No products in the cart.
Sale
Octreotide – Freeze-Dried Powder | High Purity | Factory Manufactured | Low-Price Wholesale Supply
Original price was: $42.00.$28.00Current price is: $28.00.
High-purity Octreotide freeze-dried powder produced in GMP-aligned facilities, suitable for laboratory-only biochemical, receptor-binding, and molecular-mechanism research. Factory-direct pricing and bulk availability support large-scale institutional studies.(For research use only. Not for human or veterinary use.)
Description
Product Description
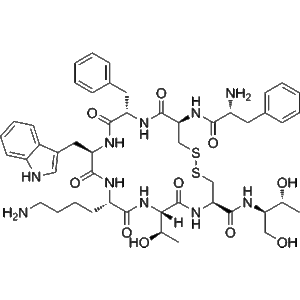
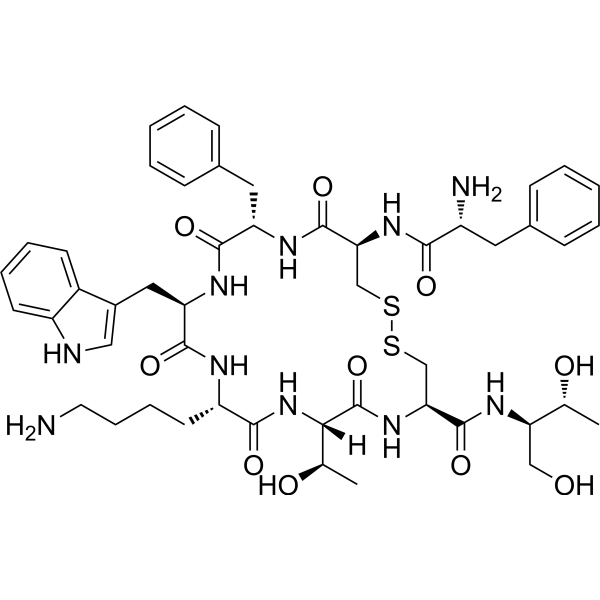
Octreotide is a synthetic octapeptide widely utilized in laboratory settings to study molecular mechanisms associated with somatostatin-related pathways, receptor signaling, and peptide–receptor interactions. As a highly stable and well-characterized analog, Octreotide provides researchers with a robust tool for evaluating biochemical responses, receptor affinity profiles, and downstream signaling cascades under controlled experimental conditions. Its lyophilized form ensures extended shelf stability and consistent reconstitution properties, enabling reproducible results across diverse research workflows.
The molecular structure of Octreotide incorporates key amino acid modifications designed to enhance stability and resistance to degradation, making it suitable for extended study durations and multi-step biochemical assays. Because of this high structural integrity, researchers frequently employ Octreotide in receptor-binding investigations, signal transduction analyses, and studies involving somatostatin-related pathways. Its affinity for specific receptor subtypes allows precise interrogation of receptor behavior in vitro, supporting mechanistic explorations in controlled laboratory environments.
The freeze-dried presentation of Octreotide ensures ease of handling while maintaining the peptide’s integrity during long-term storage. Laboratories appreciate the consistent batch-to-batch purity, which allows experimental designs to remain dependable, especially when quantifying molecular interactions or analyzing peptide-protein complex stability. The form also offers flexibility in preparing stock solutions or aliquots suitable for kinetic assays, receptor profiling, and biochemical modeling.
Researchers further utilize Octreotide to observe regulatory influences on enzyme activity, protein conformational changes, and intracellular signaling pathway modulation. Its precision and reliability make it valuable for comparative experiments, standard curve generation, and functional receptor assays. Because Octreotide interacts selectively with somatostatin receptors, it supports controlled laboratory exploration of receptor subtype preference, desensitization patterns, and ligand–receptor kinetics.
Quality-controlled, factory-manufactured Octreotide ensures that each batch adheres to stringent purity criteria validated through HPLC, MS, and other analytical methods. This provides researchers with confidence in the molecule’s consistency and suitability for advanced biochemical research. Whether used in structural analysis, receptor-ligand mechanistic studies, or molecular interaction screening, Octreotide remains a key component in peptide-focused laboratory research.

