No products in the cart.
Fulzerasib 150mg High Purity | Factory Manufactured
$1.00
High-purity Fulzerasib (also known as IBI351, GFH925) is a factory-manufactured small-molecule research reagent optimized for in vitro mechanistic studies, KRAS G12C pathway inhibition analysis, and molecular signaling research. Available for bulk and wholesale laboratory use with batch-verified purity and consistent quality.
Description
Product Description
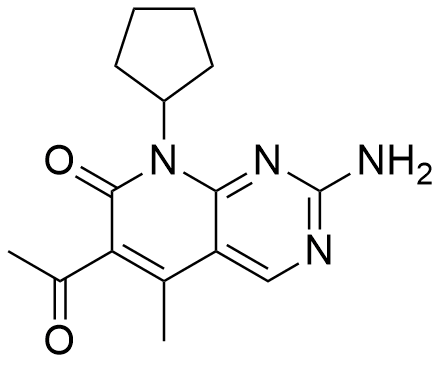
Fulzerasib is a high-purity small-molecule research reagent manufactured under strict factory quality control to support advanced in vitro mechanistic research, biochemical pathway analysis, and receptor-modulated signaling studies. Known also by its research codes IBI351 and GFH925, Fulzerasib is characterized by a potent and selective inhibitory profile against the KRAS G12C mutant protein, a key molecular driver in numerous oncogenic signaling pathways. Selleckchem
In laboratory environments, Fulzerasib facilitates investigation of mutant KRAS-dependent signaling mechanisms, enabling researchers to probe covalent binding dynamics, downstream signal transduction, and associated biochemical networks. Its high affinity for KRAS G12C enables detailed exploration of how small-molecule intervention modulates the RAS-MAPK/PI3K signaling axis, which is pivotal in many cellular regulatory processes. Synapse
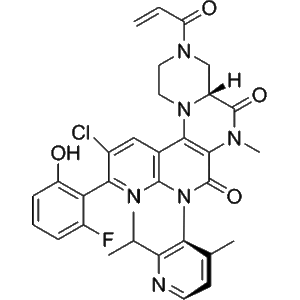
Fulzerasib’s molecular structure, a benzisoxazole-derived scaffold linked to a functional group optimized for covalent engagement, supports irreversible interaction with the KRAS G12C protein at the switch-II pocket. This covalent modification locks the protein in an inactive, GDP-bound state, preventing nucleotide exchange and subsequent activation of downstream effectors. Such mechanistic features make Fulzerasib a valuable molecular tool for dissecting structure–activity relationships (SAR), ligand–target interactions, and conformational dynamics in sophisticated in vitro workflows. Synapse
Because the KRAS G12C mutation represents a well-defined molecular target with unique biochemical properties, Fulzerasib is ideal for cell-free assays, kinase pathway screens, and protein interaction studies. Research applications include mapping downstream phosphorylation cascades, evaluating feedback regulatory circuits, and characterizing compensatory mechanisms triggered by targeted inhibition. Its reproducible activity and high purity make it suitable for high-throughput screening (HTS), quantitative imaging assays, and integrated multi-omic projects. Selleckchem
In addition to traditional biochemical assays, Fulzerasib supports computational research such as molecular docking, dynamics simulations, and predictive network analysis. High-quality experimental binding data generated with this compound can provide essential input for in silico modeling of protein–ligand interactions, helping researchers refine hypotheses and generate data-driven mechanistic insights.
Factory manufacturing ensures consistent lot homogeneity, stringent purity verification, and reliable performance, supporting long-term research initiatives and multi-lab collaborations. Each batch is verified via analytical profiling and quality testing, ensuring suitability for mechanistic and pathway-focused research without variability that can confound interpretation.
