Description
Product Description
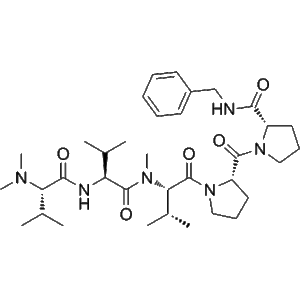
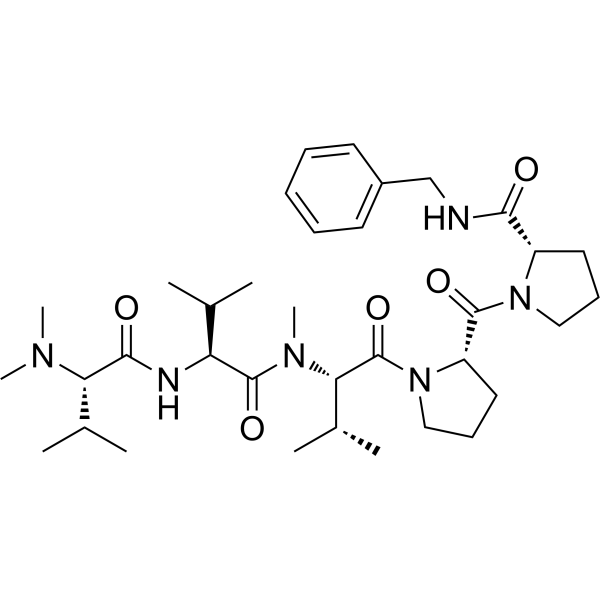
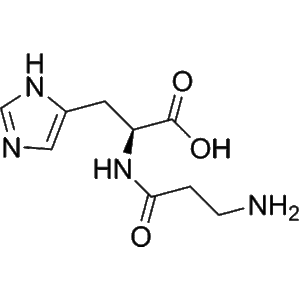
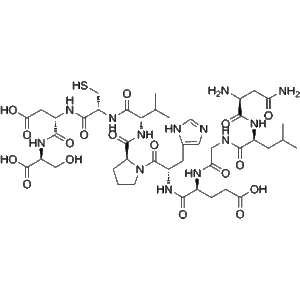
Cemadotin, also known by its research code LU103793, is a fully synthetic, water-soluble analogue of the marine natural product Dolastatin 15. This compound represents a key development in the field of microtubule-targeting agents due to its potent inhibitory activity against tubulin polymerization and its capacity to arrest cells at mitosis. As a cytostatic compound, Cemadotin has been extensively employed in the study of anticancer mechanisms, specifically focusing on microtubule dynamics, mitotic checkpoint control, and apoptosis induction.
The design of Cemadotin was inspired by Dolastatin 15, a peptide originally isolated from the sea hare Dolabella auricularia. Dolastatin analogs, including Cemadotin, have gained significant research interest as they mimic the structural motifs responsible for tubulin interaction but with improved pharmacological stability and solubility. Cemadotin’s molecular configuration allows selective binding to the Vinca domain on β-tubulin, thereby preventing microtubule assembly and disrupting the mitotic spindle apparatus required for cell division.
Synthetic Origin and Structural Significance
is composed of modified amino acid residues that preserve the pharmacophore of Dolastatin 15 while increasing its hydrophilicity and cellular permeability. This modification allows it to retain strong inhibitory potency (Ki ≈ 1 µM for tubulin binding) while facilitating in vitro experimentation under aqueous conditions. The design of Cemadotin represents an important milestone in the evolution of synthetic peptide analogs aimed at reproducing and enhancing marine-derived bioactivity.
Applications in Cancer Mechanism Research
Cemadotin serves as a highly valuable tool compound for dissecting the mechanisms of mitotic arrest and programmed cell death (apoptosis). By disrupting the formation of mitotic spindles, Cemadotin halts cells at the G₂/M phase transition, leading to accumulation of multinucleated or apoptotic cells. These effects make it particularly useful for studying tumor cell proliferation and microtubule-associated protein interactions.
Experimental data have demonstrated that Cemadotin effectively inhibits proliferation in a wide variety of cancer cell lines, including leukemia, colon carcinoma, and breast carcinoma models. Moreover, in mouse xenograft models, it has been shown to significantly suppress tumor growth, making it an essential agent for preclinical mechanistic investigations of antimitotic therapies.