Product Specifications
| Parameter | Specification | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Product Name | Octreotide | Synthetic somatostatin analog |
| CAS Number | 83150-76-9 | Verified and batch-traceable |
| Molecular Formula | C₄₉H₆₆N₁₀O₁₀S₂ | Confirms peptide structure |
| Molecular Weight | 1019.27 g/mol | Suitable for LC-MS quantification |
| Form | Freeze-dried powder | Protects from hydrolysis and oxidation |
| Purity | ≥98% (HPLC) | Higher grades available for specialized assays |
| Appearance | White to off-white lyophilized powder | Typical of high-stability peptides |
| Solubility | Water, acetic acid, buffered saline | Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles after reconstitution |
| Storage | −20 °C (dry, protected from light) | Ensures maximum long-term stability |
| Grade | Research grade | GMP-aligned factory production available |
| Customization | Bulk, OEM, high-purity options | Tailored for analytical or animal studies |
Additional Notes:
Each batch includes COA, MSDS, and impurity chromatograms for traceability.
Sterile-filtered preparation can be provided upon request for cell-culture applications.
Mechanism of Action
Octreotide functions as a synthetic somatostatin analog engineered to interact with a subset of somatostatin receptors (primarily SSTR2 and SSTR5) with significantly higher stability and prolonged activity compared with endogenous somatostatin-14. Its mechanism is centered on high-affinity GPCR-mediated inhibitory signaling, making it a valuable tool for controlled perturbation studies across neuroendocrine, metabolic, and cellular-signaling research domains.
Receptor Binding & Primary Signal Initiation
Upon contact with responsive cellular systems, Octreotide binds to somatostatin receptors, which belong to the G-protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily. The interaction is strongest with SSTR2, followed by SSTR5, both of which regulate secretory and proliferative processes in many endocrine and neuroendocrine model systems. Receptor engagement triggers coupling with Gi/o proteins, resulting in suppression of adenylyl cyclase activity. This decreases intracellular cAMP levels, altering downstream kinase activity (PKA and related signaling intermediates). Reduced cAMP serves as a major checkpoint that reshapes hormonal secretion pathways, ion-channel modulation, and vesicle-dynamics patterns.
Ion Channel & Calcium Regulation
Octreotide-driven GPCR activation also modulates voltage-gated calcium channels, reducing calcium influx and consequently lowering the activity of calcium-dependent exocytotic machinery. This regulatory action is essential for studies focused on hormone-release mechanisms, as it provides a consistent and quantifiable method to evaluate how reduced intracellular calcium impacts synaptic-like vesicle fusion, SNARE-complex behavior, and endocrine system responsiveness.
MAPK, PI3K/AKT, and Additional Downstream Nodes
In addition to cAMP suppression, Octreotide influences several major regulatory pathways, including MAPK/ERK, PI3K/AKT, and PLC/PKC networks. These effects may vary by receptor subtype expression, cell type, and experimental conditions. Gene-expression analyses frequently show shifts in regulators of proliferation, differentiation markers, cytoskeletal reorganization, and metabolic enzymes. Somatostatin receptor activation can also influence apoptotic pathway mediators, contributing to its widespread use in tumor and stress-response modeling.
Modulation of Secretory Networks
A central functional feature of Octreotide is its ability to downregulate multiple endocrine secretion pathways. It suppresses synthesis-associated transcriptional regulators and reduces exocytosis from secretory granules via altered ion-channel and vesicle-trafficking behavior. This makes Octreotide a powerful reference compound in endocrine circuit mapping, hormone-regulation screens, and peptide-secretion research.
Systems-Level Implications
Because Octreotide targets highly conserved GPCR networks, its influence spans transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic systems. It introduces predictable inhibitory signatures across multiple biological layers, making it valuable in systems pharmacology, network reconstruction, signal-perturbation mapping, and somatostatin-receptor functional studies. The clarity and reproducibility of its receptor-mediated responses support its integration into multi-omic workflows and computational modeling frameworks to dissect endocrine and neuroendocrine regulatory structures.
Applications
Octreotide’s diverse biochemical activities make it suitable for a broad spectrum of laboratory investigations. In endocrine signaling research, it is widely used to explore GH axis suppression, insulin-glucagon dynamics, pancreatic β-cell regulatory mechanisms, and pituitary modulation. Its strong activity at SSTR2/5 provides targeted control of hormone-secreting cell populations for pathway-specific experiments.