Overall, Fulzerasib serves as a robust research reagent for laboratories focused on in vitro KRAS G12C pathway interrogation, covalent inhibitor profiling, mechanistic signaling analysis, and multi-omic data integration. Its stable, high-purity formulation and wholesale availability make it an efficient and scalable choice for high-impact research programs. Selleckchem
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Fulzerasib |
| Alternative Names | IBI351, GFH925 |
| Form | Solid research-grade material (powder) |
| Purity | ≥ 98% (HPLC verified; batch-tested) |
| Grade | Laboratory research grade |
| Molecular Type | Small-molecule covalent inhibitor |
| Target (Research Context) | KRAS G12C mutant protein (mechanistic research focus) |
| Mechanistic Category | Covalent switch-II pocket binder (in vitro studies) |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO and compatible organic solvents; solubility depends on experimental conditions |
| Stability | Stable under recommended storage; suitable for long-term in vitro research use |
| Storage Conditions | Store dry, protected from light, in a sealed container at −20 °C or as specified in COA |
| Handling Requirements | Handle in controlled laboratory environments with appropriate PPE |
| Recommended Applications | KRAS G12C signaling pathway analysis, protein–ligand interaction studies, SAR research, downstream pathway mapping, multi-omic integration |
| Manufacturing Standard | Factory-manufactured with strict quality control |
| Batch Consistency | Verified batch-to-batch reproducibility |
| Packaging Options | Standard laboratory vials, bulk packaging, wholesale supply |
| Customization | Bulk quantity, labeling, and packaging customization available |
| Intended Use | Research use only; strictly for in vitro and molecular mechanism studies |
Structural & Documentation Notes
Full COA (Certificate of Analysis) available upon request
Analytical data typically include HPLC purity, identity confirmation, and batch traceability
Suitable for high-throughput screening (HTS) and long-duration mechanistic studies due to stable formulation
Mechanism of Action
Fulzerasib is a high-purity small-molecule research compound designed for in vitro investigation of mutant KRAS-driven signaling mechanisms, with a specific focus on the KRAS G12C variant. Its mechanism of action is centered on selective, covalent engagement of the KRAS G12C protein, enabling detailed exploration of mutant-specific molecular regulation within controlled laboratory systems.
At the molecular level, Fulzerasib targets the switch-II pocket of KRAS G12C, a transient and mutation-dependent binding site that becomes accessible in the GDP-bound inactive conformation of the protein. The presence of the cysteine residue at position 12 (unique to the G12C mutation) allows Fulzerasib to form a covalent bond through an electrophilic warhead, resulting in irreversible modification of the target protein. This covalent interaction stabilizes KRAS in its inactive state and prevents GDP–GTP exchange, thereby suppressing downstream signal propagation in experimental models.
By locking KRAS G12C in a GDP-bound conformation, Fulzerasib effectively disrupts activation of multiple downstream signaling cascades, including pathways commonly associated with MAPK/ERK and PI3K-related signal transduction. In an in vitro research context, this enables precise dissection of how KRAS-dependent signaling networks respond to sustained inhibition, including feedback loops, compensatory signaling routes, and pathway reprogramming phenomena.
Fulzerasib’s mechanism is particularly valuable for structure–function and structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies. The covalent binding mode allows researchers to correlate chemical structure with binding efficiency, residence time, and conformational changes in KRAS G12C. These properties support detailed biochemical analyses such as protein stability assays, binding kinetics measurements, and conformational state mapping using purified proteins or cell-free systems.
In cellular and biochemical research models, Fulzerasib serves as a tool to investigate mutant-selective signaling dependency, enabling comparisons between KRAS G12C–driven systems and wild-type or alternative mutant variants. This selectivity makes it suitable for mechanistic experiments aimed at understanding mutation-specific vulnerabilities, pathway crosstalk, and adaptive signaling behavior under sustained inhibitory pressure.
Additionally, Fulzerasib is compatible with integrated computational and experimental workflows. Experimental data derived from its covalent binding behavior can inform molecular docking, dynamics simulations, and predictive network modeling, supporting hypothesis generation and validation within systems-level research frameworks.
