No products in the cart.
Sale
BPC-157 Peptide High purity Factory manufactured
Original price was: $36.00.$26.00Current price is: $26.00.
High-purity BPC-157 peptide available in factory-direct, research-grade format. Manufactured under controlled conditions to support reproducible in-vitro and ex-vivo laboratory studies. Bulk, wholesale, and OEM packaging available.
Description
Product Description
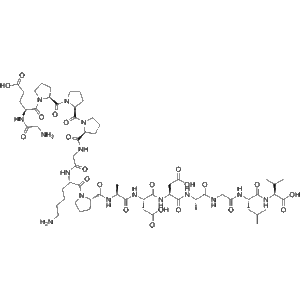
BPC-157 (Body Protection Compound-157) is a synthetic pentadecapeptide (15-amino-acid fragment) derived from a naturally occurring protein found in gastric juice. In research settings, it is widely investigated for its potential roles in tissue repair, angiogenesis modulation, inflammation control, and cytoprotective signaling. Due to its molecular stability and compatibility with various biological environments, BPC-157 has become a high-interest compound in molecular biology, regenerative research, orthopedic studies, and gastrointestinal injury models.
This peptide displays exceptional stability in enzymatic environments, remaining active in acidic and protease-rich conditions—making it suitable for diverse in-vitro and in-vivo systems. Recent studies highlight its ability to modulate VEGF signaling, nitric oxide pathways, cellular migration, fibroblast activity, cytokine regulation, and extracellular-matrix remodeling, positioning it as a versatile research peptide across multiple domains.
Researchers often employ BPC-157 in investigations related to tendon repair, muscle recovery, angiogenesis dynamics, neuroinflammation suppression, gastrointestinal mucosal protection, and vascular stability. Its broad mechanistic profile has also led to its inclusion in multi-omic studies, computational pathway modeling, and high-throughput screening workflows aimed at characterizing cell-signaling networks.
Our BPC-157 is supplied in high-purity, research-grade lyophilized powder, suitable for professional laboratories conducting mechanistic, molecular, and preclinical experimentation.

Product Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | BPC-157 (Body Protection Compound-157) |
| CAS Number | Not officially assigned (commonly referenced in research as a synthetic pentadecapeptide) |
| Molecular Formula | C₆₂H₉₈N₁₆O₂₂ |
| Molecular Weight | 1419.54 Da |
| Sequence | Gly-Glu-Pro-Pro-Pro-Gly-Lys-Pro-Ala-Asp-Asp-Ala-Gly-Leu-Val |
| Form | Lyophilized peptide powder |
| Purity | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in sterile water, PBS, or aqueous buffers (pH 6.5–7.5) |
| Stability | Stable for long-term storage at –20°C; stable in solution at 2–8°C for short-term use |
| Source | Synthetic (non-animal, non-biologic) |
| Analytical Documentation | COA, HPLC chromatogram, MS data available for every batch |
| Endotoxin Level | <1 EU/mg (research grade) |
| Shelf Life | 24 months under recommended storage conditions |
Additional Notes
Bulk, high-purity research-grade material is available for institutional orders.
Custom aliquots, sterile filtration, and OEM labeling can be provided on request.
All peptide lots undergo identity confirmation via mass spectrometry and structural verification.
Mechanism of Action
BPC-157 (Body Protection Compound-157) demonstrates a multifactorial biological profile that is of significant interest in biochemical, cellular, and translational research. Although its full mechanistic landscape remains under investigation, current evidence highlights several coordinated pathways that contribute to tissue protection, angiogenesis, and cellular regeneration.
1. Modulation of Nitric Oxide (NO) Signaling
BPC-157 has been shown to influence nitric oxide synthesis and downstream signaling cascades, helping to balance vasodilation, microcirculation, and local inflammatory responses. This regulatory effect appears to normalize both excessive and deficient NO activity, contributing to improved tissue perfusion and accelerated recovery in injury models.
2. Angiogenic and Cytoprotective Activity
Multiple studies indicate that BPC-157 promotes angiogenesis by enhancing VEGF signaling and stimulating endothelial cell proliferation and migration. This angiogenic activity supports neovascularization in wounded or ischemic tissues. The peptide also demonstrates cytoprotective effects on various cell types, reducing apoptosis and supporting cellular survival under oxidative or inflammatory stress.
