No products in the cart.
Sale
WZH-17-002 | ALK PROTAC Degrader
Original price was: $38.00.$29.00Current price is: $29.00.
WZH-17-002 is an ALK PROTAC degrader derived from WZH-15-125. It achieves a DC50 of 25 nM, showing superior activity against Lorlatinib-resistant ALK mutations. In preclinical xenograft models, WZH-17-002 significantly reduces drug resistance and tumor burden, offering a next-generation approach to studying ALK-driven NSCLC and targeted protein degradation.
Description
Contents
hide
Product Description
Introduction
WZH-17-002 represents a next-generation strategy for overcoming ALK inhibitor resistance through targeted protein degradation (PROTAC technology). Unlike conventional small-molecule inhibitors that simply block kinase activity, WZH-17-002 is designed to induce proteasomal degradation of the ALK fusion protein, leading to sustained suppression of oncogenic signaling.
The compound is based on WZH-15-125 (a highly potent ALK inhibitor effective against Lorlatinib-resistant mutations) but is extended with a linker and E3 ligase ligand to form a PROTAC. This design allows WZH-17-002 not only to inhibit but also to eliminate mutant ALK proteins, thereby reducing the likelihood of adaptive resistance.
Research Significance
Targeted Degradation vs. Inhibition
Traditional ALK inhibitors such as crizotinib, ceritinib, alectinib, brigatinib, and Lorlatinib eventually encounter resistance mutations like G1202R and compound G1202R/L1196M. WZH-17-002 degrades the ALK protein entirely, providing a stronger and more durable suppression compared to mere inhibition.Potency in Resistant Mutations
DC50 = 25 nM indicates potent degradation capacity.
Specifically designed to tackle Lorlatinib-resistant ALK compound mutations.
Demonstrated efficacy in EML4-ALK G1202R/L1196M xenograft mice, a gold-standard preclinical resistance model.
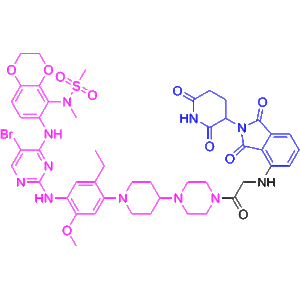
PROTAC Design Components
Pink segment (ALK ligand): Derived from WZH-15-125 (HY-174314), provides high affinity for ALK kinase.
Blue segment (CRBN ligase ligand): HY-14658, a cereblon ligand, recruits the E3 ubiquitin ligase.
Black segment (linker): HY-174316, flexible linker optimized for proximity-induced ubiquitination.
Preclinical Validation
WZH-17-002 has been shown to:Reduce tumor growth in NSCLC xenografts.
Overcome Lorlatinib resistance in compound mutant models.
Provide a novel proof-of-concept for ALK degradation therapy.
Research Applications
NSCLC resistance studies with EML4-ALK fusions.
Comparison between inhibition (WZH-15-125) and degradation (WZH-17-002).
Drug discovery for PROTAC-based therapies.
Mechanistic exploration of protein degradation pathways.
Xenograft modeling of compound ALK resistance.
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Product Name | WZH-17-002 |
| Origin | WZH-15-125-based PROTAC degrader |
| Target Protein | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) |
| DC50 | 25 nM |
| Key Activity | ALK degradation in resistant models |
| Resistance Coverage | Effective against Lorlatinib-resistant compound mutations (e.g., G1202R/L1196M) |
| Preclinical Model | Inhibits tumor growth in EML4-ALK xenografts |
| Structural Components | ALK ligand (HY-174314), CRBN ligand (HY-14658), linker (HY-174316) |
| Research Use | PROTAC development, resistance studies, NSCLC models |
| Related Compounds | WZH-15-125, Lorlatinib |
| Appearance | White to off-white powder |
| Purity | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Solubility | DMSO, ethanol |
| Storage Conditions | -20°C, dry, light-protected |
| Shelf Life | ≥2 years with proper storage |
| QC Validation | HPLC, NMR, MS characterization |
Mechanism of Action
1. PROTAC Technology
WZH-17-002 follows the PROTAC (Proteolysis Targeting Chimera) paradigm:
The ALK ligand binds mutant ALK.