In cancer biology, Octreotide is employed in neuroendocrine tumor models to assess anti-proliferative signaling, angiogenesis suppression, and tumor-secretome modulation. Studies often integrate Octreotide to evaluate receptor expression profiles or as a reference agonist when screening new somatostatin-pathway modulators.
In gastrointestinal and metabolic research, Octreotide assists in examining gastric emptying dynamics, intestinal secretion rates, pancreatic exocrine control, and peptide-mediated gut-brain-axis communication. Organoid and microfluidic gut models particularly benefit from its predictable and receptor-specific actions.
Additional application domains include:
Receptor-binding studies and ligand-affinity profiling
Computational modeling of endocrine microcircuits
In vivo pharmacokinetic evaluations
High-content imaging of somatostatin receptor trafficking
Research Models
Octreotide is widely incorporated into diverse research models because of its stable activity, selective somatostatin-receptor affinity, and predictable inhibitory signaling behavior. Its reproducible performance makes it a standard reference compound across endocrine, neuroendocrine, metabolic, and cellular-signal–modulation studies. The following categories outline how laboratories integrate Octreotide into controlled experimental systems while adhering strictly to research-only parameters.
Endocrine Pathway Modulation Models
Octreotide is frequently used in in-vitro endocrine models designed to evaluate somatostatin-receptor–controlled pathways. Systems expressing SSTR2 or SSTR5 allow investigators to study receptor selectivity, second-messenger suppression, transcriptional-regulator shifts, and regulatory loops associated with hormonal suppression. These models provide a controlled environment to map peptide–GPCR interactions, modulate inhibitory signaling, and benchmark receptor-dependent transcriptional signatures.
Neuroendocrine Signal-Pathway Frameworks
In neuroendocrine research models, Octreotide serves as a consistent signaling-perturbation tool used to explore neuronal–secretory regulation, calcium-channel behavior, and the molecular dynamics of vesicle systems. Laboratory models focusing on neuropeptide regulatory axes use Octreotide to assess GPCR-coupled feedback networks, identify differential receptor expression patterns, and study cross-talk between somatostatin receptor families and downstream kinase cascades.
Cellular Signaling & GPCR Investigation Systems
Research platforms using engineered cell lines or primary cellular constructs often incorporate Octreotide to analyze GPCR-mediated inhibitory signaling across cAMP, MAPK, PI3K/AKT, and PLC pathways. Because Octreotide produces clear, dose-dependent regulatory signatures, it is well suited for mechanistic studies on kinase regulation, signal-cascade dampening, cytoskeletal remodeling, and apoptotic-pathway engagement. Multi-receptor expression models also allow comparative assessment of SSTR-subtype–specific responses.
Secretory-Granule & Exocytosis Models
A major application of Octreotide in research models centers on its ability to reduce calcium-dependent exocytotic processes. Secretory-cell culture systems—whether neuroendocrine, endocrine, or receptor-engineered—use Octreotide to quantify changes in granule trafficking, vesicle-fusion metrics, SNARE-complex configuration, and secretion-associated transcriptional adjustments. Its reproducible suppression of exocytotic activation makes it a reference compound in mechanistic secretion research.
Proliferation, Differentiation & Stress-Response Panels
Octreotide is incorporated into cellular panels exploring proliferation checkpoints, differentiation markers, oxidative-stress responses, and survival pathways. These models rely on somatostatin-receptor activation to regulate MAPK/ERK and AKT kinetics, enabling controlled perturbation of proliferative behaviors in receptor-positive systems. Studies focusing on stress signaling and homeostatic feedback also employ Octreotide to investigate how inhibitory GPCR signaling influences stress-adaptation networks.
Multi-Omic & Computational Research Models
In transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic workflows, Octreotide provides a stable inhibitory signature that supports model training, computational predictions, and systems-biology analyses. Research groups frequently integrate Octreotide into network-reconstruction frameworks to validate pathway inference, receptor-interaction modeling, and multivariate clustering linked to GPCR-driven regulatory behavior. Its predictable multi-level effects enable use in simulation-based models and algorithmic pathway-validation pipelines.
Comparative Peptide-Analog Modeling
Octreotide is also used in comparative panels evaluating synthetic peptide analogs designed to target the same receptor families. These models help establish structure–activity relationships, identify receptor-affinity differentials, and benchmark kinetic properties against known somatostatin analogs. Because Octreotide exhibits strong and consistent receptor bias, it serves as a robust reference for analog-profiling studies.

