No products in the cart.
Sale
Hepcidin-25 (human) (CAS 1356390-47-0) | Iron Metabolism Modulator for Inflammation & Antibacterial Research – GMP Manufacturer/Supplier
Original price was: $22.00.$20.00Current price is: $20.00.
Hepcidin-25 (human) is a synthetic peptide and key regulator of iron metabolism. It exhibits anti-inflammatory and antibacterial activities by modulating iron-mediated oxidative injury, making it suitable for laboratory research in preclinical inflammation and infection models.(Please contact our staff to place an order or learn about product wholesale prices, specifications, uses and lists)
Description
Product Description
Hepcidin-25 (human) (CAS 1356390-47-0) is a synthetic peptide that functions as a potent modulator of iron homeostasis in mammalian systems. Acting as the principal regulator of systemic iron metabolism, Hepcidin-25 binds to the iron exporter ferroportin, inducing its internalization and degradation. This results in the reduction of circulating iron levels, which has downstream effects on oxidative stress, inflammation, and pathogen proliferation.
In laboratory research, Hepcidin-25 is extensively employed to study iron-mediated oxidant injury, immune modulation, and antibacterial defense mechanisms. By reducing free iron availability, it limits bacterial growth and provides protective effects against iron-dependent oxidative damage in tissue and cellular models.
Supplied in GMP-certified quality, Hepcidin-25 ensures high purity, reproducibility, and stability for laboratory use. The peptide is delivered in lyophilized form, preserving biological activity during storage and transport. Researchers utilize Hepcidin-25 in studies of inflammatory disorders, infectious disease models, hepcidin signaling pathways, and iron homeostasis research, making it a versatile tool for both wholesale and retail laboratory applications.
Its ability to modulate iron metabolism while exhibiting anti-inflammatory and antibacterial activities makes Hepcidin-25 an invaluable reagent in preclinical studies exploring oxidative stress, host-pathogen interactions, and iron-dependent cellular mechanisms.
Disclaimer: For laboratory research use only, not for human or veterinary use.
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Hepcidin-25 (human) |
| Synonyms | Hepcidin-25, Human Hepcidin |
| CAS Number | 1356390-47-0 |
| Molecular Type | Synthetic peptide |
| Purity | ? 98% (HPLC) |
| Appearance | Lyophilized white to off-white powder |
| Mechanism | Modulates iron metabolism via ferroportin regulation |
| Stability | Stable at -20°C; avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C under inert atmosphere, protected from light and moisture |
| GMP Compliance | Produced in GMP-certified facility for high purity and reproducibility |
| Application | Laboratory research in inflammation, antibacterial studies, iron homeostasis, oxidative stress, and ferroportin signaling |
| Availability | Wholesale & retail supply |
| Solubility | Soluble in standard aqueous buffers used for peptide research |
| Recommended Form | Lyophilized powder for stability and experimental reproducibility |
| Research Models | Cellular and animal models of inflammation, infection, and iron metabolism |
Mechanism of Action & Research Applications
Mechanism of Action
Hepcidin-25 (human) functions as a key regulator of systemic iron metabolism. Its primary mechanisms include:
Ferroportin binding: Hepcidin-25 binds to ferroportin, the main iron exporter on enterocytes, macrophages, and hepatocytes, inducing internalization and degradation.
Reduction of circulating iron: By decreasing iron export, free serum iron levels are lowered, impacting oxidative stress and bacterial growth.
Anti-inflammatory effects: Modulates cytokine production and limits iron-mediated tissue damage during inflammatory responses.
Antibacterial activity: Limits iron availability for pathogens, reducing proliferation in infection models.
Oxidative stress modulation: Protects tissues from iron-mediated reactive oxygen species (ROS) damage.
These mechanisms make Hepcidin-25 an ideal peptide for exploring iron-dependent cellular processes, inflammation, and host-pathogen interactions.
Research Applications
Iron Homeostasis Studies: Investigate ferroportin regulation, serum iron control, and iron-related metabolic pathways.
Inflammatory Disorder Models: Study the role of iron modulation in chronic and acute inflammation.
Antibacterial Research: Examine pathogen growth inhibition via iron restriction.
Oxidative Stress Studies: Explore iron-mediated ROS production and cellular protection mechanisms.
Cellular Signaling Research: Assess downstream signaling cascades triggered by hepcidin-ferroportin interaction.
Preclinical Pharmacology: Model therapeutic effects of iron modulation in inflammatory and infection models.
Combination Therapy Studies: Test interactions with other peptides, anti-inflammatory agents, or antibiotics.
Molecular Mechanism Research: Explore gene expression, protein regulation, and iron-dependent cellular pathways.
Translational Research: Investigate iron modulation as a potential strategy for inflammatory or infectious disease management.
Host-Pathogen Interaction Studies: Examine how iron limitation impacts bacterial proliferation and immune defense.

Side Effects (For Reference in Research Models)
In laboratory research, Hepcidin-25 (human) may produce the following experimental effects:
Reduced extracellular iron levels: Leading to decreased bacterial proliferation in vitro or in vivo.
Modulation of inflammatory cytokines: Altered TNF-?, IL-6, and IL-1? profiles in cellular or animal models.
Oxidative stress attenuation: Reduced ROS generation in iron-rich conditions.
Altered cell proliferation: Effects on iron-dependent cell lines may vary with dose.
Dose-dependent responses: High concentrations may amplify iron restriction effects.
Potential tissue remodeling: Observed in chronic exposure models affecting iron-dependent metabolic pathways.
Note: These effects are strictly for laboratory research purposes and do not constitute clinical safety or efficacy data.
Keywords
Hepcidin-25 (human)
Hepcidin-25 CAS 1356390-47-0
Iron metabolism modulator peptide
GMP supplier Hepcidin-25
Anti-inflammatory peptide
Antibacterial research peptide
Laboratory iron homeostasis studies
Oxidative stress peptide
Ferroportin signaling research
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 28 × 53 × 28 cm |

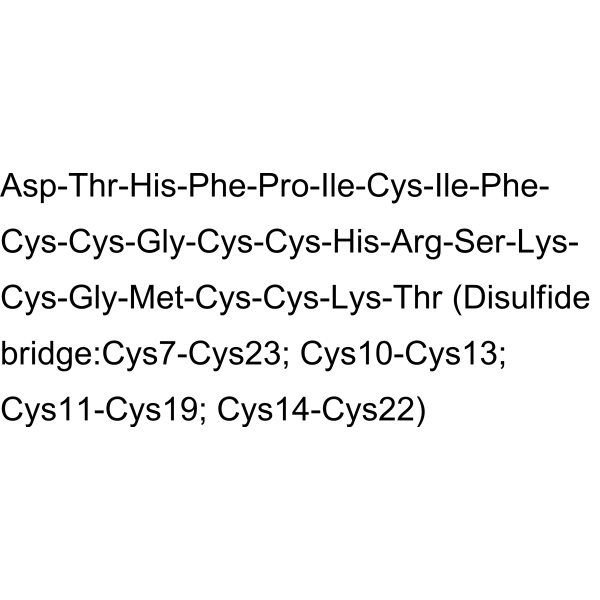












dogutierrezde –
I need it for a long time, please remember to prepare it for me