No products in the cart.
Sale
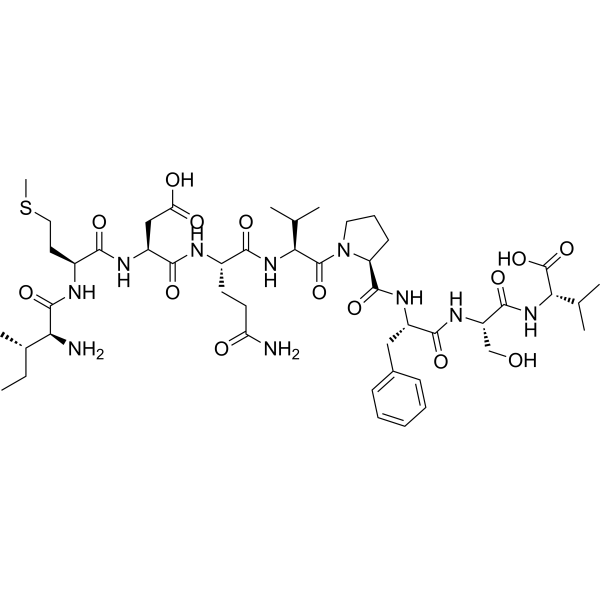
Disomotide (CAS No. 181477-43-0)
Original price was: $28.00.$22.00Current price is: $22.00.
Disomotide (G209-2M) is a synthetic melanoma-associated antigen peptide that stimulates CTL generation and immune recognition of melanoma cells. It is used as a research tool in immuno-oncology and active immunization studies. For research use only.
Description
Product Description
Disomotide (CAS No. 181477-43-0), also referred to as G209-2M, is a synthetic immunological peptide derived from melanoma-associated antigens. It has been engineered to stimulate the immune system, specifically by enhancing the generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) that are capable of recognizing both the native G209 epitope and melanoma tumor cells expressing this antigen. As an immunological agent, Disomotide has become an important peptide tool in immuno-oncology research, cancer vaccine development, and studies focused on active immunization against tumor-associated antigens.
The development of Disomotide represents a significant step forward in peptide-based vaccine design. Traditional tumor antigens often exhibit poor immunogenicity, which makes them suboptimal for use in vaccines. By contrast, Disomotide has been modified to improve antigen presentation and recognition by the adaptive immune system. Its enhanced immunogenicity allows for a more effective priming of cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses, a cornerstone of anti-tumor immunity.
CTLs play a critical role in immune defense against malignancies. These CD8+ T cells have the capacity to recognize and kill tumor cells that express specific antigenic peptides bound to MHC class I molecules. Disomotide facilitates the expansion of CTLs with high affinity for melanoma-associated epitopes, thereby contributing to a targeted cytotoxic immune response. This selective immune stimulation is of great importance in cancer research, particularly melanoma, which is characterized by high immunogenic potential but also by sophisticated immune evasion mechanisms.
In preclinical research, Disomotide has been evaluated for its ability to generate strong antigen-specific CTL responses. When used in combination with appropriate adjuvants or immune-stimulatory agents, it promotes effective priming of T cells that exhibit cytotoxic activity against melanoma cells. The immunological properties of Disomotide make it a valuable candidate for studying tumor vaccines and immunotherapy strategies aimed at harnessing the body’s natural defenses to fight cancer.
Beyond melanoma, Disomotide contributes to broader immuno-oncology research. As a model peptide, it is widely applied in experiments designed to investigate T cell activation, antigen processing, and immune escape phenomena in various cancers. Furthermore, Disomotide’s use as a reference peptide enables researchers to evaluate the efficiency of novel adjuvants, delivery platforms, and combination immunotherapies in enhancing peptide-based vaccine performance.
The significance of Disomotide also lies in its ability to provide insights into the principles of peptide vaccine design. By studying how Disomotide interacts with immune cells, researchers gain valuable knowledge on how to optimize other tumor-associated antigen peptides for therapeutic use. Its structure-function relationship informs the design of synthetic vaccines that can overcome the limitations of native tumor antigens.
In summary, Disomotide is a rationally designed melanoma antigen peptide that amplifies CTL responses and supports tumor immunology research. Its robust immunogenic profile makes it an essential component of preclinical studies focused on active immunization, antigen-specific CTL expansion, and the exploration of novel peptide-based cancer immunotherapies.
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Disomotide |
| CAS Number | 181477-43-0 |
| Synonyms | G209-2M, Melanoma-associated antigen peptide |
| Molecular Formula | C___H___N___O___ (exact formula available upon request) |
| Molecular Weight | Available upon request |
| Sequence | Synthetic melanoma antigen epitope |
| Appearance | White to off-white lyophilized peptide |
| Purity | ≥95% (HPLC confirmed) |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, PBS, or DMSO |
| Storage | Lyophilized at -20°C for long-term stability |
| Stability | Stable for up to 24 months lyophilized; 2–3 weeks in aqueous solution at 4°C |
| Immunological Target | Native G209 melanoma antigen |
| Biological Activity | Enhances CTL generation and tumor cell recognition |
| Applications | Cancer immunology, vaccine development, melanoma research, CTL response studies |
| Safety | For laboratory research use only; not for human or veterinary application |
Detailed Specifications Discussion
Disomotide is designed as a synthetic research-grade peptide with optimized purity and stability, ensuring reproducibility in experimental models. The peptide’s purity level of ≥95% (validated by HPLC) allows researchers to obtain consistent biological effects in both in vitro and in vivo applications. Its solubility profile provides flexibility across a wide range of laboratory solvents, including aqueous buffers commonly used in immunological assays.