Role in Microtubule Dynamics Studies
Microtubules form the structural backbone of the mitotic spindle, and their polymerization is essential for chromosomal segregation. Cemadotin binds to tubulin dimers, preventing them from assembling into microtubules and destabilizing existing ones. This dual mechanism — inhibition of polymerization and promotion of depolymerization — leads to microtubule network collapse.
Researchers use Cemadotin to explore the kinetics of tubulin polymerization, the structural biology of microtubule inhibitors, and the conformational changes that occur in tubulin upon ligand binding. Cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography studies involving Cemadotin have provided insights into the binding interfaces that control tubulin inhibition and downstream apoptotic signaling pathways.
Comparative Analysis with Other Tubulin Inhibitors
Cemadotin belongs to the broader family of antimitotic agents that includes vinca alkaloids (vinblastine, vincristine) and taxanes (paclitaxel, docetaxel). Unlike the taxanes, which stabilize microtubules, Cemadotin and other Dolastatin derivatives destabilize them by blocking polymerization. This destabilizing effect offers a contrasting approach for studying mitotic checkpoint signaling and spindle assembly failure.
is particularly advantageous in cell-based assays because it exhibits high selectivity for proliferating cells while sparing quiescent ones. Its reversible binding to tubulin also allows researchers to study recovery kinetics following drug removal, an important model for understanding reversible mitotic arrest.
Pharmacological Research Applications
In pharmacological research, Cemadotin has been utilized as a molecular scaffold for developing novel peptide-based anticancer compounds. Its defined mechanism of tubulin inhibition makes it a reference standard for screening analogs with altered bioavailability or selectivity. Cemadotin’s solubility profile and stability under physiological conditions also make it suitable for in vitro pharmacokinetic simulations and mechanistic assays.
Overall, Cemadotin represents a cornerstone tool for exploring mitotic regulation, cytoskeletal dynamics, and microtubule-associated signal transduction in cancer research laboratories.
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|
| Product Name | Cemadotin |
| CAS Number | 159776-69-9 |
| Synonyms | LU103793, Dolastatin 15 analogue |
| Molecular Formula | C₃₆H₆₁N₅O₇ |
| Molecular Weight | 675.91 g/mol |
| Purity | ≥99% |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, DMSO, and ethanol |
| Storage Conditions | -20°C, desiccated, protect from light |
| Applications | Anticancer mechanism research, microtubule inhibition studies, mitotic checkpoint assays, apoptosis research |
Mechanism of Action
Cemadotin acts as a potent inhibitor of tubulin polymerization, targeting the Vinca binding domain on β-tubulin. Through this interaction, it prevents the assembly of microtubules from tubulin dimers, leading to mitotic arrest and subsequent apoptosis in dividing cells.
Tubulin Binding and Microtubule Destabilization
The compound’s primary target, tubulin, is a globular protein that polymerizes to form microtubules — dynamic structures essential for maintaining cell shape, intracellular transport, and mitotic spindle formation. Cemadotin’s binding alters the conformational flexibility of the tubulin dimer, preventing longitudinal contacts between protofilaments. This disruption halts microtubule elongation and induces depolymerization, dismantling existing microtubule structures.
Mitotic Arrest and Apoptotic Signaling
By suppressing microtubule formation, Cemadotin triggers mitotic checkpoint activation. Cells become trapped in metaphase, unable to proceed to anaphase due to improper spindle assembly. This sustained arrest leads to activation of intrinsic apoptotic pathways, including caspase-3 activation, mitochondrial cytochrome c release, and DNA fragmentation.
Researchers have observed that Cemadotin-treated cells exhibit chromosomal condensation and fragmentation characteristic of apoptosis. This process is tightly linked to the activation of stress kinases such as JNK and p38 MAPK, which further amplify apoptotic signaling.
Selectivity Toward Proliferating Cells
One of Cemadotin’s defining properties is its preference for rapidly dividing cells. Quiescent or differentiated cells with low mitotic activity are largely unaffected. This makes Cemadotin an excellent model for studying selective toxicity mechanisms and tumor-specific proliferation inhibition.