Experimental Design Considerations
When designing Octreotide experiments, ensure that dosing concentration matches the receptor density and metabolic turnover of the selected model. Lyophilized stocks should be reconstituted with sterile saline or dilute acetic acid at the desired molarity and prepared fresh when possible to avoid peptide oxidation.
Time-course sampling is essential for accurate interpretation of endocrine suppression dynamics, as Octreotide exhibits sustained receptor activity relative to native somatostatin. Parallel controls—such as untreated samples, receptor antagonist groups, or natural somatostatin comparators—are recommended to differentiate mechanism-specific outcomes.
For in vivo studies, consider circadian variations in hormone release and administer Octreotide at consistent intervals. For in vitro work, avoid buffers with high protease activity and validate peptide stability using LC-MS or HPLC when conducting long experiments.
Laboratory Safety & Handling Guidelines
Proper laboratory practice is essential when working with Octreotide in its freeze-dried powder form, particularly because peptide-based research materials require controlled handling to maintain stability, purity, and reproducibility across experiments. Although Octreotide is not intended for human or veterinary use, rigorous adherence to institutional biosafety protocols ensures safe operation and preserves the integrity of scientific results.
Storage & Stability Management
Octreotide should be stored at –20 °C or below in its sealed, lyophilized state to maintain structural fidelity and minimize degradation. The peptide is hygroscopic, meaning exposure to moisture may alter its stability; therefore, vials must remain tightly sealed until use. Once reconstituted, working solutions should be handled under low-temperature conditions, protected from light, and used promptly to minimize peptide oxidation or aggregation. Where possible, single-use aliquots are recommended to reduce repeated freeze–thaw cycles, as these can compromise experimental consistency.
Handling Precautions
Standard PPE—including laboratory gloves, protective eyewear, and appropriate lab coats—should be worn whenever handling Octreotide, whether in powder or solution form. Opening vials should be performed in a clean, low-particulate workspace such as a chemical safety cabinet or laminar-flow hood when feasible. Peptide powders can become airborne if mishandled; therefore, avoid direct airflow, rapid uncapping, or mechanical shocks that may disturb the lyophilized material. Use calibrated micropipettes and sterile vessels for accurate reconstitution and measurement.
Contamination Avoidance & Traceability
To safeguard against cross-contamination, all contact surfaces, tools, and containers must be cleaned or sterilized before interacting with the material. Dedicated consumables should be used when conducting sequential assays. Maintaining precise chain-of-custody and documentation—including lot numbers, dates of opening, and storage conditions—ensures traceability and supports reproducible research outcomes. Researchers should follow internal QA/QC policies, including regular equipment calibration and proper sample-labeling procedures.
Waste Disposal & Environmental Controls
Unused or expired Octreotide, along with materials contaminated during experimental work, must be disposed of according to chemical and institutional biosafety rules. Although peptides typically pose low environmental hazard, they should never be released into wastewater systems. Solid waste should be placed in designated chemical-biological collection containers. Laboratories should maintain adequate ventilation, temperature monitoring, and humidity control to prevent unintentional degradation of stored materials.
Emergency Guidelines & Risk Mitigation
In the event of accidental spills, the affected area should be isolated, and personnel must follow spill-response protocols—typically involving gentle wet wiping with suitable cleaning agents and disposal of materials as chemical waste. Direct skin or eye contact should be managed through immediate washing with water and reporting incidents according to safety-office requirements. Training in chemical-handling procedures and familiarity with the product’s MSDS are essential for all users before beginning any research involving Octreotide.

Integration with Multi-Omic & Computational Studies
Integration of Octreotide into multi-omic and computational research pipelines significantly enhances the resolution and interpretability of endocrine and neuroendocrine signaling studies. Because Octreotide modulates well-defined receptor pathways—primarily SSTR2 and SSTR5—it serves as a highly controlled perturbation agent for systems biology analysis. Researchers can map how its receptor activation cascades influence transcriptomic, proteomic, metabolomic, phosphoproteomic, and secretomic signatures across diverse biological contexts.
Multi-Omic Profiling
In transcriptomic studies (bulk RNA-seq or single-cell RNA-seq), Octreotide enables structured investigation of downstream gene-expression responses associated with cAMP suppression, vesicle-trafficking regulation, and hormonal secretion pathways. Somatostatin receptor modulation often produces measurable gene shifts linked to endocrine differentiation, ion-channel regulation, stress-response networks, and tumor-microenvironment remodeling.
