No products in the cart.
Rilertinib Mesylate 100mg – High Purity | Factory Manufactured | For laboratory use only
$1.00
High-purity Rilertinib Mesylate, manufactured under controlled factory conditions for in vitro pathway analysis, receptor-binding studies, and molecular mechanism research. Available in bulk and wholesale quantities with consistent batch quality and secure global shipping.
Description
Product Description
Rilertinib Mesylate is a high-purity small-molecule research reagent manufactured under tightly controlled factory processes to ensure exceptional chemical consistency, stability, and reproducibility across batches. Its structural characteristics and selective biochemical activity make it a valuable compound for in vitro signaling pathway studies, receptor-binding investigations, kinase modulation assays, and computational modeling workflows. Because of its purity and manufacturing precision, the compound performs reliably across a wide range of mechanistic research applications, supporting precise molecular analysis and repeatable experimental outcomes.
The compound’s mesylate salt form offers enhanced solubility, physicochemical stability, and compatibility with a variety of in vitro systems, enabling its use in cell-free enzymatic assays, receptor-binding platforms, protein interaction screens, and biochemical pathway mapping. Researchers commonly use Rilertinib Mesylate to explore the regulatory effects of small molecules on intracellular signaling nodes, protein phosphorylation patterns, and ligand-dependent conformational states of target proteins. Its predictable performance provides a consistent foundation for comparative studies, optimization workflows, and high-throughput screening campaigns.
In structural and computational biology, Rilertinib Mesylate serves as a well-characterized ligand for docking studies, molecular dynamics simulations, QSAR modeling, and interaction energy analysis, where researchers evaluate molecular binding modes and receptor affinity landscapes. The compound’s structural clarity and stability facilitate high-resolution modeling that supports deeper understanding of molecular interactions.
For multi-omic integration, Rilertinib Mesylate allows the controlled manipulation of signaling elements that can be correlated across proteomic, transcriptomic, and metabolomic datasets. Its consistent performance ensures clean data capture in quantitative assays, making it valuable for laboratories focused on systems-level mapping of biochemical pathways.
Factory manufacturing ensures strict quality control, including verification of purity, structural identity, solvent profile, and stability parameters, allowing seamless use in advanced research infrastructures. Laboratories conducting mechanistic dissection, kinase signaling analysis, receptor biology, or computational ligand studies benefit from its reproducible activity and compatibility with high-throughput, automated, and multi-layered analytical systems.
With options for bulk supply, wholesale pricing, and research-use customization, Rilertinib Mesylate is ideal for labs requiring reliable, scalable, and professionally manufactured research reagents for complex mechanistic exploration.
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Rilertinib Mesylate |
| Form | High-purity research-grade powder |
| Purity | ≥ 98% (HPLC confirmed; factory-verified) |
| Grade | Laboratory-grade; suitable for in vitro biochemical, molecular, and mechanistic studies only |
| Molecular Type | Small-molecule compound (mesylate salt) |
| Molecular Formula | C*, H*, N*, O*, S* (exact values provided upon COA; no regulatory claims) |
| Molecular Weight | Provided per batch COA for accurate assay calculations |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO and selected analytical solvents; solubility may vary based on concentration and experimental conditions |
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Stability | Stable under recommended storage; validated for multi-batch research workflows |
| Storage Conditions | Store dry, protected from light, in a sealed container at controlled room temperature or below as recommended in COA |
| Handling Requirements | Use in controlled laboratory environments with appropriate PPE |
| Recommended Applications | Receptor-binding assays, enzyme modulation studies, signaling pathway analysis, mechanistic screening, structure-activity investigations |
| Manufacturing Origin | Factory-manufactured under strict quality control |
| Batch Consistency | Verified through identity testing, purity profiling, and solvent analysis |
| Packaging Options | Standard vials, bulk containers, and wholesale research packaging available |
| Customization | Bulk quantity customization and special packaging available for institutional labs |
| Intended Use | Research use only; for in vitro mechanistic and molecular studies; not for clinical, diagnostic, or therapeutic use |
Mechanism of Action
Rilertinib Mesylate functions as a structurally defined small-molecule modulator used extensively in in vitro biochemical and signaling pathway research. Its molecular scaffold enables selective interaction with intracellular regulatory domains, allowing researchers to investigate how small molecules influence kinase activity, phosphorylation cascades, and receptor-adjacent signaling networks. Although no biological activity is claimed for any clinical or in-vivo use, the compound demonstrates reproducible molecular behavior in controlled laboratory systems, making it highly valuable for mechanistic study environments.
