No products in the cart.
Ibandronate Sodium | CAS 114084-78-5 | Bisphosphonate Compound for Bone Metabolism Research
$2.00
Ibandronate Sodium is a nitrogen-containing bisphosphonate compound extensively used in laboratory research investigating bone metabolism, osteoclast inhibition, and calcium homeostasis. It is widely studied for its ability to suppress bone resorption through interference with farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase activity in the mevalonate pathway, making it a core tool in skeletal biology and mineralization studies.
Description
Product Description
Ibandronate Sodium is a potent, nitrogen-containing bisphosphonate that serves as a model compound in the study of bone resorption and mineral metabolism. It belongs to a class of small molecules designed to inhibit osteoclast-mediated bone degradation by targeting specific enzymatic processes essential for cellular energy and membrane synthesis.
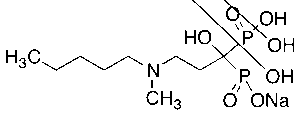
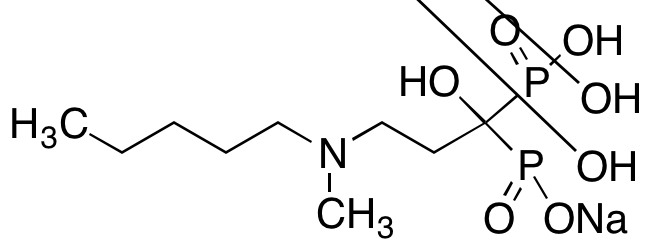
From a structural perspective, Ibandronate Sodium contains two phosphonate groups attached to a central carbon atom, creating a P-C-P backbone characteristic of all bisphosphonates. This structure allows it to chelate calcium ions with high affinity, anchoring the molecule to hydroxyapatite crystals in bone tissue. Once bound, it exerts localized effects on osteoclast function and survival.
In preclinical settings, Ibandronate Sodium is frequently utilized to examine the biochemistry of bone turnover, mineralization, and the molecular regulation of osteoclastic differentiation. Its strong affinity for bone mineral makes it a valuable probe for labeling bone surfaces and assessing mineral deposition rates in vitro and in vivo animal models.
Chemical and Biological Characteristics
At the cellular level, Ibandronate Sodium inhibits the farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (FPPS) enzyme in the mevalonate pathway. This inhibition blocks the biosynthesis of isoprenoid lipids necessary for post-translational modification (prenylation) of small GTP-binding proteins such as Ras, Rho, and Rac. These proteins are critical regulators of cytoskeletal organization, vesicular trafficking, and apoptosis in osteoclasts. Consequently, inhibition of FPPS leads to loss of osteoclast function and induction of programmed cell death, reducing bone resorption activity.
The compound’s selectivity and strong binding affinity to bone mineral surfaces make it an indispensable reference molecule for understanding bisphosphonate pharmacodynamics, biomineralization, and skeletal drug targeting. Researchers employ it to evaluate the kinetics of mineral binding, the reversibility of adsorption, and the structure–activity relationship of related analogues.
Applications in Experimental Research
Ibandronate Sodium is widely applied in biochemical assays, cell culture studies, and animal models aimed at exploring the molecular basis of bone diseases and calcium metabolism. Key research areas include:
Bone resorption and remodeling studies, where the compound is used to quantify osteoclast activity.
Osteoblast–osteoclast co-culture experiments, to assess crosstalk and signaling regulation.
In vitro mineralization models, for examining hydroxyapatite formation and dissolution.
Pharmacokinetic modeling, to evaluate distribution, clearance, and tissue retention of bisphosphonates.
Mevalonate pathway inhibition, as a biochemical framework for studying enzyme inhibition and metabolic consequences in bone cells.
Researchers also utilize Ibandronate Sodium as a benchmark compound when testing new antiresorptive agents or modified bisphosphonate analogues. Its predictable binding characteristics and well-defined mechanism make it a consistent control standard for quantitative comparison.
Analytical Verification and Quality Control
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry (MS) are routinely employed to confirm the purity (≥ 99 %) and molecular integrity of Ibandronate Sodium. Additional testing methods such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and infrared (IR) analysis verify the expected functional groups and salt form. The product’s physicochemical stability under controlled storage ensures reproducibility across experiments.
