No products in the cart.
Sale
Pexiganan (MSI-78 Free Base) 10mg – Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Peptide
Original price was: $56.00.$53.00Current price is: $53.00.
Pexiganan (MSI-78 Free Base) is a synthetic broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptide supplied as a high-purity lyophilized powder for research use. It is widely studied in microbiology and antimicrobial mechanism research.
Description
Product Description
Pexiganan (MSI-78 Free Base) is a synthetic antimicrobial peptide derived from magainin analogs and is provided in lyophilized powder form for research and laboratory use only. It is characterized by strong amphipathic and cationic properties, making it a widely used model compound in studies of antimicrobial peptide (AMP) activity.
In research settings, Pexiganan is commonly employed to investigate bacterial membrane disruption mechanisms, peptide–membrane interactions, and resistance-related phenomena across a broad range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative microorganisms. Its well-defined amino acid sequence and reproducible physicochemical profile make it suitable for controlled in vitro antimicrobial and biophysical studies.
Product Specifications
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Pexiganan (MSI-78 Free Base) |
| Synonyms | MSI-78, Pexiganan |
| CAS Number | Not officially assigned |
| Molecular Formula | C107H202N34O26 |
| Molecular Weight | ~2477.1 g/mol |
| Amino Acid Sequence | GIGKFLKKAKKFGKAFVKILKK |
| Peptide Type | Synthetic linear antimicrobial peptide |
| Form | Lyophilized powder |
| Purity | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Strength Options | 1 mg / 5 mg / 10 mg |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder |
| Identity Verification | HPLC, Mass Spectrometry |
| Solubility | Soluble in water |
| Packaging | Sterile, sealed research vials |
| Storage Condition | −20 °C, dry and light-protected |
| Intended Use | Research use only (RUO) |
Applications
Pexiganan (MSI-78 Free Base) is commonly used in the following research areas:
Antimicrobial peptide (AMP) mechanism studies
Bacterial membrane disruption and permeability research
Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria assays
Peptide–lipid interaction and biophysical studies
Antimicrobial resistance and tolerance investigations
For mechanistic and pathway-level analysis, refer to the corresponding Pexiganan (MSI-78) 03 template research article.
Usage & Reconstitution Guidelines
Pexiganan (MSI-78 Free Base) should be handled using standard sterile laboratory techniques. The lyophilized powder is typically reconstituted in sterile water or suitable aqueous buffers to prepare stock solutions for experimental use.
Aliquoting after reconstitution is recommended to minimize repeated freeze–thaw cycles. Experimental concentrations should be optimized according to specific microbial models and research objectives.
Storage & Stability
Store unopened vials at −8 °C
Protect from moisture and light
Avoid repeated freeze–thaw cycles
Properly stored aliquots remain stable for extended research periods
Trade Assurance
Each batch of Pexiganan (MSI-78 Free Base) undergoes internal quality verification prior to release.
Identity and purity confirmation
Specification conformity checks
Batch consistency review
Lot-level traceability documentation
Contact & Inquiry
For inquiries regarding Pexiganan (MSI-78 Free Base) specifications, bulk availability, technical documentation, or research collaboration support, please contact our team through the available inquiry channels.
Our support team can assist with:
Bulk quantity and packaging options
Product specifications and batch information
Technical documentation requests (COA, HPLC, MS)
Order process and logistics coordination
Disclaimer
This product is intended for research and laboratory use only.
Not for human or veterinary use.
All handling and experimental applications must comply with applicable laws, institutional policies, and laboratory safety regulations.
Additional information
| Weight | 1 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 26 × 42 × 26 cm |
1. What is Pexiganan mainly used for in research?
It is primarily used to study antimicrobial peptide mechanisms and bacterial membrane disruption.
2. Is Pexiganan suitable for in vitro antimicrobial assays?
Yes, it is widely applied in in vitro microbiological and antimicrobial activity studies.
3. What purity level is provided?
The product is supplied with a purity of ≥98%, verified by HPLC.
4. How is the identity of Pexiganan confirmed?
Identity is verified using HPLC and mass spectrometry.
5. How should Pexiganan be reconstituted?
It is typically reconstituted in sterile water or appropriate aqueous buffers under aseptic conditions.
6. What storage conditions are recommended?
Store at −20 °C, protected from light and moisture.
7. Can Pexiganan be used in membrane interaction studies?
Yes, it is commonly used in peptide–lipid and membrane permeability research.
8. Is this product intended for clinical or therapeutic use?
No. It is supplied strictly for research and laboratory use only.
9. What factors should be considered when designing experiments?
Researchers should consider peptide concentration, microbial strain selection, and assay conditions.
10. Can documentation be provided for this product?
Yes, documentation such as COA and analytical reports may be provided upon request.

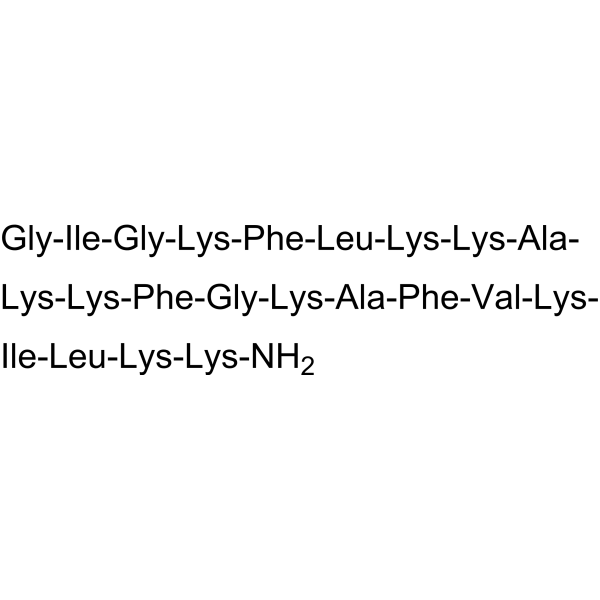












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.