Overall, the mechanism of action of Fulzerasib makes it a robust molecular probe for in vitro KRAS G12C pathway interrogation, covalent inhibitor research, and advanced mechanistic studies that require high specificity, reproducibility, and molecular precision under laboratory-controlled conditions.
Applications
Fulzerasib is widely applied as a laboratory research reagent in studies focused on in vitro molecular mechanisms, signaling pathway interrogation, and mutant-specific protein regulation. Its high purity, covalent binding profile, and KRAS G12C selectivity make it particularly suitable for controlled experimental systems where precise mechanistic insights are required.
KRAS G12C Pathway Analysis
Fulzerasib is commonly used to investigate KRAS G12C–dependent signaling networks in cell-free and in vitro cellular models. By selectively inactivating the mutant KRAS protein, researchers can analyze downstream pathway modulation, including changes in phosphorylation patterns, signal amplitude, and temporal dynamics across KRAS-regulated cascades. This application supports mechanistic mapping of pathway dependencies and feedback regulation.
Protein–Ligand Interaction Studies
Due to its covalent engagement with KRAS G12C, Fulzerasib serves as a valuable tool in protein–ligand interaction research. It enables detailed examination of binding kinetics, irreversible interaction behavior, and conformational stabilization of the target protein. These studies are particularly relevant for understanding covalent inhibitor design principles and switch-II pocket accessibility under various experimental conditions.
Structure–Activity Relationship (SAR) Research
Fulzerasib is suitable for SAR investigations that explore how chemical structure influences binding efficiency, selectivity, and functional outcomes. Researchers can compare Fulzerasib with structurally related compounds to assess changes in potency, binding mode, and mechanistic impact, providing insights into rational small-molecule optimization strategies.
High-Throughput and Mechanistic Screening
In high-throughput screening (HTS) platforms, Fulzerasib is used as a reference or benchmark compound for evaluating KRAS G12C pathway modulation. Its reproducible activity profile supports assay validation, control comparisons, and screening of novel molecular entities targeting related signaling mechanisms.
Integrated Multi-Omic Experiments
Fulzerasib is compatible with transcriptomic, proteomic, and phosphoproteomic workflows, enabling researchers to study global molecular responses to KRAS G12C inhibition. These applications support system-level analysis of pathway rewiring, adaptive signaling, and molecular network modulation under controlled in vitro conditions.
Computational and Systems Biology Research
Experimental data generated using Fulzerasib can be integrated into computational modeling, molecular docking, and systems biology analyses. Such applications help refine predictive models of KRAS signaling behavior and support data-driven hypothesis testing in complex molecular systems.
Research Models
Fulzerasib is well suited for a broad range of in vitro and mechanistic research models designed to investigate KRAS G12C–driven molecular signaling, covalent inhibitor interactions, and pathway-level regulation. Its high purity and reproducible performance allow consistent use across multiple experimental platforms, supporting both exploratory and hypothesis-driven studies.
Cell-Free Biochemical Models
Fulzerasib is frequently applied in cell-free assay systems utilizing purified KRAS G12C protein. These models enable precise analysis of covalent binding kinetics, target engagement efficiency, and conformational stabilization of the inactive GDP-bound state. Techniques such as thermal shift assays, surface plasmon resonance (SPR), and mass spectrometry-based binding confirmation are commonly employed to characterize molecular interactions at high resolution.
In Vitro Cellular Models
In vitro cellular systems expressing KRAS G12C are used to examine downstream signaling modulation following Fulzerasib exposure. These models support analysis of pathway-specific readouts, including changes in phosphorylation status, protein–protein interactions, and signaling flux. Comparative studies between KRAS G12C–expressing systems and non-G12C controls enable mutation-selective mechanistic insights under controlled laboratory conditions.
Reporter and Pathway-Specific Assays
Fulzerasib is compatible with reporter-based assay systems designed to monitor activity within KRAS-regulated pathways. Luciferase or fluorescence-based reporters can be used to quantify pathway output and assess dynamic responses over time, facilitating mechanistic interpretation of signal attenuation and recovery.