Storage and Handling
As a sodium salt, Ibandronate demonstrates enhanced solubility in water compared with the free acid form. The compound should be stored at 2–8 °C in a moisture-controlled environment, away from strong acids or oxidizing agents. Solutions should be freshly prepared in sterile water or buffer to maintain chemical stability for in vitro use. Proper laboratory safety procedures and personal protective equipment (PPE) are required when handling the powder or preparing stock solutions.
Product Specifications
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Ibandronate Sodium |
| CAS Number | 114084-78-5 |
| Synonyms | Ibandronic acid sodium salt; BM 21.0955; Boniva sodium |
| Molecular Formula | C9H22NO7P2Na |
| Molecular Weight | 359.21 g/mol |
| Purity | ≥ 99 % |
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in water; slightly soluble in methanol |
| Storage Temperature | 2–8 °C |
| Category | Bisphosphonate small-molecule compound |
| Applications | Bone metabolism studies, osteoclast inhibition, mineral binding assays, enzymatic pathway research |
| Formulation | Suitable for in vitro and in vivo experimental models |
| Stability | Stable under recommended storage conditions |
| Shelf Life | 24 months |
| Supplier Type | Research chemical manufacturer |
| Intended Use | For laboratory research use only |
Mechanism of Action
Interaction with Bone Mineral Matrix
Ibandronate Sodium exhibits a strong affinity for hydroxyapatite crystals, the primary mineral component of bone. Upon systemic or in vitro exposure, the compound preferentially accumulates at sites of active bone remodeling, where mineral surfaces are exposed. The bisphosphonate moiety (P-C-P) anchors the molecule through chelation with calcium ions, effectively localizing the compound to bone surfaces undergoing resorption.
This localization ensures that when osteoclasts attach to the mineral matrix to initiate resorption, they simultaneously internalize Ibandronate molecules bound within the bone surface. This targeted uptake underlies the compound’s selectivity and its utility in bone metabolism research.
Inhibition of Farnesyl Pyrophosphate Synthase (FPPS)
The intracellular target of Ibandronate Sodium is farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase, a key enzyme in the mevalonate pathway responsible for synthesizing isoprenoid intermediates such as farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP). These intermediates are critical for prenylation of small GTP-binding proteins that regulate cytoskeletal dynamics, vesicle transport, and survival signaling in osteoclasts.
By inhibiting FPPS, Ibandronate Sodium prevents the proper prenylation of these GTPases, leading to cytoskeletal disorganization, loss of ruffled borders, and impaired resorptive capacity in osteoclasts. Ultimately, osteoclasts undergo apoptosis, reducing bone degradation rates in laboratory models.
Downstream Effects on Cellular Pathways
Inhibition of FPPS triggers a cascade of intracellular effects, including:
Decreased membrane localization of small GTPases (Ras, Rho, Rac).
Disruption of actin ring formation, essential for osteoclast attachment and bone resorption.
Reduction in secretion of proteolytic enzymes such as cathepsin K and tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP).
Induction of apoptotic pathways via mitochondrial dysfunction and caspase activation.
These cellular events collectively contribute to the reduction of osteoclastic bone resorption observed in vitro and in preclinical animal models. Researchers utilize these measurable effects as endpoints to evaluate the potency of bisphosphonate compounds and to model bone metabolism processes.
Molecular Pathways and Research Utility
Ibandronate Sodium serves as a vital reference compound for mechanistic investigations into the mevalonate pathway—a biochemical route shared between bone metabolism, cholesterol synthesis, and cell signaling. Through FPPS inhibition, it provides a direct link between metabolic enzyme regulation and bone resorption outcomes. Researchers often employ the compound in:
Gene expression assays analyzing upregulation of apoptosis markers such as caspase-3, caspase-9, and BAX.
Proteomics studies to identify proteins whose prenylation is disrupted under bisphosphonate treatment.
Fluorescent imaging to monitor cellular uptake of bone-targeting compounds and localization within mineralized matrices.
The compound’s predictable pharmacodynamic behavior supports quantitative modeling of bisphosphonate kinetics and distribution, assisting in the rational design of improved bone-targeting molecules.
Side Effects
In laboratory research, Ibandronate Sodium demonstrates a favorable safety profile when handled under proper experimental conditions. Toxicological data from preclinical studies show minimal cytotoxicity at concentrations relevant for biochemical assays and cellular experiments. However, certain concentration-dependent effects have been observed, including:
Mild reductions in cell viability at supra-physiological doses.
Temporary mitochondrial stress in highly metabolically active cell lines.