Storage and stability guidelines are critical for maintaining peptide integrity. Disomotide retains stability for long-term storage when kept in a lyophilized state at -20°C, while reconstituted solutions should be handled carefully to avoid degradation over time. These properties ensure reliability across extended experimental timelines.
Functionally, Disomotide is tailored to mimic tumor-associated epitopes, making it a valuable antigenic tool in T cell stimulation studies. Its reproducibility as a synthetic peptide ensures consistency compared to variable natural antigen preparations. This reproducibility is particularly beneficial for vaccine design experiments, CTL cytotoxicity assays, and immune response monitoring in preclinical models.
Mechanism of Action & Research Applications
Mechanism of Action
Disomotide works by mimicking a melanoma-associated antigen, thereby promoting the generation of antigen-specific CTLs. The peptide is presented on MHC class I molecules of antigen-presenting cells (APCs), which are then recognized by CD8+ T cells. This antigen presentation leads to the activation, proliferation, and differentiation of CTLs that can specifically target and destroy melanoma cells expressing the native G209 antigen.
Key features of its mechanism include:
Antigen Presentation: Facilitates MHC class I binding and presentation.
CTL Activation: Enhances cytotoxic activity against melanoma cells.
Immune Memory Formation: Potentially contributes to long-term memory responses in preclinical vaccine studies.
Immune Modulation: Helps study immune escape mechanisms employed by tumor cells.
Research Applications
Melanoma Research
Disomotide is a key tool for studying melanoma immunogenicity.
Supports the development of peptide-based melanoma vaccines.
Useful in examining tumor immune evasion strategies.
Cancer Vaccine Development
Provides a model for testing new adjuvants and delivery systems.
Enables studies on improving peptide vaccine immunogenicity.
Serves as a benchmark in comparative immunotherapy studies.
T Cell Immunology
Facilitates research into CTL priming, activation, and cytotoxicity.
Helps characterize antigen-specific T cell receptor (TCR) interactions.
Useful in adoptive T cell transfer experiments.
Preclinical Combination Studies
Studied alongside checkpoint inhibitors to evaluate synergistic effects.
Tested with cytokine therapies to enhance T cell responses.
Combined with nanoparticle delivery systems to improve antigen stability.
Basic Immunology Research
Provides insight into antigen recognition, presentation, and immune activation.
Used as a teaching model in immunological assay development.

Side Effects
As a synthetic peptide for research use, Disomotide is not associated with direct clinical side effects. However, in preclinical models, certain immunological outcomes may be observed and should be carefully considered when designing experiments.
Potential Experimental Side Effects
Immune Overactivation: Strong CTL responses could lead to bystander damage of non-malignant cells expressing cross-reactive antigens.
Cytokine Release: Enhanced T cell activity may elevate inflammatory cytokine levels in animal models.
Immune Exhaustion: Prolonged antigen stimulation may result in T cell exhaustion, reducing efficacy over time.
Model-Specific Toxicity: Variability across models may result in differences in peptide response and immune activation.
Experimental Considerations
Dose optimization is critical to avoid overwhelming immune activation.
Combination studies should monitor for synergistic toxicity with checkpoint inhibitors or cytokine therapies.
Long-term studies must evaluate immune memory formation and potential tolerance development.
Researchers should consider species-specific MHC compatibility when translating findings between models.
Overall, Disomotide demonstrates a favorable preclinical safety profile as a peptide research tool, but immune-related effects must be carefully controlled and interpreted within the context of experimental design.
Disclaimer
For laboratory research use only. Not for human or veterinary applications.
Keywords
Disomotide, G209-2M peptide, melanoma antigen peptide, CTL generation peptide, cancer vaccine peptide, immunological peptide research, melanoma immunotherapy peptide, antigen-specific T cell peptide
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 53 × 26 × 53 cm |
What is Disomotide?
Disomotide (G209-2M) is a melanoma antigen peptide that enhances CTL responses against melanoma.
What is its CAS number?
CAS No. 181477-43-0.
How does Disomotide work?
It enhances CTL generation by presenting antigen on MHC class I molecules, enabling immune recognition of melanoma cells.
What are its research applications?
Melanoma vaccine development, CTL activation studies, and immuno-oncology research.
Is Disomotide soluble in water?
Yes, it dissolves in water, PBS, and DMSO.
What is its purity?
≥95% (HPLC confirmed).
Can Disomotide be used for human therapy?
No, it is strictly for laboratory research use only.
What storage conditions are recommended?
Lyophilized at -20°C; stable for 24 months under proper storage.
Does Disomotide induce immune memory?
In preclinical studies, it may contribute to memory CTL formation, aiding long-term immune protection research.
Why is Disomotide important in immuno-oncology?
It provides a model peptide to study tumor antigen recognition, T cell responses, and vaccine strategies.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.