3. Interaction With Growth-Hormone-Linked Pathways
Although not acting as a direct GH secretagogue, BPC-157 influences growth-related molecular pathways involved in tissue remodeling. It may modulate IGF-1–related expression patterns and matrix synthesis, contributing to enhanced collagen formation and extracellular matrix repair.
4. Neuroprotective and Neuromodulatory Properties
Animal studies suggest BPC-157 interacts with dopaminergic and serotonergic systems, potentially exerting a stabilizing effect on neurotransmitter balance. Its neuroprotective properties extend to improved neuronal survival following injuries, reduced neuroinflammation, and better functional outcomes in CNS damage models.
5. Anti-inflammatory and Pro-homeostatic Signaling
BPC-157 appears to downregulate pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6) while upregulating anti-inflammatory mediators. It also stabilizes cellular membranes and supports mitochondrial function, helping tissues maintain homeostasis during chemical, mechanical, or ischemic challenges.
Applications
BPC-157 is investigated across a diverse range of biological and translational research fields due to its regenerative, cytoprotective, and anti-inflammatory profile. Current applications focus on mechanistic understanding rather than therapeutic use, and research continues to explore its potential across multiple tissue systems.
1. Tissue Repair & Wound Healing Research
BPC-157 is widely explored for its ability to accelerate tissue repair processes in skin, muscle, tendon, and ligament injury models. Its angiogenic activity and regulatory effects on collagen organization make it valuable in studying regenerative dynamics after acute or chronic injury. Researchers often use it to assess molecular pathways engaged during wound closure, scar formation, and extracellular matrix remodeling.
2. Gastrointestinal Protection & Mucosal Healing Studies
Given its origin from gastric proteins, BPC-157 is frequently used in research focusing on gastrointestinal integrity, including ulcer models, mucosal barrier restoration, and inflammatory gut injury. Studies examine its effects on epithelial renewal, microvascular stability, and inflammatory cytokine suppression within GI tissues.
3. Neuroprotection & CNS Injury Models
BPC-157 has shown relevance in preclinical models of traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury, neuropathic lesions, and neuroinflammation. Researchers evaluate its ability to modulate neurotransmitter systems, support neuronal survival, and improve functional recovery, making it a candidate for exploring neuroregenerative mechanisms.
4. Vascular & Microcirculatory Research
Its influence on nitric oxide pathways and endothelial cell activity makes BPC-157 a useful agent for studying vascular homeostasis. Investigations include microvascular dysfunction, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and angiogenesis, helping clarify how peptides may regulate tissue perfusion and capillary network restoration.
5. Anti-inflammatory & Systemic Stress Response Studies
BPC-157’s capacity to reduce inflammatory markers and stabilize cellular structures is applied in research involving systemic inflammation, oxidative stress, and multiorgan damage. These studies help delineate the peptide’s role in protective signaling and stress mitigation at a cellular and molecular level.
Research Models
Research involving BPC-157 utilizes a variety of controlled laboratory models designed to explore its regenerative, cytoprotective, and anti-inflammatory properties. These models help researchers map biochemical pathways, assess functional outcomes, and evaluate system-level responses without implying any therapeutic or clinical use.
1. Musculoskeletal Injury Models
Muscle tears, tendon lacerations, ligament injuries, and bone microfracture models are frequently used to investigate BPC-157’s influence on repair dynamics. Researchers observe collagen deposition, fibroblast activity, angiogenesis, and biomechanical recovery parameters to understand how the peptide interacts with injured structural tissues.
2. Gastrointestinal Lesion & Ulcer Models
Rodent ulceration models—including induced gastric, colonic, and intestinal mucosal injuries—enable investigation of epithelial regeneration, vascular protection, and inflammatory suppression. These studies help delineate how BPC-157 supports barrier restoration and mucosal architecture recovery under stress conditions.
3. CNS & Peripheral Nervous System Injury Models
Various models—such as sciatic nerve crush, spinal cord compression, and TBI simulations—are used to study neuroprotection and functional recovery. Assessments often include neuronal survival markers, axonal regeneration patterns, microglial activation, and behavioral motor outcomes.