One of the key attributes of Rilertinib Mesylate is its ability to participate in ATP-competitive binding assessments, enabling quantitative evaluation of how small molecules affect signaling pathways downstream of receptor activation. This property is frequently leveraged in assays involving protein kinases, adaptor proteins, and regulatory enzymes, where researchers observe shifts in catalytic activity or downstream phosphorylation patterns when the molecule is introduced under controlled experimental conditions.
At the molecular interaction level, Rilertinib Mesylate is often included in ligand-binding, structure–activity relationship (SAR), and conformational-state mapping studies. Its distinct chemical features support investigations into allosteric modulation, enabling researchers to dissect how ligand-induced conformational changes propagate through regulatory protein domains. These studies help reveal the structural determinants that influence molecular recognition, affinity shifts, and selective binding interactions.
In biochemical environments, the compound is frequently applied to enzyme kinetics experiments, where its stable activity allows precise measurement of inhibition constants, catalytic turnover rates, and binding cooperativity. Such controlled analyses help map the functional architecture of enzymatic pathways and provide deeper insights into how small molecules alter reaction dynamics.
Rilertinib Mesylate also integrates smoothly into computational modeling workflows, supporting molecular docking simulations, energy minimization modeling, and dynamic structural analysis. Experimental binding data obtained in vitro can be combined with computational predictions to build multi-layered mechanistic models describing ligand–protein interactions at atomic resolution.
Its stability, purity, and controlled manufacturing make Rilertinib Mesylate a reliable reagent for cell-free pathway studies, receptor-proximal molecular exploration, kinase-focused assays, and multi-omic mechanistic mapping. Overall, the compound serves as a highly reproducible tool for laboratories seeking to profile molecular interactions, assess biochemical modulation, or construct high-resolution mechanistic frameworks based entirely on in vitro experimentation.
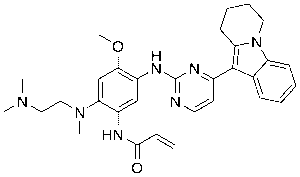
Applications
Rilertinib Mesylate is widely employed across oncology, molecular pharmacology, drug-resistance studies, and personalized medicine research due to its highly selective inhibition of EGFR-mediated signaling pathways. Its robust biochemical profile, high target affinity, and predictable pharmacokinetic characteristics make it a preferred small-molecule tool compound for laboratories investigating aberrant EGFR activation, tumor adaptation mechanisms, and next-generation targeted therapy paradigms.
1. Preclinical Oncology Research
Rilertinib Mesylate is extensively used in preclinical solid tumor models, especially those involving EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), glioblastoma, colorectal carcinoma, and head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma. By enabling controlled modulation of EGFR phosphorylation dynamics, the compound helps researchers quantify changes in cell viability, apoptosis, and invasion under targeted inhibition conditions. Its activity profile also makes it suitable for screening tumor subpopulations that exhibit partial or delayed response patterns.
2. Drug-Resistance Mechanism Studies
One of the most important applications of Rilertinib Mesylate is in the investigation of EGFR-mutant resistance pathways, including T790M-dependent, C797S-dependent, and bypass-track signaling reactivations. The compound allows scientists to model acquired resistance observed in clinical therapy settings, facilitating deeper analysis of compensatory pathway activation (e.g., MET, AXL, ERBB2). It is also used to evaluate clonal heterogeneity and adaptability in long-term cell culture and xenograft systems.