The CRBN ligand recruits cereblon E3 ubiquitin ligase.
The linker brings both proteins into proximity.
ALK is ubiquitinated and degraded via the 26S proteasome.
This mechanism eliminates the target protein, offering a fundamentally different strategy from inhibition.
2. Overcoming Lorlatinib Resistance
G1202R mutation disrupts Lorlatinib binding.
L1196M gatekeeper mutation adds steric hindrance.
Combined G1202R/L1196M compound mutations are essentially untreatable with inhibitors.
WZH-17-002 bypasses binding dependency, instead degrading ALK altogether.
3. Preclinical Validation
In xenograft models, WZH-17-002 significantly inhibited tumor growth.
Reduction of ALK protein expression was confirmed in tumor tissues.
Sustained suppression suggests lower probability of secondary resistance.
4. Broader Implications
WZH-17-002 exemplifies how PROTACs can expand druggable space, tackling mutations that render inhibitors ineffective. It also provides a model scaffold for other kinase-targeted degraders.
Side Effects
As a research compound, WZH-17-002’s toxicity profile is extrapolated from:
On-target degradation risks: Excessive ALK removal may affect normal neuronal development and immune regulation.
CNS effects: ALK plays roles in brain development; off-target degradation may alter cognitive/behavioral outcomes.
Metabolic changes: Possible lipid/glucose dysregulation.
Hepatotoxicity: As with many PROTACs, liver enzyme elevation is a potential concern.
Immunological concerns: CRBN-based ligands may affect immune signaling pathways.
Handling Precautions
Research use only.
Not approved for human or animal therapeutic use.
Use PPE and BSL-2 handling conditions.
Disclaimer
WZH-17-002 is intended for laboratory research only. It is not approved for clinical or veterinary use.
Keywords
WZH-17-002, ALK PROTAC degrader, WZH-15-125-based PROTAC, ALK G1202R/L1196M degradation, Lorlatinib resistance, NSCLC xenograft, targeted protein degradation, PROTAC technology, CAS WZH-17-002.
Shipping Guarantee
All shipments are delivered with customs clearance, insurance, and tracking. Damaged or lost parcels are fully compensated.
Transaction Guarantee
We support T/T, PayPal, cryptocurrency, and other secure international payment methods.
Additional information
| Weight | 0.8 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 56 × 38 × 56 cm |
1. What is WZH-17-002?
It is a WZH-15-125-based ALK PROTAC degrader with DC50 = 25 nM.
2. What is its main application?
Studying ALK degradation and resistance overcoming in NSCLC research.
3. How does it differ from WZH-15-125?
WZH-15-125 is an inhibitor, while WZH-17-002 is a degrader that removes ALK proteins.
4. What mutations does it cover?
Effective against Lorlatinib-resistant ALK compound mutations, including G1202R/L1196M.
5. Has it been tested in vivo?
Yes, it significantly inhibited tumor growth in EML4-ALK xenograft models.
6. What is the degradation potency?
DC50 = 25 nM.
7. Can it be used in PROTAC research?
Yes, it is an excellent tool for validating ALK-targeted PROTAC strategies.
8. What are its components?
ALK ligand (HY-174314)
CRBN ligand (HY-14658)
Linker (HY-174316)
9. How should it be stored?
At -20°C, dry, and protected from light.
10. Is it approved for therapeutic use?
No, it is for research use only.
11. Can it cross the blood-brain barrier?
Like Lorlatinib and its derivatives, it is designed with CNS penetration potential.
12. What payment methods are supported?
T/T, PayPal, and cryptocurrency.














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.