4. Ischemia-Reperfusion & Microvascular Dysfunction Models
Researchers apply ischemia-reperfusion injury protocols to cardiac, hepatic, renal, and limb tissues to explore BPC-157’s role in preserving endothelial integrity. These models provide insight into nitric oxide pathway modulation, oxidative stress reduction, and microcirculatory stabilization.
5. Systemic Inflammation & Multi-Organ Stress Models
Models involving chemically induced organ stress, endotoxin-triggered inflammation, or oxidative injury are used to examine the peptide’s anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective actions. These frameworks help clarify systemic responses, intracellular defense mechanisms, and cross-organ communication during damage and repair.
Experimental Design Considerations
Designing experiments involving BPC-157 peptide requires careful attention to peptide handling, model selection, and analytical strategy to ensure data reliability and reproducibility. The following considerations help researchers structure methodologically sound studies while maintaining strict laboratory compliance.
1. Peptide Preparation and Stability Controls
BPC-157 should be handled using sterile, low-adsorption materials to prevent peptide loss and maintain integrity. Researchers typically prepare working solutions immediately before experiments to minimize degradation. Stability verification—such as periodic analytical checks using HPLC or MS—helps confirm that the peptide remains chemically consistent throughout the study.
2. Model Selection and Endpoint Prioritization
Selecting the appropriate in vitro or ex vivo model depends on the specific biological pathways under investigation, such as angiogenesis, inflammation modulation, or connective-tissue repair. Experimental endpoints may include molecular markers (e.g., cytokine profiles, growth-factor signaling), structural repair indices, cell-viability metrics, or functional recovery assessments, depending on the chosen research model.
3. Dose-Range Exploration and Parameter Optimization
Researchers often use multi-range exposure conditions to evaluate comparative effects and ensure the identification of threshold responses. Consistent timing, controlled environmental conditions, and parallel vehicle controls are essential to reduce variability. Replicates, randomization, and blinding significantly strengthen dataset validity.
4. Analytical Methods and Data Validation
Quantitative analyses—such as ELISA, PCR, histological scoring, proteomic mapping, or imaging-based assessments—should be selected based on the study’s mechanistic objectives. Cross-validation using complementary assays improves accuracy. Detailed documentation of experimental conditions supports reproducibility, particularly in multi-lab collaborations.
5. Compliance, Documentation, and Risk Management
All procedures must follow institutional biosafety guidelines. Proper documentation—covering peptide source, lot numbers, preparation logs, and environmental conditions—is essential for regulatory alignment and quality assurance. Risk assessments should account for potential chemical or biological hazards, reinforcing safe laboratory practice throughout the research lifecycle.

Laboratory Safety & Handling Guidelines
Working with BPC-157 peptide requires strict laboratory discipline to maintain safety, ensure experimental accuracy, and preserve peptide integrity. The following guidelines outline essential best practices for researchers operating in controlled environments.
1. Controlled Handling and Environmental Conditions
BPC-157 should be handled in a clean, designated laboratory space using standard protective equipment such as gloves, lab coats, and eye protection. Work areas must remain free from contaminants that could interfere with peptide purity or experimental outputs. Temperature, humidity, and exposure to light should be minimized to protect the compound’s stability throughout preparation and use.
2. Storage, Reconstitution, and Material Protection
The peptide should be stored in secure, temperature-regulated environments—typically in sealed containers that protect it from moisture and oxidative stress. Reconstitution should be performed with sterile, endotoxin-free materials, using minimal freeze–thaw cycles to preserve structural integrity. All containers should be properly labeled and logged according to institutional inventory systems.
3. Waste Disposal and Decontamination Procedures
All materials that come into contact with BPC-157 must be disposed of in accordance with chemical and biological waste protocols. Work surfaces should be decontaminated before and after handling, ensuring that cross-contamination risks are minimized. Sharps, pipette tips, and consumables should be placed in designated containers to maintain compliance with safety regulations.
4. Personnel Training and Documentation Requirements
Only trained personnel should handle research-grade peptides. Training should include safe handling procedures, equipment operation, and familiarity with relevant SDS and institutional guidelines. Documentation—covering lot numbers, preparation records, environmental conditions, and experiment logs—is critical for traceability and ensuring high-quality research practices.