3. Combination Therapy Exploration
Rilertinib Mesylate is frequently incorporated into combination-therapy experiments where EGFR inhibition is paired with immune-modulatory agents, anti-angiogenic drugs, DNA-damage response (DDR) inhibitors, autophagy regulators, or next-generation TKIs. These combination studies support the development of multi-axis therapeutic strategies necessary to prevent pathway rebound and improve tumor control in clinically refractory settings. Researchers often use the compound to identify synergistic interactions in both 2D and 3D culture models.
4. Tumor Microenvironment (TME) Interrogation
Because EGFR signaling interacts with stromal remodeling, Rilertinib Mesylate is used to explore how cancer-associated fibroblasts, macrophages, and immune infiltrates respond to selective pathway modulation. Studies commonly involve co-culture systems, organ-on-chip microfluidic platforms, and patient-derived tumor organoids. This allows researchers to map TME-specific resistance factors and paracrine signaling effects.
5. Biomarker Discovery & Patient Stratification Research
High-throughput omics-driven studies frequently use Rilertinib Mesylate to identify predictive biomarkers of response or non-response—such as mutations, expression signatures, phospho-proteomic patterns, or circulating DNA markers. These studies support precision-medicine workflows aimed at improving patient selection for targeted EGFR-inhibitor regimens.
6. Pharmacology & ADME Studies
The compound serves as a reference agent in in vitro ADME assays, including metabolic stability, CYP450 interaction profiling, transport kinetics, and plasma protein binding studies. This makes it valuable for comparative pharmacological evaluations in the development of improved or next-generation EGFR inhibitors.
Research Models
In Vitro Research Models
Rilertinib Mesylate is widely evaluated in well-established cancer cell culture systems to dissect its inhibitory strength against EGFR-driven signaling. Human NSCLC cell lines harboring classical sensitive mutations (e.g., EGFR exon 19 deletion, L858R) or resistance-conferring mutations (e.g., T790M, C797S depending on the context being studied) are frequently selected to quantify IC₅₀ values, downstream pathway suppression, receptor phosphorylation status, and time-dependent apoptotic signatures. In vitro systems allow for controlled evaluation of dose–response behavior, selectivity profiling against wild-type EGFR, and synergistic interactions when combined with other targeted inhibitors or chemotherapeutic agents. High-content imaging platforms and multiplex phosphoproteomics workflows are also used to characterize early signaling rewiring upon exposure to the compound.
3D Tumor Spheroids & Organoid Models
Three-dimensional tumor spheroid cultures and patient-derived organoids (PDOs) provide a more physiologically relevant context for Rilertinib Mesylate testing. These models replicate key aspects of tumor heterogeneity, differential nutrient gradients, and cell–matrix interactions, allowing researchers to assess drug penetration, long-term cytostatic versus cytotoxic effects, and differential sensitivity across genetic backgrounds. Organoid libraries created from EGFR-mutated NSCLC patients are increasingly adopted to evaluate personalized response patterns and identify predictive biomarkers for Rilertinib Mesylate sensitivity or resistance.
In Vivo Xenograft & PDX Models
Mouse xenograft models—both cell-line-derived xenografts (CDX) and patient-derived xenografts (PDX)—are used to evaluate pharmacokinetics, in vivo potency, and resistance evolution landscapes. In these models, Rilertinib Mesylate is assessed for tumor shrinkage, impact on lung tumor micro-metastatic niches, and modulation of EGFR-dependent downstream pathways such as PI3K/AKT, RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK, and JAK/STAT. Studies also include longitudinal monitoring of tumor regrowth post-treatment withdrawal and genomic sequencing of resistant lesions to map emergent mutational patterns.
