotin-Bradykinin can serve as a probe in cancer models to study receptor expression in tumors.Drug Discovery and Screening
As a biotinylated ligand, Biotin-Bradykinin is compatible with high-throughput screening platforms. It can help identify potential inhibitors, antagonists, or allosteric modulators of the Bradykinin receptor system.Protein–Peptide Interaction Studies
Using pull-down assays, Biotin-Bradykinin allows the identification of receptor-associated proteins, scaffolding molecules, and downstream effectors.
Side Effects
As with native Bradykinin, the biotinylated derivative is associated with specific biological activities that may lead to observable side effects in research models:
Vasodilation: May cause hypotension in animal studies due to strong vascular relaxation.
Increased vascular permeability: Leads to edema formation in certain experimental conditions.
Smooth muscle contraction: May result in bronchoconstriction or intestinal motility changes.
Pain induction: Bradykinin is a known pain mediator, so enhanced nociceptive responses may be observed.
Immune activation: Inflammatory cascades may be upregulated, complicating long-term studies.
Experimental Considerations
The addition of biotin does not eliminate Bradykinin’s side effects but may alter its pharmacokinetics. Care must be taken in dose selection and monitoring of experimental endpoints. Researchers should account for the possibility of exaggerated vascular or nociceptive responses, especially when testing in vivo systems.
Disclaimer
For laboratory research use only. Not for human or veterinary applications.
Keywords
Biotin-Bradykinin CAS 477319-71-4, Biotin-HY-P0206, Bradykinin biotinylated peptide, Bradykinin receptor ligand, peptide–protein interaction, vasodilator peptide research, GPCR binding peptide, inflammation pathway peptide
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 53 × 26 × 53 cm |
1 review for Biotin-Bradykinin (CAS No. 477319-71-4) | Biotin-Labeled Bioactive Peptide
What is Biotin-Bradykinin?
It is a biotin-labeled derivative of Bradykinin, used for receptor-binding and molecular tracking.
What is the CAS number?
CAS No. 477319-71-4.
What is the molecular weight?
1384.7 g/mol.
What are its main applications?
Cardiovascular, pain, inflammation, oncology, and receptor-binding research.
How is it stored?
Lyophilized at -20°C; avoid repeated freeze-thaw.
Does it retain biological activity?
Yes, biotinylation preserves Bradykinin’s receptor-binding properties.
What are potential side effects?
Vasodilation, edema, pain induction, smooth muscle contraction.
Is it suitable for pull-down assays?
Yes, the biotin tag is designed for streptavidin/avidin-based pull-down.
Is it used clinically?
No, it is for laboratory research only.
What receptors does it target?
Bradykinin B1 and B2 receptors.













sanchez –
Fast processing and careful packaging. Very pleased with this order.