No products in the cart.
Sale
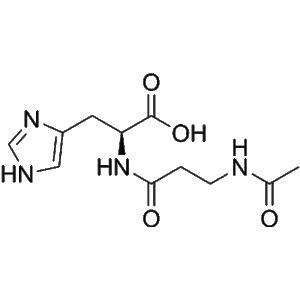
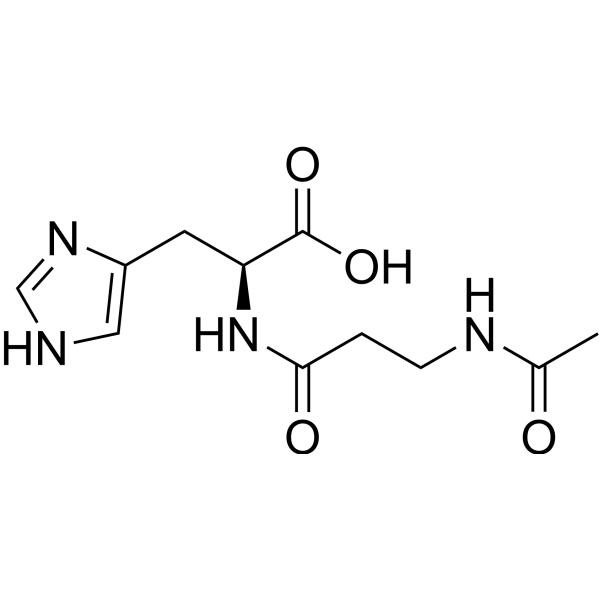
N-Acetylcarnosine | CAS 56353-15-2 | Antioxidant Peptide for Skin Brightening and Anti-Aging Research
Original price was: $3.00.$1.00Current price is: $1.00.
N-Acetylcarnosine (NAC) is a histidine-containing dipeptide derivative of L-carnosine, widely recognized in cosmetic research for its antioxidant, brightening, and anti-aging properties. It supports collagen preservation, cellular repair, and oxidative balance in skin and ocular oxidative stress models.
Description
Product Description
N-Acetylcarnosine (CAS 56353-15-2), also known as Acetyl-L-carnosine or NAC, is an acetylated dipeptide derivative of L-carnosine composed of β-alanine and L-histidine. As an endogenous antioxidant analog, NAC has become a central focus in cosmetic peptide research due to its multifunctional biological properties, including free radical scavenging, antiglycation, metal ion chelation, and collagen stabilization. These characteristics make it an ideal compound for studying anti-aging, brightening, and skin renewal mechanisms at the molecular level.
In the context of dermatological research, oxidative stress is one of the primary factors contributing to premature skin aging, pigmentation, and loss of elasticity. NAC serves as a powerful antioxidant molecule capable of neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS), preventing lipid peroxidation, and protecting proteins and DNA from oxidative degradation. Its acetylated structure enhances its bioavailability and stability against enzymatic hydrolysis, making it suitable for long-term laboratory formulations and skin model studies.
NAC also exhibits strong antiglycation activity, inhibiting the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) that stiffen collagen fibers and accelerate visible aging. By mitigating AGEs and free radical formation, N-Acetylcarnosine contributes to maintaining skin firmness, luminosity, and youthful appearance. Moreover, research indicates that NAC influences matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) regulation, reducing excessive collagen degradation and supporting the extracellular matrix’s structural integrity.
Beyond dermatological research, N-Acetylcarnosine has also attracted scientific attention in ocular oxidative stress studies. Researchers have explored its antioxidant effects in corneal and lens tissue models to better understand the biochemical pathways associated with age-related oxidative damage in the eye. Its ability to stabilize biomolecules and maintain redox balance provides valuable insights into cellular defense systems that protect visual and epithelial tissues from oxidative degradation. These findings expand its relevance not only in skin research but also in broader studies on oxidative stress and cellular protection.
From a cosmetic science perspective, N-Acetylcarnosine is frequently investigated for its ability to restore radiance and even out skin tone by mitigating oxidative pigmentation pathways. It also enhances barrier recovery and supports fibroblast vitality, contributing to improved elasticity and hydration in skin cell models. Because it is both hydrophilic and amphiphilic, it can be incorporated into aqueous and emulsion-based experimental systems for anti-aging and skin-brightening peptide research.
N-Acetylcarnosine’s multifunctionality lies in its synergistic mechanisms—its antioxidant properties reduce oxidative load, its antiglycation effects delay collagen stiffening, and its chelating activity neutralizes transition metals such as copper and iron that catalyze oxidative reactions. Collectively, these mechanisms make NAC one of the most promising biomolecules in cosmetic peptide science, helping researchers uncover the biochemical pathways that define youthful, resilient, and bright skin.