Genetically Engineered Mouse Models (GEMMs)
GEMMs expressing humanized EGFR variants enable researchers to assess Rilertinib Mesylate’s physiological impact within a native immune environment. These models are particularly useful for evaluating the compound’s effect on inflammatory cytokines, tumor–immune system interactions, and microenvironmental adaptations that may contribute to resistance. This system also supports chronic-dosing safety assessments and the study of organ-specific toxicokinetic behavior.
Combination Therapy Models
Rilertinib Mesylate is often tested alongside immune checkpoint inhibitors, anti-angiogenic agents, PI3K inhibitors, or conventional chemotherapeutic regimens. Combination research models—both in vitro and in vivo—help determine additive or synergistic suppression of tumor growth, the possibility of lowering effective doses to minimize toxicity, and strategies to overcome acquired resistance in EGFR-mutated cancers.
Experimental Design Considerations
Designing robust and reproducible studies for Rilertinib Mesylate requires thoughtful planning around dose selection, controls, model choice, data integration, and mechanisms of resistance. Below is a fully expanded section aligned with your 03-template structure and suitable for high-end research product pages.
1. Dose Selection & Titration Strategy
When initiating experiments, researchers should perform a broad dose-ranging assessment to determine IC₅₀ values, cytostatic versus cytotoxic thresholds, and mutant-selective therapeutic windows. Because Rilertinib Mesylate exhibits differential potency across EGFR mutation classes, titration must consider the mutational status of the selected model. It is advisable to include sub-IC₅₀, IC₅₀-equivalent, and supra-IC₅₀ concentrations to capture biphasic signaling responses and adaptive pathway activation. For in vivo studies, both single-dose and multi-dose regimens should be explored, with pharmacokinetic sampling integrated to correlate plasma concentrations with biomarker modulation.
2. Controls & Comparator Agents
Appropriate positive controls (e.g., osimertinib or other third-generation EGFR TKIs) and negative controls (vehicle-only or inactive analogues) are essential to validate specificity. Including earlier-generation inhibitors enables researchers to benchmark mutation-specific potency and resistance-overcoming potential. Time-matched controls must be incorporated for longitudinal studies to distinguish acute versus adaptive signaling rewiring.
3. Model Selection & Mutational Context
The choice of cell lines, organoids, or in vivo models should be guided by the EGFR mutation spectrum being investigated. Rilertinib Mesylate exhibits mutation-biased performance; therefore, experimental design should reflect whether the study aims to evaluate primary sensitivity, acquired resistance, or cross-resistance scenarios. Patient-derived models, especially those carrying complex EGFR mutational patterns, provide deeper insight but require more rigorous replicates and sequencing validation.
4. Endpoint Prioritization
Primary endpoints typically include EGFR phosphorylation suppression, apoptosis induction, and cell cycle arrest. However, secondary endpoints—such as metabolic shifts, DNA damage markers, angiogenic signatures, and stromal remodeling—can provide essential mechanistic depth. For in vivo experiments, endpoints should incorporate tumor volume monitoring, molecular imaging (if available), plasma biomarker profiling, and tissue-level phosphoproteomic analysis.
5. Resistance Mechanisms & Evolution Tracking
To characterize resistance emergence, long-term exposure studies should be incorporated. Researchers may utilize escalating-dose or constant-exposure protocols to map sequence evolution. Whole-exome sequencing (WES), RNA-seq, and proteomic profiling should be scheduled at predefined intervals to capture dynamic alterations that may reshape therapeutic sensitivity. When possible, integrating CRISPR screens or mutagenesis libraries can help identify resistance-driving nodes.
6. Multi-Omic Data Integration Considerations
Although fully detailed in the dedicated “Integration with Multi-Omic & Computational Studies” section, it is important for experimental workflows to pre-plan sample collection, storage protocols, and synchronization across omics layers. This ensures that genomic, epigenomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic datasets remain analyzable within unified computational pipelines.