Downstream Cellular Effects
Cemadotin-induced microtubule disassembly also affects cellular trafficking and morphology. The collapse of the cytoskeleton disrupts endosomal movement, Golgi organization, and cell polarity, providing an ideal model to study microtubule-dependent cellular processes. Additionally, changes in cell adhesion and migration can be monitored following Cemadotin treatment to assess its role in metastasis-related studies.
Structure–Activity Relationship (SAR) Insights
Cemadotin’s potency stems from its optimized sequence that mimics the key binding residues of Dolastatin 15. SAR studies indicate that minor modifications in side-chain composition can significantly alter tubulin binding affinity. Cemadotin’s backbone rigidity and terminal group substitutions stabilize its conformation for optimal tubulin interaction.
The combination of water solubility, structural precision, and high binding affinity makes Cemadotin an indispensable model for drug design and structural biology studies related to tubulin-targeting agents.
Side Effects
In vitro research indicates that Cemadotin’s cytotoxicity is primarily limited to rapidly proliferating cells. Its effects include mitotic spindle disruption, metaphase arrest, and apoptosis via caspase activation. At higher concentrations, secondary effects may include mitochondrial membrane depolarization and elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS) production.
Prolonged exposure can cause irreversible cytoskeletal disorganization, but these effects are dose-dependent and reversible upon compound removal. Cemadotin is generally well-tolerated in experimental systems when handled within recommended concentration ranges (nanomolar to low micromolar).
Researchers should handle Cemadotin with caution, following standard laboratory chemical safety protocols. It should not be used in clinical or veterinary contexts.
Keywords
LU103793, Dolastatin 15 analog, tubulin polymerization inhibitor, antimitotic peptide, cytoskeletal research, mitotic arrest, apoptosis induction, anticancer mechanism, microtubule dynamics
Shipping Guarantee
All shipments are handled using validated cold-chain logistics to preserve peptide integrity. Each package is sealed in moisture-proof containers with secondary protective wrapping and continuous temperature monitoring. Products are shipped via express international couriers with full tracking and insurance coverage.
Trade Assurance
We ensure product authenticity, verified ≥99% purity, and compliance with analytical standards (HPLC, MS, and NMR). Each batch is supplied with a Certificate of Analysis (CoA). Our trade assurance policy guarantees replacement or refund for any deviation from listed specifications.
Payment Support
We provide flexible and secure global payment options to support international research transactions. Accepted payment methods include PayPal, major credit cards (Visa, MasterCard, American Express), telegraphic transfer (T/T), and cryptocurrencies (USDT, Bitcoin, Ethereum). All transactions are protected by industry-standard encryption and verified payment gateways to ensure confidentiality and fund security.
Disclaimer
All products listed are intended for laboratory research use only and not for human or veterinary use. They are not drugs, medical devices, or diagnostics and should not be administered to humans or animals. Researchers must handle all materials in accordance with institutional biosafety and chemical safety guidelines. The information provided is for scientific reference only and does not imply therapeutic efficacy, safety, or regulatory approval.

 USA-Peptide-Janoshik Lyophilized Peptide Raw Powder for Muscle Building & Weight Loss
10 × $24.00
USA-Peptide-Janoshik Lyophilized Peptide Raw Powder for Muscle Building & Weight Loss
10 × $24.00 GLP-1/GIP/glucagon combination therapy The Future of Metabolic Treatment (Wholesale Supplier Guide)
10 × $23.00
GLP-1/GIP/glucagon combination therapy The Future of Metabolic Treatment (Wholesale Supplier Guide)
10 × $23.00 Tirzepatide Raw Material Factory: Low-Price Wholesale for High-Purity Peptides
10 × $23.00
Tirzepatide Raw Material Factory: Low-Price Wholesale for High-Purity Peptides
10 × $23.00 Anti-Aging Peptide Raw Powder CAS 307297-39-8 Epitalon - Low Price Wholesale
10 × $23.00
Anti-Aging Peptide Raw Powder CAS 307297-39-8 Epitalon - Low Price Wholesale
10 × $23.00










Reviews
There are no reviews yet.