No products in the cart.
Sale
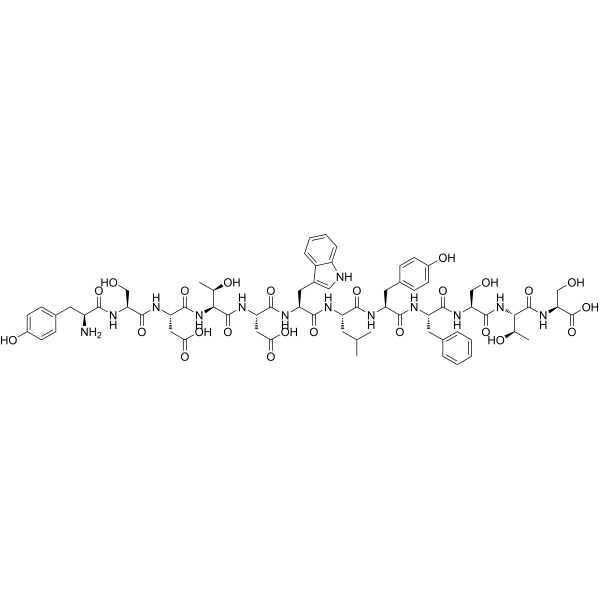
Pep-10L Peptide | CAS 1159846-95-3 | GPVI Antagonist for Anti-Thrombotic Research
Original price was: $38.00.$27.00Current price is: $27.00.
Pep-10L peptide is a selective glycoprotein VI (GPVI) antagonist that inhibits platelet activation induced by collagen and related ligands. It exhibits anti-thrombotic properties by disrupting GPVI-mediated signaling, making it a key research tool for studying platelet aggregation, thrombosis, and cardiovascular diseases.
Description
Contents
hide
Product Description
Pep-10L peptide is a synthetic research peptide identified as a selective antagonist of glycoprotein VI (GPVI)—a critical platelet receptor for collagen involved in thrombus formation and hemostasis. By binding competitively to GPVI and blocking its interaction with collagen or collagen-mimetic ligands, Pep-10L peptide inhibits platelet activation and aggregation, thereby exerting anti-thrombotic activity without severely impairing normal hemostasis.
Scientific Background
Platelets play an essential role in maintaining vascular integrity, responding to endothelial injury through adhesion, activation, and aggregation. While this process is vital for preventing bleeding, excessive or uncontrolled platelet activation leads to pathological thrombosis, contributing to diseases such as myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, and venous thromboembolism.
Among the receptors on platelet membranes, glycoprotein VI (GPVI) is the principal signaling receptor for collagen and collagen-like structures such as convulxin, CRP (collagen-related peptide), and GPO (glycoprotein-binding peptides). GPVI-mediated activation triggers downstream signaling cascades involving Src-family kinases, Syk, and PLCγ2, ultimately resulting in intracellular calcium release and platelet aggregation.
Pep-10L peptide functions as a competitive inhibitor of GPVI, preventing the receptor from binding to collagen fibrils. By disrupting this interaction, Pep-10L peptide effectively attenuates platelet activation and reduces thrombus formation in experimental settings, without the extensive bleeding risks often associated with other platelet inhibitors such as aspirin or P2Y₁₂ antagonists.
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Pep-10L Peptide |
| CAS Number | 1159846-95-3 |
| Synonyms | GPVI Antagonist Peptide; Anti-thrombotic Peptide 10L; GPVI Binding Inhibitor |
| Molecular Formula | — |
| Target | Glycoprotein VI (GPVI) |
| Ki Values | 180 μM (CRP), 225 μM (GPO-1), 179 μM (Type I Collagen) |
| Mechanism | GPVI receptor antagonism, inhibition of collagen-mediated platelet activation |
| Biological Effects | Anti-thrombotic, anti-platelet aggregation |
| Formulation | Synthetic peptide (lyophilized powder) |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder |
| Purity | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, DMSO, and PBS |
| Storage Conditions | -20°C, desiccated, protected from light |
| Applications | Cardiovascular research, thrombosis modeling, platelet biology |
| Stability | Stable for 24 months under recommended conditions |
| QC Tests | HPLC, Mass Spectrometry, Amino Acid Analysis |
Mechanism of Action
Pep-10L peptide’s mechanism of action centers on selective inhibition of GPVI-collagen binding, which is critical for platelet activation during vascular injury and thrombus formation.