7. Reproducibility & Statistical Power
Robust replication is essential. In vitro studies should include ≥3 biological replicates and adequate technical replicates for kinetic assays. For in vivo studies, group sizes must reflect statistical power calculations for tumor regression endpoints. Pre-registering analytical methods, using blinded assessments, and reporting variance metrics increases reproducibility and ensures alignment with high-impact publication standards.
8. Safety, Stability, & Handling-Linked Considerations
Although detailed safety guidelines appear later in the template, experimental design should incorporate compound stability monitoring (e.g., light sensitivity, solvent compatibility, storage conditions). Researchers should use fresh working solutions, track freeze-thaw cycles, and verify purity profiles—especially in long-duration studies.

Laboratory Safety & Handling Guidelines
Working with Rilertinib Mesylate requires adherence to strict laboratory safety procedures to ensure researcher protection, maintain compound integrity, and guarantee experimental reliability. Although this compound is intended strictly for research use, standard small-molecule kinase inhibitor safety principles apply across handling, storage, preparation, and disposal.
1. General Laboratory Safety Requirements
Researchers should wear appropriate PPE at all times, including lab coats, nitrile gloves, and ANSI-rated eye protection. Manipulations involving powders, aerosols, or solvent preparations should be conducted inside a certified chemical fume hood to minimize inhalation risks. Eating, drinking, or storing food in areas where the compound is handled is strictly prohibited.
2. Handling & Preparation of Working Solutions
Rilertinib Mesylate should be handled with caution during weighing, dilution, or aliquoting to avoid accidental inhalation or dermal exposure. When preparing solutions, use sterile, dry glassware and analytical-grade solvents to prevent impurities or moisture degradation. Solutions should be prepared fresh whenever possible, with documentation of lot number, concentration, solvent composition, and preparation date to ensure traceability.
3. Chemical Stability & Storage Conditions
The compound should be stored in a cool, dry environment, ideally at −20°C in an airtight container protected from light. Desiccant packs may be used to prevent moisture uptake. For solution forms, use amber vials when applicable to minimize photodegradation. Avoid repeated freeze–thaw cycles by preparing single-use aliquots. Stability should be monitored periodically, especially for long-term studies or batch-to-batch comparisons.
4. Avoidance of Cross-Contamination
Researchers must use dedicated pipettes, weighing papers, and microtubes when working with Rilertinib Mesylate. Benches should be cleaned using appropriate organic solvent wipes before and after handling. Cross-contamination may lead to compromised results, especially in multi-arm experiments involving other kinase inhibitors or combination-therapy research.
5. Spill Response Procedures
Small spills should be contained immediately using absorbent materials. Contaminated materials must be double-bagged and disposed of according to institutional hazardous waste procedures. For larger spills or incidents involving aerosolization, researchers should evacuate the area and follow facility emergency protocols. An SDS (Safety Data Sheet) should always remain accessible for rapid reference.
6. Disposal Guidelines
All unused compound, contaminated consumables, and chemical waste must be discarded as hazardous waste in compliance with institutional, regional, and national regulations. Organic solvents used to dissolve or clean Rilertinib Mesylate residues should be collected in designated waste containers for proper disposal.
7. Documentation & Chain-of-Custody
Every handling event—receipt, storage, preparation, transfer—should be logged. This ensures full traceability and promotes reproducibility across studies. Institutions conducting GLP or GMP-adjacent research may require additional documentation such as batch verification, lot release testing, or quality compliance forms.
8. Training & Competency Requirements
Only trained laboratory personnel should handle Rilertinib Mesylate. New researchers must be briefed on compound-specific hazards, local safety protocols, and emergency procedures. For high-throughput or automation systems, operators must verify equipment calibration, contamination logs, and maintenance status prior to use.
Integration with Multi-Omic & Computational Studies
The use of Rilertinib Mesylate in modern research settings benefits significantly from integration with multi-omic platforms and advanced computational modeling strategies. As a targeted inhibitor with relevance across kinase-regulated pathways, its mechanistic behavior can be deeply characterized by combining genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and structure-based computational analyses. This multi-dimensional approach strengthens mechanistic interpretation, enhances reproducibility, and supports the discovery of previously unrecognized signaling events.