High-Content Imaging Models
High-content imaging platforms allow visualization of subcellular signaling changes and protein localization patterns associated with KRAS G12C inhibition. Fulzerasib’s consistent activity supports reproducible imaging-based experiments that correlate molecular inhibition with phenotypic or structural cellular responses in vitro.
Comparative Mutant Screening Models
Fulzerasib is useful in comparative research models that include alternative KRAS mutations or wild-type variants. These systems enable detailed evaluation of mutation-specific selectivity, providing insight into differential pathway dependency and molecular vulnerability across KRAS-driven signaling contexts.
Integrated Systems-Level Models
Data generated from Fulzerasib-based experiments can be incorporated into systems biology frameworks, where multiple in vitro datasets are combined to model pathway interactions, feedback mechanisms, and network adaptation. Such models support comprehensive mechanistic understanding and guide further experimental design.
Experimental Design Considerations
When incorporating Fulzerasib into in vitro and mechanistic research workflows, careful experimental design is essential to ensure data reliability, reproducibility, and meaningful interpretation. The following considerations are intended to support laboratory-based molecular studies without reference to clinical, animal, or in vivo use.
Model Selection and Validation
Select experimental systems that are appropriate for KRAS G12C–dependent signaling analysis, such as purified protein assays or in vitro cellular models with verified KRAS mutation status. Prior validation of target expression and baseline pathway activity helps ensure that observed effects can be accurately attributed to Fulzerasib-mediated KRAS modulation.
Concentration and Exposure Parameters
Experimental concentration ranges should be determined empirically within the context of each assay platform. Pilot studies are recommended to identify conditions that produce clear mechanistic readouts without introducing assay interference or non-specific effects. Consistent exposure parameters across replicates are critical for comparative analysis.
Assay Controls and Benchmarking
Include appropriate negative and reference controls to establish assay performance and specificity. Fulzerasib can serve as a benchmark compound in KRAS G12C–focused assays, enabling comparison across experimental conditions and between related molecular entities in screening or SAR studies.
Time-Dependent Mechanistic Analysis
Because Fulzerasib engages its target through a covalent interaction, time-course experiments can provide valuable insight into binding kinetics, pathway suppression durability, and downstream signaling adaptation. Sampling at multiple time points supports a more comprehensive understanding of mechanistic dynamics.
Multiparametric Readouts
Integrating multiple readout types—such as biochemical activity, protein modification status, and pathway-specific reporters—enhances mechanistic interpretation. Multiparametric designs reduce reliance on single endpoints and improve confidence in pathway-level conclusions.
Reproducibility and Data Quality
Use batch-consistent material and standardized protocols to minimize variability. Detailed documentation of experimental conditions, including compound handling and assay setup, supports reproducibility within and across laboratories.
Data Integration and Interpretation
Interpret results within the broader context of KRAS signaling networks. Observed effects should be evaluated alongside pathway feedback mechanisms and compensatory responses to ensure mechanistic conclusions are well supported by the data.
Laboratory Safety & Handling Guidelines
Fulzerasib is supplied as a laboratory research reagent and should be handled exclusively within controlled research environments. The following guidelines are intended to support safe handling, storage, and use during in vitro and molecular mechanism studies.
General Laboratory Handling
All work involving Fulzerasib should be conducted by trained personnel following standard laboratory safety protocols. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including laboratory coats, gloves, and eye protection, when handling the material. Avoid direct contact with skin, eyes, or clothing.
Preparation and Transfer
Handle Fulzerasib in designated laboratory areas using clean, dry tools to prevent contamination. When preparing stock solutions or aliquots, use compatible laboratory-grade solvents and containers suitable for chemical research. Minimize repeated handling by preparing single-use or limited-use aliquots when possible.
Storage Conditions
Store Fulzerasib in a tightly sealed container, protected from light and moisture. Recommended storage conditions typically include low-temperature, dry environments as specified in the accompanying Certificate of Analysis (COA). Proper storage helps maintain chemical integrity and batch consistency over time.