1. GPVI-Collagen Interaction Blockade
GPVI is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein found exclusively on platelets and megakaryocytes. It functions as the primary collagen receptor, triggering signal transduction when platelets encounter exposed collagen following endothelial disruption.
Pep-10L peptide binds to the extracellular domain of GPVI, occupying or sterically hindering the collagen-binding interface. This interference blocks the association between GPVI and its natural ligands—CRP, GPO-1, and Type I collagen—each of which contributes to different aspects of platelet adhesion and activation.
2. Signal Transduction Inhibition
By antagonizing GPVI, Pep-10L peptide disrupts downstream phosphorylation events mediated by Src-family kinases (Fyn and Lyn) and Syk kinase, thereby inhibiting the activation of PLCγ2 and reducing cytosolic Ca²⁺ mobilization. The end result is diminished platelet granule release and reduced integrin αIIbβ3 activation, both essential for platelet aggregation.
3. Functional Outcomes in Research Models
Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation: Demonstrates significant inhibition of collagen-induced platelet clumping in vitro.
Reduction in Thrombus Formation: Reduces thrombus size and stability in collagen-dependent thrombosis models.
Maintenance of Hemostasis: Exhibits minimal prolongation of bleeding time, highlighting its selectivity for GPVI over other platelet pathways.
Reversibility: Inhibition is reversible upon peptide removal, making it suitable for controlled experimental designs.
4. Therapeutic and Research Potential
The unique selectivity of Pep-10L peptide makes it a valuable research tool for:
Investigating GPVI signaling mechanisms in platelet activation.
Developing novel anti-thrombotic strategies with lower bleeding risks.
Studying platelet-collagen interactions in cardiovascular pathology.
Screening potential GPVI-targeting compounds or combination therapies.

Side Effects
Pep-10L peptide has not been evaluated for clinical use, but research observations and in vitro data suggest potential laboratory effects:
Reduced Platelet Aggregation: Expected due to GPVI antagonism; reversible upon peptide withdrawal.
Minor Bleeding Propensity: Prolonged clotting time may be observed in overexposed samples.
No Cytotoxicity: No significant cytotoxic or off-target cellular effects have been reported at research concentrations.
Protein Binding Interference: May interfere with collagen-binding assays or other peptide-protein binding studies if used in high concentrations.
Proper laboratory handling and dosage optimization are recommended to maintain experimental accuracy.
Disclaimer
For research use only. Not intended for human or veterinary use. Do not use in diagnostic or therapeutic applications. Handle with appropriate laboratory safety procedures.
Keywords
Pep-10L peptide, GPVI antagonist, anti-thrombotic peptide, platelet activation inhibitor, collagen-binding inhibitor, cardiovascular research peptide, platelet aggregation blockade, thrombus formation research.
Shipping Guarantee
All shipments are secured, temperature-controlled, and insured against loss or damage during transit.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 56 × 43 × 56 cm |
What is Pep-10L peptide?
Pep-10L peptide is a synthetic GPVI antagonist that inhibits collagen-mediated platelet activation.
What are its Ki values?
180 μM for CRP, 225 μM for GPO-1, and 179 μM for Type I collagen.
What is GPVI and why is it important?
GPVI is a platelet collagen receptor essential for thrombus formation following vascular injury.
How does Pep-10L peptide prevent thrombosis?
It blocks GPVI-collagen binding, preventing platelet activation and aggregation.
Does it affect normal hemostasis?
It has minimal effects on normal bleeding time, showing good selectivity.
Can it be used with other anti-platelet agents?
Yes, in combination research studies to assess synergistic anti-thrombotic effects.
Is Pep-10L peptide stable in solution?
Short-term stability in aqueous solution; long-term storage recommended at -20°C.
Does it affect other platelet receptors?
It specifically targets GPVI and shows little or no effect on GPIb or P2Y₁₂.
Can it be used for in vivo studies?
Yes, suitable for preclinical thrombosis and platelet biology research models.
What’s the main application area?
Cardiovascular disease, thrombosis research, and platelet receptor biology.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.