Proteomic and phosphoproteomic workflows benefit from Octreotide’s ability to alter key kinase/phosphatase nodes, enabling mapping of SSTR-Gi/o–mediated inhibitory signaling across multiple cell types. LC-MS/MS profiling frequently reveals changes in GPCR-associated scaffolding proteins, vesicle-SNARE regulators, and metabolic enzymes tied to hormone-synthesis control.
In metabolomics, Octreotide supports targeted and untargeted assessments of glucose regulation, amino-acid metabolism, lactate flux, and neuroendocrine metabolic states. Investigators can pair these data with endocrine peptide searches or growth-factor secretion profiles to build a mechanistic multi-layer dataset.
Computational & Systems Biology Integration
Octreotide is particularly valuable in computational modeling, because its receptor-binding kinetics and downstream inhibitory effects are well-characterized. Systems-biology models can incorporate Octreotide as an externally applied perturbation, enabling simulation of endocrine microcircuit behavior, receptor occupancy curves, and hormone-feedback loops using ODE-based or agent-based frameworks.
In network modeling, Octreotide-induced suppression patterns help identify central regulatory nodes in GH, insulin, IGF-1, and angiogenic networks. Using machine learning pipelines, researchers can correlate Octreotide dose-response curves with multi-omic changes to predict receptor expression, ligand-binding variability, or tumor-suppression sensitivity.
Integrated Multi-Omic Pipelines
Modern research increasingly involves cross-platform integration—e.g., combining RNA-seq, mass-spec proteomics, cell-surface receptor profiling, and metabolite flux analysis. Octreotide fits seamlessly into these workflows as a reproducible, tunable molecular control that generates clean perturbation signatures. These datasets feed into computational frameworks to create predictive models for endocrine signaling, tumor responsiveness, or GPCR network adaptation.
Imaging, Spatial-Omics & Receptor Mapping
Fluorescently labeled or radiolabeled Octreotide analogs further support spatial-omics by enabling direct visualization of SSTR distribution in tissues or 3D organoids. When combined with spatial transcriptomics or multiplex immunostaining, researchers can assess how Octreotide reshapes local endocrine microenvironments, especially in neuroendocrine tumor systems.

Shipping Guarantee
All Octreotide shipments use validated cold-chain packaging (2–8 °C), moisture-protected containers, and tamper-evident sealing. Documentation includes COA, MSDS, batch records, and tracked delivery data to ensure full traceability and product stability throughout transport. Additional insulated or dry-ice options are available for extreme-temperature regions.
Trade Assurance
Produced in a GMP-aligned facility, Octreotide undergoes strict QC, including HPLC purity verification, peptide mapping, and microbial load testing. Researchers may request bulk quantities, OEM customization, or institution-specific packaging. Dedicated QC and logistics teams ensure consistent purity, performance reliability, and global supply support.
Payment Support
Supported payment methods include corporate bank transfer, PayPal, major credit cards, and digital-asset transactions for pre-approved institutions. Volume orders may qualify for flexible billing cycles, scheduled purchasing programs, or long-term supply agreements.
Disclaimer
Octreotide (CAS 83150-76-9) is for laboratory research use only.
Not for human or veterinary use.
Researchers must follow institutional, legal, and biosafety regulations when handling, storing, and disposing of this material.