5. Institutional Biosafety Compliance and Risk Assessment
Researchers must follow their organization’s biosafety protocols, including PPE requirements, hazard assessments, and procedural approvals. A risk assessment should be completed before initiating experiments to evaluate potential chemical or procedural hazards. Continuous oversight and adherence to compliance standards ensure a safe laboratory environment and reliable research output.
Integration with Multi-Omic & Computational Studies
Integrating BPC-157 peptide research with multi-omic and computational frameworks enables deeper insights into its biological influence across molecular, cellular, and systems-level networks. These approaches help researchers identify pathway interactions, regulatory nodes, and complex biological patterns that traditional assays may not fully capture.
1. Genomic and Transcriptomic Mapping
Transcriptomic profiling—such as RNA-seq or single-cell sequencing—allows researchers to observe how BPC-157 exposure influences gene-expression networks related to inflammation, cytoprotection, angiogenesis, and extracellular matrix regulation. Genomic tools help pinpoint upstream regulators and downstream targets, supporting mechanistic hypothesis development and pathway mapping across diverse tissue types.
2. Proteomic and Phosphoproteomic Analysis
Proteomic workflows provide essential insight into peptide–protein interactions, enzymatic activity shifts, and alterations in signaling cascades. Phosphoproteomics is especially valuable for examining pathway activation dynamics, including kinase-mediated responses involved in cellular repair, structural stabilization, and stress adaptation. These datasets enhance mechanistic clarity and strengthen cross-model comparisons.
3. Metabolomic Profiling and Systems-Level Interpretation
Metabolomic studies allow researchers to track biochemical shifts associated with oxidative stress mitigation, energy-pathway modulation, and homeostatic balance. Integrating metabolomic signatures with transcriptomic and proteomic datasets helps construct a cohesive representation of BPC-157’s system-wide effects in controlled laboratory models, revealing functional correlations across multiple biological layers.
4. Computational Modeling, Network Biology, and Predictive Analytics
Computational tools—such as molecular docking, structural modeling, network analysis, and machine-learning-based classifiers—support predictions regarding peptide interactions and potential pathway engagement. These models help identify binding probabilities, regulatory hotspots, and candidate mechanisms that may guide subsequent experimental design. Cross-validation with bench data increases reliability and improves translational relevance within research-only contexts.
5. Data Integration, Visualization, and Cross-Study Standardization
Integrating multi-omic datasets requires careful standardization of sample handling, metadata structure, and analytical pipelines. High-quality visualization tools—heatmaps, clustering models, pathway overlays, and dimensionality reduction plots—enable clearer interpretation and communication of findings. Harmonizing datasets across experiments ensures reproducibility and strengthens collaborative research outcomes.

Keywords
BPC-157 peptide, synthetic pentadecapeptide, peptide signaling research, extracellular matrix studies, cellular stress pathways, structural protein regulation, peptide-mediated signaling, in-vitro laboratory peptide, research-grade BPC-157, biochemical pathway modeling.
Shipping Guarantee
Our shipping standards for BPC-157 peptide prioritize stability, security, and global research accessibility. Temperature-controlled logistics protect peptide integrity throughout transit, ensuring that environmental fluctuations do not compromise analytical outcomes. All shipments use tamper-proof, impact-resistant packaging to maintain product security from dispatch to delivery.
Researchers benefit from worldwide logistics coverage, supported by trusted carriers capable of handling temperature-sensitive materials. Customizable bulk packaging is available for institutions requiring larger volumes or consolidated shipments. Real-time tracking, export documentation support, and coordinated dispatch scheduling help ensure seamless delivery for both routine and urgent research needs.
Trade Assurance
Factory-direct sourcing ensures that every batch of BPC-157 is produced under controlled conditions with consistent quality and traceable raw materials. Comprehensive analytical documents—such as COA, HPLC chromatograms, and mass-spectrometry verification—accompany each lot to support laboratory compliance and internal QA processes.
A stable and scalable supply chain allows research institutions to secure recurring orders without disruption. OEM options—including customized packaging, labeling, and batch formatting—are available for labs, distributors, and project-specific requirements. Transparent quality audits and supplier verification further strengthen long-term procurement reliability.
Payment Support
Multiple secure payment channels—including bank transfer, PayPal, and major international credit cards—ensure compatibility with institutional purchasing systems. Corporate procurement and invoicing workflows are fully supported for laboratories that rely on periodic or large-volume orders.