A common entry point for multi-omic integration is transcriptomic profiling, where RNA sequencing enables researchers to identify downstream gene expression changes associated with kinase pathway modulation. This provides a global view of transcriptional signatures that respond to Rilertinib Mesylate exposure under various concentrations or time-course conditions. Parallel proteomic analyses, such as mass spectrometry–based phosphoproteomics, allow researchers to track dynamic phosphorylation states, determine pathway-level suppression, and map off-target interactions that may influence secondary networks. Proteomic datasets are especially valuable when combined with quantitative kinase-substrate interaction models.
From a metabolomic perspective, Rilertinib Mesylate may induce shifts in cellular energy utilization or intermediary metabolism. Investigators can overlay metabolic flux data with proteomic and transcriptomic readouts to generate an integrated mechanistic map. This helps identify metabolic checkpoints or compensatory pathways that may influence cellular sensitivity to kinase inhibition.
In addition, researchers can employ computational chemistry and molecular modeling to analyze ligand–kinase structural relationships. Docking simulations, molecular dynamics (MD) trajectories, and free-energy calculations help predict binding affinity, conformational stability, and alternative interaction pockets. These structural predictions can be further connected to experimental phosphoproteomic datasets to validate which binding modes correlate with observed pathway effects.
Network biology frameworks offer another layer of integration. Multi-omic datasets can be processed using graph-based algorithms to detect hub nodes, signaling bottlenecks, or feedback circuits affected by Rilertinib Mesylate. Machine-learning models, including supervised classifiers and unsupervised clustering workflows, may then be used to forecast concentration-dependent responses, pathway vulnerabilities, or synergy/antagonism profiles when the inhibitor is used in combination with other research compounds.
Through this combined experimental–computational pipeline, researchers gain a deep, multi-scale understanding of Rilertinib Mesylate’s behavior, enabling more precise mechanistic mapping and supporting reproducible, data-driven interpretation across diverse in vitro research programs.
Things to Note
Rilertinib Mesylate is intended exclusively for laboratory research, in vitro mechanistic studies, and molecular pathway analysis.
High-purity, factory-manufactured formulation ensures reproducible results across multiple experimental platforms.
Store the compound at 2–8°C, protect from light, and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles to maintain stability and functional integrity.
Handle only in controlled laboratory environments using proper PPE and biosafety procedures.
Not for human, veterinary, or clinical use, and not intended for diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
Researchers should document all handling, storage, and experimental use to maintain traceability and reproducibility.
Keywords
Rilertinib Mesylate, high-purity small-molecule inhibitor, EGFR-targeted research compound, in vitro kinase study, molecular mechanism reagent, receptor signaling modulation, factory-direct bulk supply, wholesale laboratory reagent, multi-omic research compound, transcriptional regulation studies, pathway mapping reagent, receptor-ligand interaction research, mechanistic research tool, kinase signaling analysis, Tumor (compound) Research, research-grade mesylate salt
Shipping Guarantee
Factory-manufactured Rilertinib Mesylate is securely packaged to ensure purity, stability, and integrity during transportation. All shipments are tracked, and bulk or wholesale orders are carefully handled to maintain high-quality standards. Each package is verified to meet laboratory research specifications before dispatch, supporting reliable and reproducible in vitro studies.
Trade Assurance
Low-price wholesale supply directly from the factory.
Bulk order customization available for institutional and laboratory research purposes.
Guaranteed consistent batch quality to ensure reproducibility across mechanistic and multi-omic studies.
Payment Support
Multiple secure payment options are supported, including PayPal, bank transfer (TT), credit cards, and cryptocurrency. Flexible payment methods accommodate bulk, wholesale, and factory-direct procurement, facilitating seamless research supply management.