Alterations in membrane potential and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation under extended exposure.
These effects are typically reversible upon compound withdrawal and are primarily associated with its mechanism of action—disruption of intracellular isoprenoid biosynthesis.
Researchers are advised to carefully titrate doses, maintain neutral pH in culture media, and prepare fresh solutions to ensure reproducible results.
It must be emphasized that Ibandronate Sodium is strictly intended for laboratory research use only and should not be used for human or veterinary applications.
Keywords
Ibandronate Sodium, bisphosphonate compound, bone metabolism research, osteoclast inhibition, hydroxyapatite binding, mevalonate pathway, FPPS inhibitor, skeletal biology, mineralization studies, bone resorption assay, preclinical pharmacology, research chemical supplier, high-purity bisphosphonate, calcium chelation research.
Shipping Guarantee
All Ibandronate Sodium shipments are handled using validated cold-chain logistics to preserve compound integrity. Each package is sealed in moisture-proof containers with secondary protective wrapping and continuous temperature monitoring. Products are shipped via express international couriers with full tracking and insurance coverage.
Trade Assurance
We Ibandronate Sodium ensure product authenticity, verified ≥99% purity, and compliance with analytical standards (HPLC, MS, and NMR). Each batch is supplied with a Certificate of Analysis (CoA). Our trade assurance policy guarantees replacement or refund for any deviation from listed specifications.
Payment Support
We Ibandronate Sodium provide flexible and secure global payment options to support international research transactions. Accepted payment methods include PayPal, major credit cards (Visa, MasterCard, American Express), telegraphic transfer (T/T), and cryptocurrencies (USDT, Bitcoin, Ethereum). All transactions are protected by industry-standard encryption and verified payment gateways to ensure confidentiality and fund security.
Disclaimer
All products listed are intended for laboratory research use only and not for human or veterinary use. They are not drugs, medical devices, or diagnostics and should not be administered to humans or animals. Researchers must handle all materials in accordance with institutional biosafety and chemical safety guidelines. The information provided is for scientific reference only and does not imply therapeutic efficacy, safety, or regulatory approval.
Additional information
| Weight | 1.1 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 18 × 16 × 18 cm |
What is Ibandronate Sodium used for in research?
It is primarily used in bone metabolism and osteoclast inhibition studies, serving as a bisphosphonate reference compound in antiresorptive mechanism research.
What is the purity of Ibandronate Sodium provided?
Each batch is verified to have a high purity of ≥99%, confirmed by analytical techniques such as HPLC and NMR.
Is Ibandronate Sodium soluble in water?
Yes. It dissolves readily in water and aqueous buffers due to its sodium salt form, allowing direct use in biochemical assays.
How should Ibandronate Sodium be stored?
Store at 2–8 °C in a tightly sealed container, away from moisture and light, to preserve stability and prevent hydrolysis.
Can it be used in combination studies with other compounds?
Yes. Researchers often combine it with agents affecting osteoblasts or mevalonate pathway enzymes to study synergistic or competitive effects.
What is the typical appearance of Ibandronate Sodium?
It appears as a white to off-white crystalline powder with high water solubility and stability.
Does Ibandronate Sodium affect other enzymes?
At experimental concentrations, it selectively inhibits farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase, though excessive exposure may influence related metabolic enzymes.
Where is this product manufactured?
Produced under research-grade conditions in China, adhering to international analytical standards for laboratory compounds.
Do you offer OEM or bulk production options?
Yes. OEM, bulk, and custom synthesis services are available for research institutions and industry partners.
What type of supplier provides Ibandronate Sodium?
We are a professional factory peptide supplier and research chemical manufacturer specializing in high-purity small molecules and bisphosphonate compounds.
Is this compound suitable for long-term studies?
Yes, it is stable under proper storage and suitable for long-duration bone resorption or mineralization experiments.
Can Ibandronate Sodium be ordered in bulk?
Absolutely. We support OEM & bulk peptide production and small-molecule chemical supply with international logistics.
How do you ensure shipping stability?
Cold-chain packaging, temperature monitoring, and express international couriers guarantee compound stability during shipment.
Is Ibandronate Sodium considered a high-purity product?
Yes, it is classified as a high-purity research-grade compound (≥99%), ideal for precise biochemical assays.
Do you support international academic purchases?
Yes, we accept institutional orders worldwide, providing secure payment, export documentation, and quality assurance for every batch.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.