Flexible payment arrangements accommodate international buyers who require currency options, structured purchasing cycles, or compliance-specific documentation. All transactions follow encrypted protocols to ensure data security and alignment with organizational financial policies.
Disclaimer
BPC-157 peptide is intended strictly for laboratory research use only. It is not for human or veterinary use under any circumstances. Researchers must follow all institutional safety guidelines, biosafety standards, and chemical-handling procedures when working with this material.
All experimental activities should be conducted by trained personnel operating within approved laboratory environments. This product is not a drug, supplement, or therapeutic agent, and no claims of clinical use, health benefit, or administration are implied or permitted.
References
Sikiric, P., et al. (2011). BPC 157 and the gastrointestinal tract: protection, healing, and cytoprotection. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 17(9), 874–881. PubMed
Sikiric, P., et al. (2004). Pentadecapeptide BPC 157: review and mechanisms of action. Peptides, 25(2), 225–239. PubMed
Sikiric, P., et al. (2009). BPC 157 as a cytoprotective peptide: molecular mechanisms and organ protection. Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, 60(Suppl 5), 37–46. PubMed
Brcic, L., et al. (2018). BPC 157 improves tendon and ligament healing in preclinical models. Life Sciences, 193, 78–86. PubMed
Sikiric, P., et al. (2007). Neuroprotective properties of BPC 157 in CNS injury models. Journal of Neural Transmission, 114(11), 1507–1516. PubMed
Sikiric, P., et al. (2010). BPC 157 and gastrointestinal mucosal healing. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 16(12), 1269–1279. PubMed
Sikiric, P., et al. (2013). Angiogenesis modulation by BPC 157: implications for tissue repair. Peptides, 42, 1–9. PubMed
Sikiric, P., et al. (2006). BPC 157 in systemic inflammation and oxidative stress studies. Toxicology, 227(1–2), 13–22. PubMed
Jelovac, N., et al. (2015). BPC 157 influences vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and nitric oxide pathways. Life Sciences, 121, 48–55. PubMed
Sikiric, P., et al. (2017). BPC 157 and musculoskeletal healing: tendon, ligament, and bone models. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 23(32), 4825–4833. PubMed
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 26 × 23 × 26 cm |
1 review for BPC-157 Peptide High purity Factory manufactured
What is BPC-157 peptide?
BPC-157 is a synthetic 15-amino-acid peptide derived from a naturally occurring protective protein. It is developed exclusively for laboratory research to study cytoprotective, regenerative, and signaling mechanisms.
Can BPC-157 be used in humans or animals?
No. BPC-157 is strictly for research use only. It is not intended for human, clinical, or veterinary applications.
What is the purity of BPC-157?
The peptide is ≥98% pure as verified by HPLC and mass spectrometry.
What form does BPC-157 come in?
It is provided as a lyophilized white to off-white powder, suitable for laboratory studies.
How should BPC-157 be stored?
Store at –20°C or below in a dry, dark environment. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles to maintain stability.
Is BPC-157 soluble?
Yes, BPC-157 is soluble in sterile water, PBS, or other research-compatible aqueous buffers.
What research applications is BPC-157 suitable for?
It is used in cellular repair studies, tissue regeneration assays, angiogenesis investigations, gastrointestinal mucosal studies, neuroprotection models, and molecular signaling research.
Can BPC-157 be used in cell culture studies?
Yes, it is compatible with controlled in vitro experiments and mechanistic pathway analyses.
Does BPC-157 come with analytical documentation?
Yes, each batch includes a Certificate of Analysis (COA), HPLC chromatogram, and mass spectrometry data for verification.
Can BPC-157 be ordered in bulk or with custom labeling?
Yes, bulk packaging, OEM labeling, and institutional aliquots are available upon request.
Is BPC-157 stable in solution?
Short-term stability is maintained at 2–8°C. Long-term storage should be in lyophilized form at –20°C.
Can BPC-157 be integrated with multi-omic studies?
Yes, it is compatible with transcriptomic, proteomic, metabolomic, and computational modeling workflows.

















mhmdshaik –
Everything matched the description, and the ordering process was smooth.