Environmental Controls
Perform handling and preparation procedures in well-ventilated areas or appropriate containment systems, such as chemical fume hoods, to reduce exposure risk. Maintain clean workspaces and follow institutional guidelines for chemical hygiene.
Spill and Waste Management
In the event of accidental spills, follow established laboratory spill response procedures. Collect waste materials, including unused compound and contaminated consumables, according to local regulations for chemical research waste disposal. Do not release materials into the environment.
Documentation and Traceability
Maintain accurate records of compound receipt, storage conditions, and usage. Traceability supports quality assurance, reproducibility, and compliance with internal laboratory standards.
Integration with Multi-Omic & Computational Studies
Fulzerasib is well suited for integration into multi-omic and computational research frameworks aimed at elucidating KRAS G12C–driven molecular mechanisms under controlled in vitro conditions. Its high specificity and reproducible activity enable generation of high-quality datasets that support systems-level analysis and predictive modeling.
Transcriptomic Integration
In transcriptomic workflows, Fulzerasib can be used to examine gene expression changes associated with selective KRAS G12C pathway modulation. RNA-based profiling approaches enable identification of transcriptional programs linked to downstream signaling suppression, feedback regulation, and pathway adaptation. These datasets provide insight into regulatory networks influenced by mutant KRAS activity.
Proteomic and Phosphoproteomic Analysis
Fulzerasib supports proteomic and phosphoproteomic studies that map changes in protein abundance, modification status, and signaling flux following KRAS G12C inhibition. High-resolution mass spectrometry data can be used to characterize pathway-specific phosphorylation events and uncover compensatory signaling nodes within interconnected molecular networks.
Metabolomic Correlation
Although primarily used for signaling research, Fulzerasib-generated data can be correlated with metabolomic profiles to explore how KRAS-regulated pathways influence cellular metabolic states in vitro. Integrated datasets help clarify functional consequences of pathway modulation at the systems level.
Computational Modeling and Simulation
Experimental findings obtained with Fulzerasib can be incorporated into molecular docking studies, dynamics simulations, and network-based computational models. Covalent binding data are particularly valuable for refining structural models of the KRAS switch-II pocket and predicting interaction stability over time.
Data Integration and Network Analysis
Multi-omic datasets derived from Fulzerasib-based experiments can be integrated using network analysis tools to identify key regulatory hubs, signaling bottlenecks, and adaptive pathways. Such integrative approaches support hypothesis generation and guide subsequent mechanistic experiments.
Reproducible Research Pipelines
The consistency of factory-manufactured Fulzerasib supports reproducible data generation across platforms, enabling cross-study comparisons and collaborative research. Standardized compound performance enhances confidence in integrated analytical outcomes.
Keywords
Fulzerasib, KRAS G12C inhibitor, high-purity research compound, covalent small-molecule inhibitor, in vitro mechanistic studies, KRAS signaling pathway research, switch-II pocket binder, molecular mechanism analysis, protein–ligand interaction studies, structure–activity relationship research, laboratory research reagent, factory manufactured compound, low-price wholesale supply, bulk research chemical, multi-omic integration, computational modeling support, Tumor (compound) Research, pathway modulation research, batch-consistent laboratory material
Shipping Guarantee
Factory-manufactured Fulzerasib is packaged under controlled conditions to preserve chemical integrity, purity, and batch consistency during transportation. Secure, contamination-resistant packaging is used for both standard and bulk shipments. Wholesale and large-volume orders are supported with reliable logistics coordination and shipment tracking to ensure safe delivery for laboratory research use.
Trade Assurance
Direct factory supply with low-price wholesale advantages
Stable batch-to-batch quality verified by analytical documentation
Bulk order support with flexible packaging and labeling options
Long-term supply capability for continuous research programs
Payment Support
Multiple secure payment methods are supported to accommodate international research procurement, including PayPal, credit card payments, bank transfer (T/T), and selected cryptocurrency options. All transactions are processed through verified channels to ensure security, transparency, and efficiency for wholesale and bulk laboratory orders.
