No products in the cart.
Sale
Saralasin – Competitive Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonist (CAS No. 34273-10-4) | GMP Supplier
Original price was: $18.00.$16.00Current price is: $16.00.
Saralasin (CAS No. 34273-10-4) is an octapeptide analog of angiotensin II, functioning as a competitive angiotensin II receptor antagonist with partial agonist activity. Produced under GMP standards, Saralasin is essential for studies in renovascular hypertension and renin-dependent hypertension. Available for bulk and small-scale orders. For laboratory research use only.?If you need to place an order or inquire about wholesale product prices, specifications and uses, please contact our staff?
Description
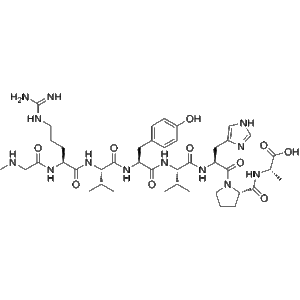
Saralasin, also known as [Sar1, Ala8] Angiotensin II, is a synthetic octapeptide designed as a structural analog of angiotensin II. By binding to angiotensin II receptors, Saralasin acts as a competitive antagonist while also demonstrating partial agonist activity. Its dual functional profile has made it a widely studied molecule in the fields of cardiovascular physiology, hypertension, and renal function regulation.
One of the defining characteristics of Saralasin is its high affinity for angiotensin II receptor binding sites, with a Ki value of 0.32 nM for approximately 74% of the binding sites. This high receptor affinity underscores its ability to effectively block angiotensin II–mediated vasoconstriction while retaining measurable partial agonist activity, which provides valuable insights into receptor signaling dynamics.
As a GMP-manufactured research compound, Saralasin is produced to ensure high purity (98.71%) and consistency across research applications. It has been widely utilized in preclinical research exploring the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), renovascular hypertension, and renin-dependent (angiotensinogenic) hypertension. Its ability to act as both a receptor blocker and weak agonist allows researchers to investigate the fine balance of angiotensin II receptor signaling in vascular and renal pathophysiology.
Saralasin is available in both bulk and smaller research quantities, supporting laboratories engaged in cardiovascular, renal, and hypertension-related investigations.
For laboratory research use only. Not for human consumption.
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Saralasin |
| Synonyms | [Sar1, Ala8] Angiotensin II |
| CAS No. | 34273-10-4 |
| Molecular Formula | C41H64N12O11 |
| Molecular Weight | 909.02 g/mol |
| Purity | 98.71% (HPLC) |
| Form | Lyophilized powder |
| Source | Synthetic peptide |
| Storage Conditions | Store at –20°C, protected from light and moisture |
| Manufacturer | GMP Certified Supplier |
| Applications | Research on renovascular hypertension, renin-dependent hypertension, RAAS studies |
Mechanism of Action & Research Applications
Saralasin exerts its primary pharmacological effect through competitive antagonism at angiotensin II receptors. By displacing angiotensin II from its binding sites, Saralasin prevents vasoconstrictive and hypertensive effects normally induced by angiotensin II. At the same time, its partial agonist activity allows researchers to investigate receptor activation thresholds and partial receptor signaling.
Key research applications of Saralasin include:
Renovascular Hypertension Research – has been widely used as a diagnostic and investigative tool for renovascular hypertension. Its ability to block angiotensin II–induced responses makes it useful in distinguishing renin-dependent from non-renin-dependent forms of hypertension.
Renin-Dependent Hypertension Studies – By antagonizing angiotensin II, Saralasin helps delineate the contribution of RAAS hyperactivity to hypertensive conditions.
RAAS Physiology and Pathophysiology – is valuable for exploring the role of angiotensin II in cardiovascular regulation, renal perfusion, and systemic blood pressure control.
Comparative Pharmacology – Its dual antagonist/partial agonist behavior provides a unique tool for studying receptor pharmacodynamics.
Development & Research Background
The development of Saralasin represents a critical milestone in the pharmacological investigation of the renin–angiotensin system. As one of the earliest angiotensin II analogs designed to act as a receptor antagonist, it provided researchers with unprecedented insights into the role of angiotensin II in blood pressure regulation.
In clinical research settings, Saralasin was once considered as a therapeutic candidate for hypertension, but its partial agonist activity limited its long-term therapeutic potential. However, its importance in research remains significant, as it paved the way for the development of more selective and clinically effective angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) such as losartan and valsartan.
Today, Saralasin continues to be utilized in laboratory research to explore renovascular hypertension, renin-dependent mechanisms, and receptor signaling modulation. Its role as both a research probe and a historical steppingstone in cardiovascular drug development underscores its continued relevance.
Side Effects
In research models, Saralasin has been reported to cause:
Transient hypotension or hypertension (depending on dose and receptor context)
Vascular reactivity changes
Partial agonist responses complicating dose-response interpretation
Potential renal perfusion effects
These observations are based on experimental and preclinical data. Side effects are provided for reference only in laboratory research contexts.
Disclaimer
is supplied strictly for laboratory research use only. It is not intended for human or veterinary use, nor for clinical, diagnostic, or therapeutic applications. All handling should follow appropriate laboratory safety protocols.
Keywords
CAS 34273-10-4, Saralasin peptide, angiotensin II antagonist, RAAS research compound, renovascular hypertension research, renin-dependent hypertension research, cardiovascular research peptides, GMP Saralasin supplier
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 38 × 85 × 38 cm |
What is Saralasin?
Saralasin is an octapeptide analog of angiotensin II that functions as a competitive receptor antagonist with partial agonist activity.
What is the CAS number of Saralasin?
The CAS number of Saralasin is 34273-10-4.
What are the main research applications of Saralasin?
Saralasin is primarily used in research on renovascular hypertension, renin-dependent hypertension, and RAAS physiology.
How does Saralasin work?
Saralasin binds to angiotensin II receptors, blocking angiotensin II–mediated responses while also demonstrating partial agonist activity.
Why is Saralasin important in hypertension research?
Saralasin helps differentiate renin-dependent hypertension from other types by blocking angiotensin II–induced blood pressure effects.
What is the purity of Saralasin provided by your supplier?
Our GMP-certified Saralasin is manufactured to a purity level of 98.71% (HPLC).
Can Saralasin be used in clinical treatment?
No. Saralasin is for laboratory research use only and is not approved for therapeutic or clinical applications.
Is Saralasin available in bulk quantities?
Yes. We provide Saralasin in both retail and wholesale quantities to support various research needs.
How should Saralasin be stored?
Saralasin should be stored at –20°C, protected from light and moisture, to maintain stability and integrity.
Who manufactures Saralasin?
Saralasin is produced by a GMP-certified manufacturer to ensure high-quality and reliable research supply.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.