Keywords
Octreotide, freeze-dried powder, somatostatin analog, peptide research, receptor binding, laboratory-only peptide, CAS 83150-76-9, high purity peptide, factory manufactured peptide, wholesale peptide supply
References
Patel, Y. C. Somatostatin and its Receptor Family. Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology, 1999;20(3):157–198.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10433861Lamberts, S. W., et al. Octreotide: Mechanisms of Action and Research Applications. Endocrine Reviews, 1996;17(4):501–537.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8897020Reisine, T., & Bell, G. I. Molecular Biology of Somatostatin Receptors. Endocrine Reviews, 1995;16(4):427–442.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8521778Weckbecker, G., et al. Opportunities in Somatostatin Receptor Pharmacology: Insights from Octreotide Analogs. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 2003;2(12):999–1017.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14654796Ben-Shlomo, A., & Melmed, S. Somatostatin Analogs and Signaling Pathways in Endocrine Research. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2001;108(6):799–804.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11560946Bruns, C., et al. Somatostatin Receptor Subtype Selectivity of Octreotide and Related Analogs. European Journal of Pharmacology, 1994;262(1-2):17–25.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7957610Hoyer, D., et al. Classification and Nomenclature of Somatostatin Receptors. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 1995;16(3):86–88.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7792931Olias, G., et al. Somatostatin Receptors and Receptor Signaling: Molecular Mechanisms and Functional Regulation. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, 2004;32(3):453–474.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15072552Csaba, Z., & Dournaud, P. SSTR2 and SSTR5 Distribution in Neuroendocrine Systems: Mechanistic Insights Relevant to Octreotide. Neuroscience, 2001;106(1):233–254.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11535309Shimon, I., et al. Somatostatin Receptor Signaling Diversity and Functional Implications in Endocrine Models. Endocrinology, 1997;138(4):1461–1469.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9075688Schonbrunn, A. Selective Somatostatin Receptor Modulation: From Molecular Pharmacology to Research Applications. Annual Review of Physiology, 1999;61:257–281.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10099692
Additional information
| Weight | 1 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 26 × 23 × 26 cm |
1. What is Octreotide and how is it typically used in research?
Octreotide is a synthetic octapeptide analog of somatostatin widely used in receptor-binding studies, endocrine signaling assays, and tumor biology research. Its long half-life and high affinity for SSTR2 and SSTR5 make it ideal for mechanistic experiments, in vitro modeling, and radiolabeled tracer development.
2. What is the purity of your Octreotide freeze-dried powder?
Our factory-manufactured Octreotide is produced under GMP-aligned conditions with ≥98% purity verified by HPLC, MS, and peptide mapping. Each batch includes a COA and full analytical documentation.
3. How should Octreotide lyophilized powder be reconstituted for experiments?
Reconstitute the powder using sterile water, PBS, or low-ionic buffer depending on assay requirements. Gentle vortexing is recommended. Avoid extended exposure to room temperature to maintain peptide stability.
4. What is the recommended storage temperature after reconstitution?
For short-term use (≤7 days), store aliquoted solutions at 2–8 °C. For longer-term storage, freeze at –20 °C or –80 °C to preserve biological activity.
5. Does Octreotide require sterile handling?
Yes. All peptide manipulations should be conducted in sterile conditions to prevent contamination artifacts in cell-based experiments, receptor assays, or secretory pathway studies.
6. Can Octreotide be used in animal models?
Yes, but only for approved research protocols. It is commonly used in endocrine tumor models, metabolic disorder models, gastrointestinal motility models, and neuroendocrine pathway studies.
7. Is this Octreotide suitable for radiolabeling or tracer studies?
Yes. The high purity, low water content, and minimal excipient profile make it suitable for ^111In, ^68Ga, and ^177Lu labeling, as well as fluorescence-tagging strategies.
8. What are the solubility characteristics of Octreotide?
Octreotide dissolves readily in aqueous buffers (pH 4–7). Solubility decreases in highly alkaline solutions. Mild heating (<40 °C) may assist dissolution but is not recommended for routine use.
9. Can I request custom peptide modifications or bulk manufacturing?
Yes. We offer OEM/ODM customization including acetylation, amidation, PEGylation, fluorescent labeling, and kilogram-scale synthesis with competitive factory pricing.
10. How is Octreotide shipped to maintain peptide integrity?
Shipments use validated cold-chain systems (2–8 °C) with insulation, moisture protection, and tamper-evident seals. Bulk orders may use dry-ice logistics when required.
11. What analytical data is provided with each batch?
Each order includes a COA, MS spectrum, HPLC chromatogram, peptide mapping, residual solvent analysis, and endotoxin testing (where applicable).
12. Is Octreotide stable at room temperature during shipment?
Yes. Stability studies show the lyophilized powder remains stable for short transport windows. However, products are shipped refrigerated to ensure maximal integrity.
13. Are there any special precautions for handling peptides like Octreotide?
Wear gloves, lab coat, and eye protection. Avoid inhalation or contact with mucous membranes. Use calibrated tools to prevent dosing inaccuracies during experiments.
14. Does this product contain any additives, fillers, or excipients?
No. The freeze-dried powder contains pure Octreotide peptide without stabilizers or additional components unless specifically requested in custom formulations.


















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.