Product Specifications
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Name | N-Acetylcarnosine |
| CAS Number | 56353-15-2 |
| Synonyms | Acetyl-L-carnosine; NAC; β-Alanyl-L-histidine N-acetyl derivative |
| Molecular Formula | C11H16N4O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 268.27 g/mol |
| Purity | ≥99% |
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in water and ethanol |
| Storage | Store at -20°C in a dry, dark place |
| Category | Cosmetic Peptides; Antioxidant Research Compounds |
| Applications | Skin brightening, anti-aging, ocular oxidative stress, collagen protection research |
| Research Area | Dermatology, Cosmetology, Biochemistry |
| Intended Use | For laboratory research use only |
Mechanism of Action
N-Acetylcarnosine acts primarily as a redox regulator, neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and preventing oxidative stress-induced molecular damage. Its acetylated structure increases lipophilicity and stability, allowing it to cross biological membranes more efficiently and protect intracellular components from oxidative reactions. Within dermal cells, NAC enhances endogenous antioxidant enzyme systems, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase, and glutathione peroxidase, which collectively maintain redox equilibrium.
It also exhibits significant antiglycation activity by forming transient bonds with carbonyl intermediates, thereby preventing the crosslinking of proteins and collagen fibers. This property supports long-term structural resilience of the skin and maintains elasticity. In addition, NAC inhibits matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), preventing excessive breakdown of extracellular matrix proteins under stress conditions.
In ocular research models, NAC provides antioxidative stabilization to lens proteins and corneal cells, serving as a model compound for understanding age-related oxidative degradation pathways. By reducing reactive aldehydes and peroxide intermediates, it aids in maintaining cellular transparency and homeostasis in epithelial tissues—offering broader insight into antioxidative peptide mechanisms relevant to both dermatological and ocular science.
Overall, NAC’s multi-targeted biochemical interactions—free radical scavenging, metal ion chelation, antiglycation, and MMP modulation—make it a cornerstone molecule in peptide-based anti-aging and antioxidative research.
Side Effects
N-Acetylcarnosine demonstrates excellent safety and biocompatibility in laboratory research settings. Studies have shown minimal cytotoxicity in both dermal and ocular cell models at experimental concentrations. However, as with all research-grade peptides, it is intended strictly for scientific investigation and not for clinical or cosmetic use on humans. Researchers should follow proper safety and storage protocols to maintain compound stability and reliability of experimental results.
Keywords
N-Acetylcarnosine; antioxidant peptide; anti-aging peptide; skin brightening research; collagen protection; ocular oxidative stress; redox regulation; glycation inhibition; cosmetic peptide; skin rejuvenation.
Shipping Guarantee
All shipments are handled using validated cold-chain logistics to preserve peptide integrity. Each package is sealed in moisture-proof containers with secondary protective wrapping and continuous temperature monitoring. Products are shipped via express international couriers with full tracking and insurance coverage.

Trade Assurance
We ensure product authenticity, verified ≥99% purity, and compliance with analytical standards (HPLC, MS, and NMR). Each batch is supplied with a Certificate of Analysis (CoA). Our trade assurance policy guarantees replacement or refund for any deviation from listed specifications.
Payment Support
We provide flexible and secure global payment options to support international research transactions. Accepted payment methods include PayPal, major credit cards (Visa, MasterCard, American Express), telegraphic transfer (T/T), and cryptocurrencies (USDT, Bitcoin, Ethereum). All transactions are protected by industry-standard encryption and verified payment gateways to ensure confidentiality and fund security.
Disclaimer
All products listed are intended for laboratory research use only and not for human or veterinary use. They are not drugs, medical devices, or diagnostics and should not be administered to humans or animals. Researchers must handle all materials in accordance with institutional biosafety and chemical safety guidelines. The information provided is for scientific reference only and does not imply therapeutic efficacy, safety, or regulatory approval.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 65 × 43 × 65 cm |
What is N-Acetylcarnosine used for in research?
It is primarily used in cosmetic and dermatological research to study antioxidant, anti-aging, and ocular oxidative stress mechanisms.
Yes, NAC acts as a potent antioxidant, scavenging reactive oxygen species and protecting biomolecules from oxidative damage.
Is it suitable for cosmetic peptide studies?
Yes, NAC is widely used as a reference compound in anti-aging and brightening peptide research.
What is the difference between N-Acetylcarnosine and L-Carnosine?
NAC is the acetylated form of L-carnosine, offering greater stability and resistance to enzymatic degradation.
Can it be used in ocular oxidative stress research?
Yes, NAC is studied in lens and corneal models to explore oxidative protection mechanisms.
What is its purity?
The compound is verified at ≥99% purity through analytical testing.
How should N-Acetylcarnosine be stored?
Store at -20°C, in a dry, dark environment to preserve stability.
What is its molecular formula and weight?
Molecular formula C11H16N4O4; molecular weight 268.27 g/mol.
Is it soluble in water?
Yes, N-Acetylcarnosine is water-soluble and compatible with aqueous systems.
Is a Certificate of Analysis provided?
Yes, every batch includes a CoA verifying purity and analytical results.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.