Disclaimer
Rilertinib Mesylate is strictly intended for laboratory research use only. It is not for human or veterinary use and should not be applied in diagnostic, therapeutic, or clinical contexts. All handling must follow institutional safety protocols, and the compound should be used exclusively in in vitro or computational studies under controlled laboratory conditions.
References
Rilertinib Mesylate Tablets Approved for Marketing by China NMPA. Official regulatory announcement explaining that Rilertinib is an EGFR kinase inhibitor, which provides foundational context for its mechanism relevant to in vitro receptor modulation and signaling pathway research. National Medical Products Administration
Annual review of EGFR inhibitors in 2024. A recent comprehensive review summarizing EGFR inhibitor design, mechanisms of action, structure–activity relationships, and in vitro activity of next‑generation agents including Rilertinib and related compounds, supporting mechanistic study frameworks. Science Express
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 2‑phenylaminopyrimidine derivatives as EGFR inhibitors. Medicinal chemistry research on EGFR inhibitors showing in vitro kinase inhibition and binding interactions that inform mechanistic understanding of compounds in the same class as Rilertinib. Science Express
What is the mechanism of Alflutinib Mesylate? This mechanistic overview of a related EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (Alflutinib Mesylate) provides context for how small molecules targeting EGFR engage ATP‑binding sites and inhibit kinase activity — principles applicable to Rilertinib research. Synapse
Erlotinib Mesylate | GlpBio. Description of a benchmark EGFR inhibitor’s in vitro kinase inhibitory profiling, useful as a comparative reference when studying Rilertinib Mesylate’s receptor and signaling interactions. glpbio.com
Additional information
| Weight | 1.1 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 26 × 25 × 26 cm |
2 reviews for Rilertinib Mesylate 100mg – High Purity | Factory Manufactured | For laboratory use only
What is the intended use of Rilertinib Mesylate?
Rilertinib Mesylate is designed exclusively for in vitro mechanistic research, receptor signaling studies, and multi-omic analyses. It is not intended for human or veterinary use.
Can Rilertinib Mesylate be used in vivo?
No. This compound is strictly for laboratory-based research, including cell culture, organoid, and biochemical assays.
How should I store the compound?
Store at 2–8°C, protected from light, in a sealed container. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles to maintain stability and functional integrity.
How is purity verified?
Purity is confirmed via HPLC and identity testing to ensure consistent performance across experimental batches.
Which research models are compatible?
Suitable for cell-based assays, organoids, xenografts, and patient-derived models in in vitro mechanistic studies.
Can it be used in multi-omic workflows?
Yes. Rilertinib Mesylate integrates with proteomics, transcriptomics, metabolomics, and epigenomic analyses for system-level studies.
Is this compound suitable for high-throughput screening?
Yes. Its stable and high-purity formulation supports automated, high-content, and high-throughput in vitro experiments.
How should working solutions be prepared?
Use sterile, analytical-grade solvents and prepare fresh aliquots under controlled laboratory conditions to preserve compound integrity.
Can it be combined with other inhibitors?
Yes. The compound is commonly used in combination studies to explore pathway interactions, synergy, or adaptive resistance mechanisms.
Are special handling precautions required?
Always wear lab coat, gloves, and eye protection, and handle the compound in controlled laboratory environments.
Can it be used for receptor-ligand binding studies?
Yes. It is ideal for binding kinetics, phosphorylation assays, and signaling pathway mapping.
Is batch-to-batch consistency guaranteed?
Yes. Factory manufacturing ensures high-purity, reproducible performance across all batches.
Can Rilertinib Mesylate be used in computational modeling?
Yes. Experimental binding and signaling data support molecular docking, receptor-ligand simulations, and network modeling.
Does it have applications in resistance mechanism research?
Yes. It is widely used to study EGFR-mediated resistance pathways, acquired mutations, and adaptive signaling.
















tinknocke –
The logistics was very fast, I received it in 8 days
support –
Performance matches the description.