Disclaimer
Fulzerasib is intended strictly for laboratory research use only. This product is not intended for human or veterinary use, diagnostic applications, or therapeutic purposes. All handling and experimentation should be conducted by qualified professionals in appropriate research facilities and in accordance with applicable regulations.
References
Discovery of Fulzerasib (GFH925) for KRAS G12C–Mutated Tumors — An authoritative PubMed entry describing the identification of Fulzerasib (also known as IBI351/GFH925) via structure‑based design with high in vitro potency and selectivity against KRAS G12C, including mechanistic insight into its covalent interaction with the switch‑II pocket. Discovery of Fulzerasib (GFH925) for KRAS G12C Inhibition – PubMed PubMed
Fulzerasib Ras Inhibitor Profile — A detailed research‑grade catalogue entry summarizing in vitro inhibitory activity of Fulzerasib on KRAS pathway signaling, including IC₅₀ metrics and biochemical assay results relevant for mechanistic studies. Fulzerasib Ras Inhibitor – Selleck Chemicals Selleckchem
In Vitro Mechanistic Evaluations of Fulzerasib — Research reagent profile showing Fulzerasib’s ability to irreversibly inhibit KRAS G12C nucleotide exchange and downstream pathway signaling in controlled experimental assays. Fulzerasib In Vitro Activity – TargetMol Targetmol
IBI351 (Fulzerasib) – Efficacy and Safety Pooled Analysis — A peer‑reviewed article from Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy reporting on in vitro and translational research context of IBI351 (Fulzerasib), including mechanistic relevance of KRAS G12C targeting. Fulzerasib (IBI351) Pooled Analysis – Nature Publication Nature
Efficacy and Tolerability of Fulzerasib in KRAS G12C Models — Industry news summarizing research findings on Fulzerasib’s activity in KRAS G12C systems, supporting its use as a molecular research tool for signaling pathway modulation and mechanistic studies. Fulzerasib Displays Efficacy and Tolerability in KRAS G12C Models – OncLive OncLive
Additional information
| Weight | 1.3 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 58 × 63 × 58 cm |
1 review for Fulzerasib 150mg High Purity | Factory Manufactured
Q1: What is the primary research use of Fulzerasib?
Fulzerasib is used for in vitro studies focused on KRAS G12C–related molecular mechanisms and signaling pathway analysis.
Q2: Is this product suitable for in vivo or clinical research?
No. Fulzerasib is supplied strictly for laboratory and in vitro research use only.
Q3: What purity level is provided?
Each batch is verified to meet high-purity standards (typically ≥98% by HPLC), with supporting documentation available.
Q4: Can Fulzerasib be ordered in bulk quantities?
Yes. Bulk and wholesale orders are supported directly from factory manufacturing.
Q5: Is batch consistency guaranteed?
Yes. Factory production and quality control ensure reliable batch-to-batch consistency for reproducible research results.
Q6: What documentation is available with the product?
A Certificate of Analysis (COA) and related analytical data are available upon request.
Q7: How should Fulzerasib be stored?
Store in a sealed container, protected from light and moisture, under conditions specified in the COA.
Q8: Is customization available for packaging or labeling?
Yes. Custom packaging and labeling options are available for bulk research orders.
Q9: Can this compound be used in multi-omic studies?
Yes. Fulzerasib is compatible with transcriptomic, proteomic, and computational research workflows.
Q10: What payment methods are accepted?
Payments can be made via PayPal, credit card, bank transfer (T/T), and selected cryptocurrencies.
Q11: Is international shipping supported?
Yes. International laboratory shipments are supported with secure logistics.
Q12: Does this product support high-throughput screening?
Yes. Its reproducible activity makes it suitable for HTS and benchmark assays.












barras –
Thanks